Abstract
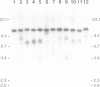
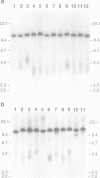
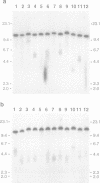
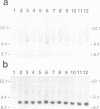
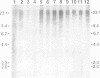
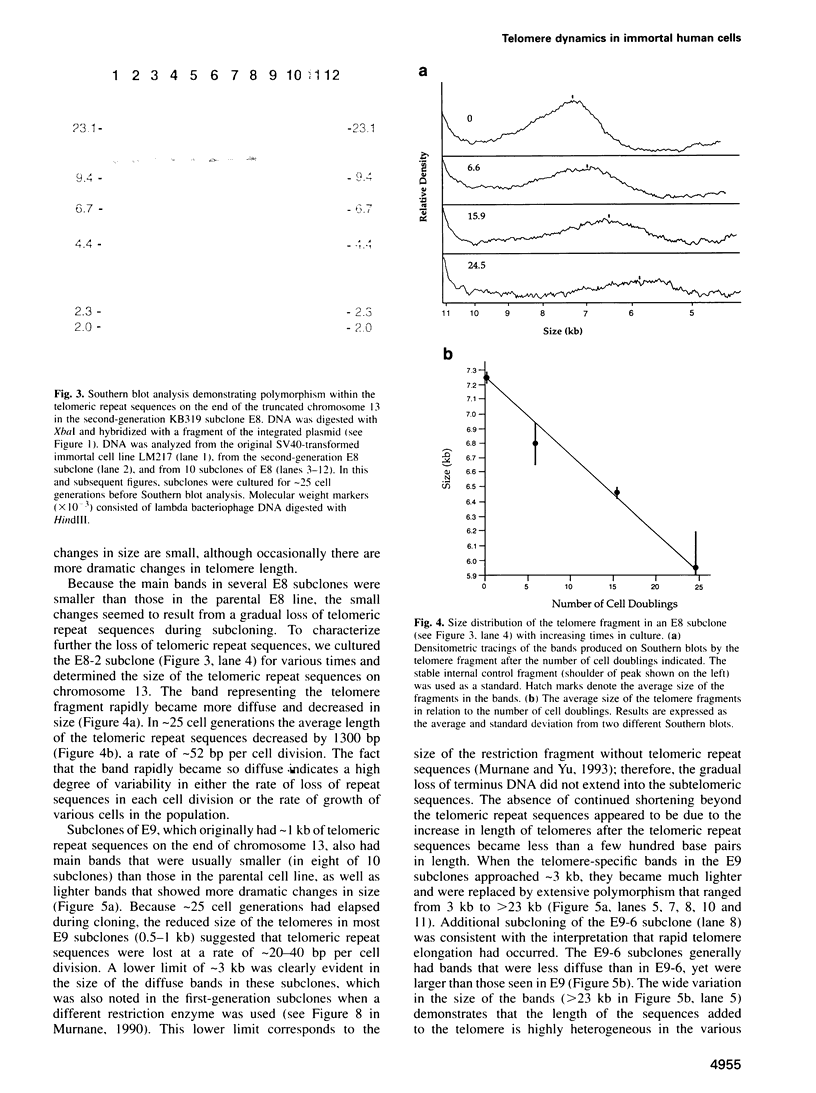
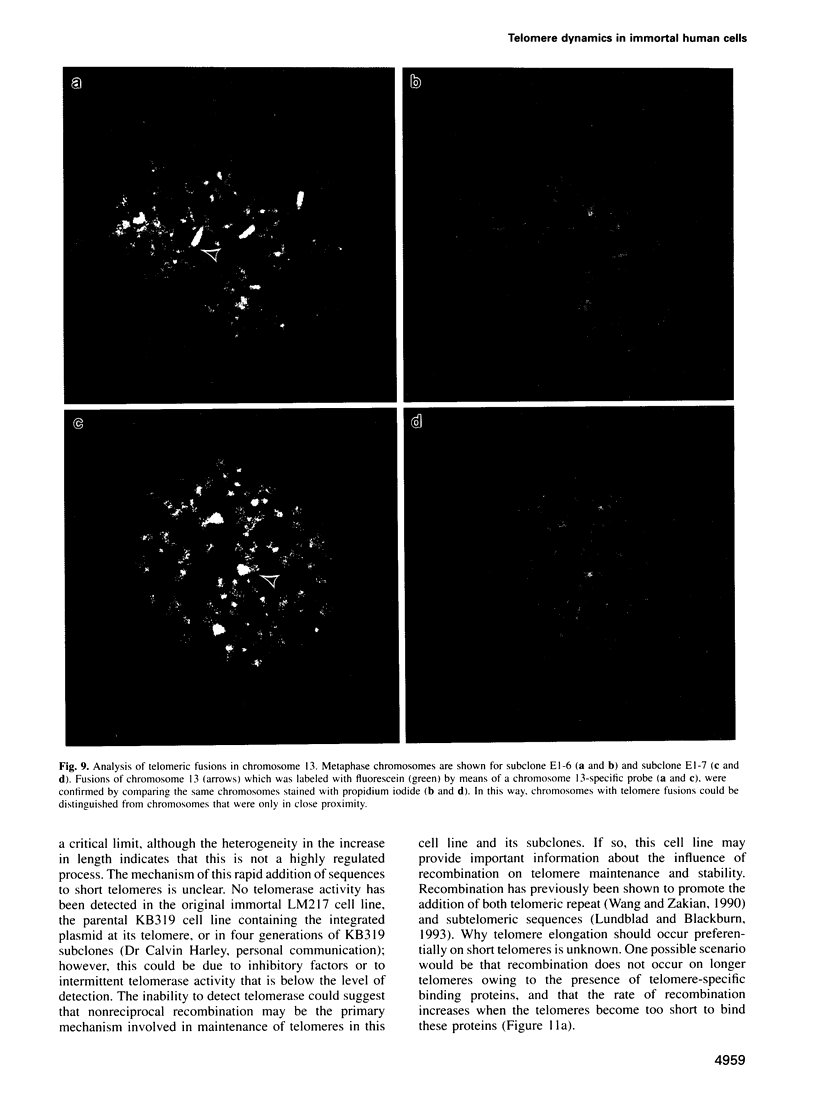
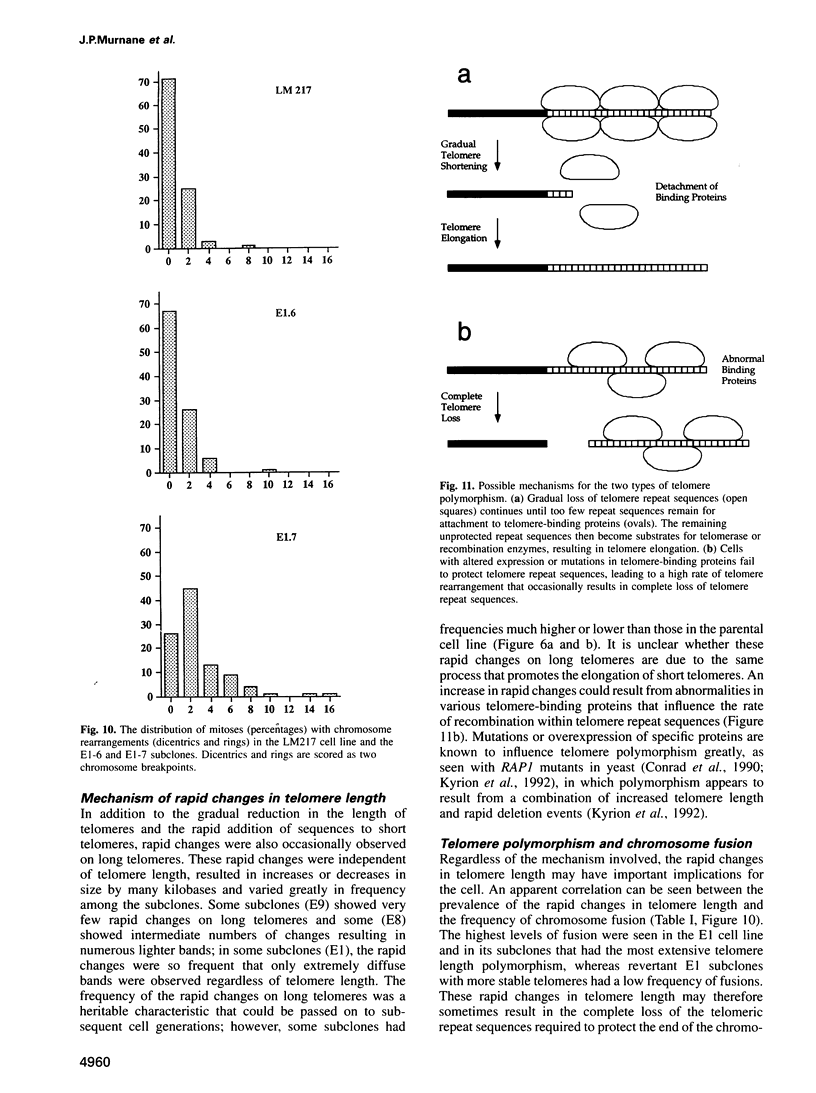
The integration of transfected plasmid DNA at the telomere of chromosome 13 in an immortalized simian virus 40-transformed human cell line provided the first opportunity to study polymorphism in the number of telomeric repeat sequences on the end of a single chromosome. Three subclones of this cell line were selected for analysis: one with a long telomere on chromosome 13, one with a short telomere, and one with such extreme polymorphism that no distinct band was discernible. Further subcloning demonstrated that telomere polymorphism resulted from both gradual changes and rapid changes that sometimes involved many kilobases. The gradual changes were due to the shortening of telomeres at a rate similar to that reported for telomeres of somatic cells without telomerase, eventually resulting in the loss of nearly all of the telomere. However, telomeres were not generally lost completely, as shown by the absence of polymorphism in the subtelomeric plasmid sequences. Instead, telomeres that were less than a few hundred base pairs in length showed a rapid, highly heterogeneous increase in size. Rapid changes in telomere length also occurred on longer telomeres. The frequency of this type of change in telomere length varied among the subclones and correlated with chromosome fusion. Therefore, the rapid changes in telomere length appeared occasionally to result in the complete loss of telomeric repeat sequences. Rapid changes in telomere length have been associated with telomere loss and chromosome instability in yeast and could be responsible for the high rate of chromosome fusion observed in many human tumor cell lines.
Full text
PDF






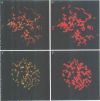
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett M. A., Buckle V. J., Evans E. P., Porter A. C., Rout D., Smith A. G., Brown W. R. Telomere directed fragmentation of mammalian chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):27–36. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Preston R. J., Leonard R. C., Pyatt B. E., Gooch P. C. Chromosomal aberration and sister-chromatid exchange frequencies in peripheral blood lymphocytes of a large human population sample. II. Extension of age range. Mutat Res. 1989 Jun;212(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benn P. A. Specific chromosome aberrations in senescent fibroblast cell lines derived from human embryos. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):465–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres and their synthesis. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):489–490. doi: 10.1126/science.2200120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouffler S., Silver A., Papworth D., Coates J., Cox R. Murine radiation myeloid leukaemogenesis: relationship between interstitial telomere-like sequences and chromosome 2 fragile sites. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993 Feb;6(2):98–106. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870060206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., MacKinnon P. J., Villasanté A., Spurr N., Buckle V. J., Dobson M. J. Structure and polymorphism of human telomere-associated DNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90293-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad M. N., Wright J. H., Wolf A. J., Zakian V. A. RAP1 protein interacts with yeast telomeres in vivo: overproduction alters telomere structure and decreases chromosome stability. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):739–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90140-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Avilion A. A., LeFeuvre C. E., Stewart N. G., Greider C. W., Harley C. B., Bacchetti S. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1921–1929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Hirte H. W., Bacchetti S., Harley C. B. Telomerase activity in human ovarian carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):2900–2904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.2900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C., Fantes J., Goodfellow P., Cooke H. Functional reintroduction of human telomeres into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7006–7010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):458–460. doi: 10.1038/345458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Telomere loss: mitotic clock or genetic time bomb? Mutat Res. 1991 Mar-Nov;256(2-6):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Allshire R. C. Human telomeres: fusion and interstitial sites. Trends Genet. 1989 Oct;5(10):326–331. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Dempster M., Dunlop M. G., Thompson A. M., Green D. K., Allshire R. C. Telomere reduction in human colorectal carcinoma and with ageing. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):866–868. doi: 10.1038/346866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyrion G., Boakye K. A., Lustig A. J. C-terminal truncation of RAP1 results in the deregulation of telomere size, stability, and function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5159–5173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux N., Dutrillaux B., Viegas-Péquignot E. A simple method for simultaneous R- or G-banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization of small single-copy genes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;59(4):311–312. doi: 10.1159/000133277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Blackburn E. H. An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1- senescence. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90234-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Szostak J. W. A mutant with a defect in telomere elongation leads to senescence in yeast. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C., Martin S., Trask B., Hamlin J. L. Sister chromatid fusion initiates amplification of the dihydrofolate reductase gene in Chinese hamster cells. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):605–620. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder B. A., Morgan W. F. Delayed chromosomal instability induced by DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6667–6677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Stability of Broken Ends of Chromosomes in Zea Mays. Genetics. 1941 Mar;26(2):234–282. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P., Fuller L. F., Painter R. B. Establishment and characterization of a permanent pSV ori--transformed ataxia-telangiectasia cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1985 May;158(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P. Inducible gene expression by DNA rearrangements in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):549–558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P. Influence of cellular sequences on instability of plasmid integration sites in human cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 May;16(3):195–209. doi: 10.1007/BF01233356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murnane J. P., Yu L. C. Acquisition of telomere repeat sequences by transfected DNA integrated at the site of a chromosome break. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):977–983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltman D., Morgan R., Cleary M. L., de Lange T. Telomeric structure in cells with chromosome end associations. Chromosoma. 1993 Jan;102(2):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00356029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandell L. L., Zakian V. A. Loss of a yeast telomere: arrest, recovery, and chromosome loss. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90493-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shampay J., Blackburn E. H. Generation of telomere-length heterogeneity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Stark M. B., Gorman P. A., Stark G. R. Fusions near telomeres occur very early in the amplification of CAD genes in Syrian hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5427–5431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo F., Buttin G., Debatisse M. The origin of chromosome rearrangements at early stages of AMPD2 gene amplification in Chinese hamster cells. Curr Biol. 1993 May 1;3(5):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90175-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo F., Le Roscouet D., Buttin G., Debatisse M. Co-amplified markers alternate in megabase long chromosomal inverted repeats and cluster independently in interphase nuclei at early steps of mammalian gene amplification. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2665–2673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Zakian V. A. Telomere-telomere recombination provides an express pathway for telomere acquisition. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):456–458. doi: 10.1038/345456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Lamb J., Harris P. C., Finney R. D., Higgs D. R. A truncated human chromosome 16 associated with alpha thalassaemia is stabilized by addition of telomeric repeat (TTAGGG)n. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):868–871. doi: 10.1038/346868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Bradley J. D., Attardi L. D., Blackburn E. H. In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):126–132. doi: 10.1038/344126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkin J. Sugar and disease. Nature. 1972 Sep 22;239(5369):197–199. doi: 10.1038/239197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T., Shiue L., Myers R. M., Cox D. R., Naylor S. L., Killery A. M., Varmus H. E. Structure and variability of human chromosome ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):518–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]