Abstract
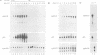
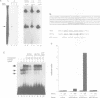
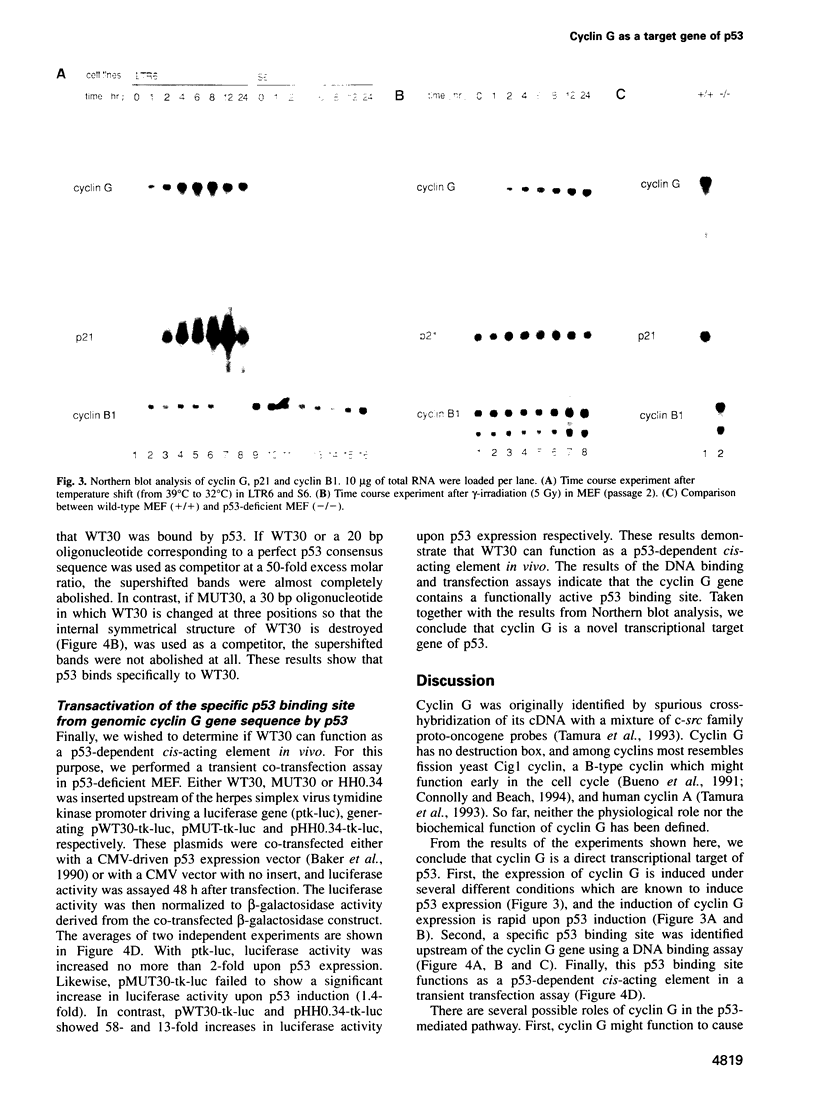
Through a PCR-based differential screening method, cyclin G was identified as a novel transcriptional target of the p53 tumor suppressor gene product. In both a mouse p53 temperature-sensitive leukemic cell line and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) after gamma-irradiation, cyclin G mRNA was rapidly induced. MEF from a p53-deficient mouse expressed cyclin G at a level > 10-fold lower than that from a wild-type mouse. Using a DNA binding assay, a specific p53 binding site was identified upstream from the cyclin G gene, which functioned as a p53-dependent cis-acting element in a transient transfection assay. These results suggest that cyclin G might participate in a p53-mediated pathway to prevent tumorigenesis.
Full text
PDF

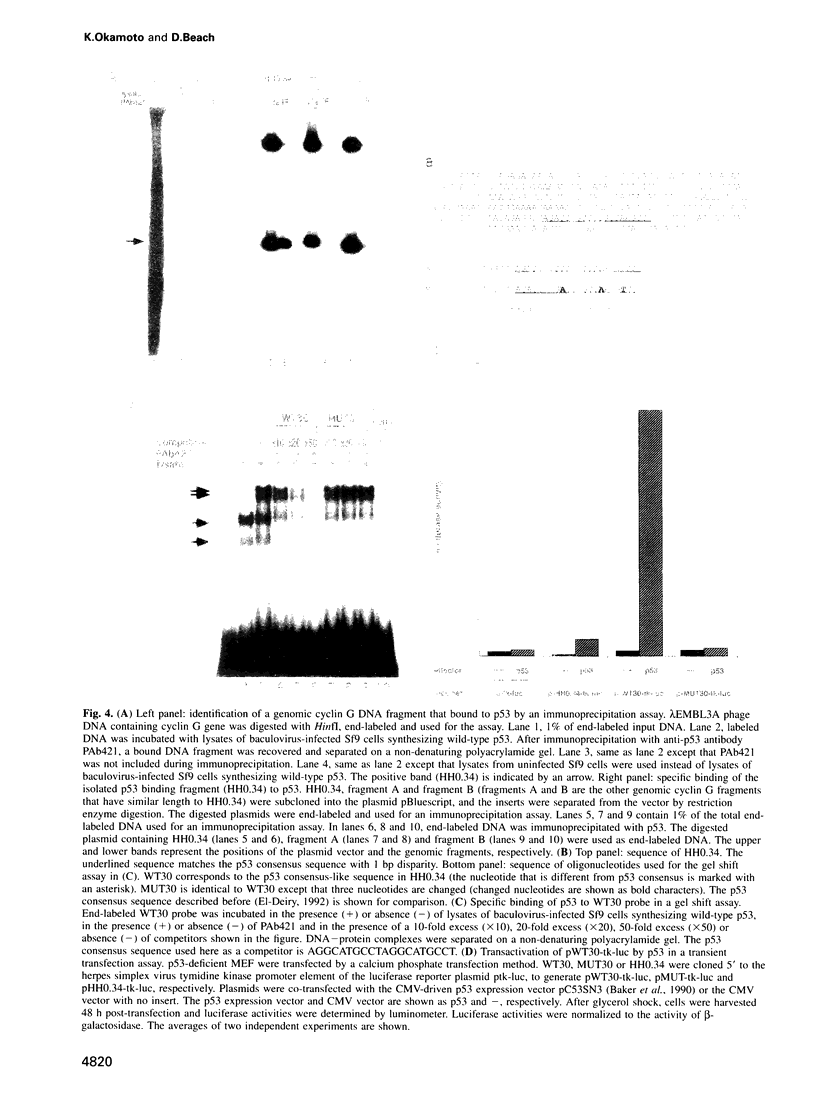


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno A., Richardson H., Reed S. I., Russell P. A fission yeast B-type cyclin functioning early in the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90147-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. L., Wolgemuth D. J. Identification of a mouse B-type cyclin which exhibits developmentally regulated expression in the germ line. Mol Reprod Dev. 1992 Nov;33(3):259–269. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080330305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Beach D. Interaction between the Cig1 and Cig2 B-type cyclins in the fission yeast cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):768–776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. A role for the human single-stranded DNA binding protein HSSB/RPA in an early stage of nucleotide excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3873–3880. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coverley D., Kenny M. K., Munn M., Rupp W. D., Lane D. P., Wood R. D. Requirement for the replication protein SSB in human DNA excision repair. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):538–541. doi: 10.1038/349538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Bradley A. The tumor suppressor p53. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Aug 23;1155(2):181–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90004-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Stillman B. cdc2 family kinases phosphorylate a human cell DNA replication factor, RPA, and activate DNA replication. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2189–2199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotedar R., Roberts J. M. Cell cycle regulated phosphorylation of RPA-32 occurs within the replication initiation complex. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2177–2187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. Defects in a cell cycle checkpoint may be responsible for the genomic instability of cancer cells. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):543–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90586-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juven T., Barak Y., Zauberman A., George D. L., Oren M. Wild type p53 can mediate sequence-specific transactivation of an internal promoter within the mdm2 gene. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N., Yonish-Rouach E., Oren M., Kimchi A. Complementation by wild-type p53 of interleukin-6 effects on M1 cells: induction of cell cycle exit and cooperativity with c-myc suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7942–7952. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Averboukh L., Pardee A. B. Distribution and cloning of eukaryotic mRNAs by means of differential display: refinements and optimization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3269–3275. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang P., Pardee A. B. Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1354393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):957–967. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Kastan M. B. DNA strand breaks: the DNA template alterations that trigger p53-dependent DNA damage response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1815–1823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L., Nishioka W. K., Th'ng J., Bradbury E. M., Litchfield D. W., Greenberg A. H. Premature p34cdc2 activation required for apoptosis. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1143–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.8108732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivji K. K., Kenny M. K., Wood R. D. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for DNA excision repair. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90416-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Kanaoka Y., Jinno S., Nagata A., Ogiso Y., Shimizu K., Hayakawa T., Nojima H., Okayama H. Cyclin G: a new mammalian cyclin with homology to fission yeast Cig1. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2113–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Bayle J. H., Olson D., Levine A. J. The p53-mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1126–1132. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Grunwald D., Wilder S., Kimchi A., May E., Lawrence J. J., May P., Oren M. p53-mediated cell death: relationship to cell cycle control. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1415–1423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Bargonetti J., Walker K., Prives C., Levine A. J. Wild-type p53 mediates positive regulation of gene expression through a specific DNA sequence element. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1143–1152. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]