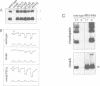
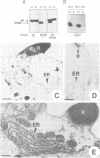
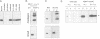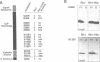Abstract
In Drosophila, biogenesis of the major rhodopsin, Rh1, is dependent on the presence of a photoreceptor cell-specific cyclophilin, NinaA. In ninaA mutants, Rh1 is retained within the endoplasmic reticulum and rhodopsin levels are reduced > 100-fold. Cyclophilins have been shown to be peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases and have been implicated in catalyzing protein folding. We have generated transgenic animals expressing different functional rhodopsins containing a histidine tag. We isolated these molecules from wild-type and ninaA mutant retinas, and have demonstrated that in vivo NinaA forms a specific stable protein complex with its target Rh1. We also expressed ninaA under an inducible promoter and showed that NinaA is required quantitatively for Rh1 biogenesis. These results provide the first evidence for a biologically relevant physical interaction between a cyclophilin and its cellular target, and suggest that the normal cellular role of this class of cyclophilins is to function as chaperones, possibly escorting their protein substrates through the secretory pathway.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bang A. G., Posakony J. W. The Drosophila gene Hairless encodes a novel basic protein that controls alternative cell fates in adult sensory organ development. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1752–1769. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clipstone N. A., Crabtree G. R. Identification of calcineurin as a key signalling enzyme in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):695–697. doi: 10.1038/357695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley N. J., Baker E. K., Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is required in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90177-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. S., Becker A., Heitman J., Hall M. N., Brennan M. B. A yeast cyclophilin gene essential for lactate metabolism at high temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11169–11173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler R., Bjornson R., Kirschfeld K., Mismer D., Rubin G. M., Smith D. P., Socolich M., Zuker C. S. Ectopic expression of ultraviolet-rhodopsins in the blue photoreceptor cells of Drosophila: visual physiology and photochemistry of transgenic animals. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3862–3868. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03862.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiler R., Harris W. A., Kirschfeld K., Wehrhahn C., Zuker C. S. Targeted misexpression of a Drosophila opsin gene leads to altered visual function. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):737–741. doi: 10.1038/333737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Schmid F. X. The mechanism of protein folding. Implications of in vitro refolding models for de novo protein folding and translocation in the cell. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2205–2212. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Corthésy B., Bram R. J., Crabtree G. R. Nuclear association of a T-cell transcription factor blocked by FK-506 and cyclosporin A. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):803–807. doi: 10.1038/352803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freskgård P. O., Bergenhem N., Jonsson B. H., Svensson M., Carlsson U. Isomerase and chaperone activity of prolyl isomerase in the folding of carbonic anhydrase. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):466–468. doi: 10.1126/science.1357751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J., Trahey M., Weissman I. Cloning and characterization of cyclophilin C-associated protein: a candidate natural cellular ligand for cyclophilin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6815–6819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J., Weissman I. Two cytoplasmic candidates for immunophilin action are revealed by affinity for a new cyclophilin: one in the presence and one in the absence of CsA. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):799–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90123-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruman D. A., Klee C. B., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J. Calcineurin phosphatase activity in T lymphocytes is inhibited by FK 506 and cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galat A. Peptidylproline cis-trans-isomerases: immunophilins. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Sep 15;216(3):689–707. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain J., McCaffrey P. G., Miner Z., Kerppola T. K., Lambert J. N., Verdine G. L., Curran T., Rao A. The T-cell transcription factor NFATp is a substrate for calcineurin and interacts with Fos and Jun. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):352–355. doi: 10.1038/365352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. C., Pak W. L. Electrophysiological study of Drosophila rhodopsin mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):651–673. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G. Assembly of functional rhodopsin requires a disulfide bond between cysteine residues 110 and 187. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17520–17524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S. S., Sakmar T. P., Chen H. B., Khorana H. G. Cysteine residues 110 and 187 are essential for the formation of correct structure in bovine rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8459–8463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz J., Hall M. N. Cyclosporin A, FK506 and rapamycin: more than just immunosuppression. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):334–338. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90069-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrivee D. C., Conrad S. K., Stephenson R. S., Pak W. L. Mutation that selectively affects rhodopsin concentration in the peripheral photoreceptors of Drosophila melanogaster. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Nov;78(5):521–545. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.5.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilie H., Lang K., Rudolph R., Buchner J. Prolyl isomerases catalyze antibody folding in vitro. Protein Sci. 1993 Sep;2(9):1490–1496. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Albers M. W., Wandless T. J., Luan S., Alberg D. G., Belshaw P. J., Cohen P., MacKintosh C., Klee C. B., Schreiber S. L. Inhibition of T cell signaling by immunophilin-ligand complexes correlates with loss of calcineurin phosphatase activity. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):3896–3901. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luban J., Bossolt K. L., Franke E. K., Kalpana G. V., Goff S. P. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag protein binds to cyclophilins A and B. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1067–1078. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90637-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey P. G., Perrino B. A., Soderling T. R., Rao A. NF-ATp, a T lymphocyte DNA-binding protein that is a target for calcineurin and immunosuppressive drugs. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3747–3752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Tamura J., Kincaid R. L., Tocci M. J., O'Neill E. A. FK-506- and CsA-sensitive activation of the interleukin-2 promoter by calcineurin. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):692–694. doi: 10.1038/357692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Tousa J. E., Baehr W., Martin R. L., Hirsh J., Pak W. L., Applebury M. L. The Drosophila ninaE gene encodes an opsin. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):839–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Hardy R. W., Baker E. K., Stamnes M. A., Shieh B. H., Zuker C. S. Genetic dissection of cyclophilin function. Saturation mutagenesis of the Drosophila cyclophilin homolog ninaA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16460–16466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. The role of heat shock proteins in regulating the function, folding, and trafficking of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21455–21458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak T., Carrello A., Mark P. J., Warner B. J., Simpson R. J., Moritz R. L., House A. K. The cyclophilin component of the unactivated estrogen receptor contains a tetratricopeptide repeat domain and shares identity with p59 (FKBP59). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13187–13192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Shortridge R. D., Larrivee D. C., Ono T., Ozaki M., Pak W. L. Drosophila ninaA gene encodes an eye-specific cyclophilin (cyclosporine A binding protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5390–5394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Chemistry and biology of the immunophilins and their immunosuppressive ligands. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90111-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh B. H., Stamnes M. A., Seavello S., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The ninaA gene required for visual transduction in Drosophila encodes a homologue of cyclosporin A-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):67–70. doi: 10.1038/338067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Baggenstoss B. A., Marion T. N., Rimerman R. A. Two FKBP-related proteins are associated with progesterone receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18365–18371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Rutherford S. L., Zuker C. S. Cyclophilins: a new family of proteins involved in intracellular folding. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;2(9):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Shieh B. H., Chuman L., Harris G. L., Zuker C. S. The cyclophilin homolog ninaA is a tissue-specific integral membrane protein required for the proper synthesis of a subset of Drosophila rhodopsins. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90156-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamnes M. A., Zuker C. S. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases, cyclophilin, FK506-binding protein, and ninaA: four of a kind. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;2(6):1104–1107. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson S. K., Born T., Zydowsky L. D., Cho H., Chang H. Y., Walsh C. T., Rusnak F. Cyclosporin-mediated inhibition of bovine calcineurin by cyclophilins A and B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3741–3745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes K., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Proline isomerases function during heat shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5853–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. K., Albers M. W., Chang H., Faber L. E., Schreiber S. L. Association of a 59-kilodalton immunophilin with the glucocorticoid receptor complex. Science. 1992 May 29;256(5061):1315–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.1376003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Ogunbumni E., Freund E., Wiederrecht G., Marks A. R., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506-binding protein. Dissociation and reconstitution of FKBP-12 to the calcium release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22992–22999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. T., Zydowsky L. D., McKeon F. D. Cyclosporin A, the cyclophilin class of peptidylprolyl isomerases, and blockade of T cell signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13115–13118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yem A. W., Tomasselli A. G., Heinrikson R. L., Zurcher-Neely H., Ruff V. A., Johnson R. A., Deibel M. R., Jr The Hsp56 component of steroid receptor complexes binds to immobilized FK506 and shows homology to FKBP-12 and FKBP-13. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2868–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount G. L., Gall C. M., White J. D. Limbic seizures increase cyclophilin mRNA levels in rat hippocampus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Jun;14(1-2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker C. S., Mismer D., Hardy R., Rubin G. M. Ectopic expression of a minor Drosophila opsin in the major photoreceptor cell class: distinguishing the role of primary receptor and cellular context. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]