Abstract
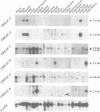
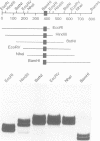
The forkhead domain is a monomeric DNA binding motif that defines a rapidly growing family of eukaryotic transcriptional regulators. Genetic and biochemical data suggest a central role in embryonic development for genes encoding forkhead proteins. We have used PCR and low stringency hybridization to isolate clones from human cDNA and genomic libraries that represent seven novel forkhead genes, freac-1 to freac-7. The spatial patterns of expression for the seven freac genes range from specific for a single tissue to nearly ubiquitous. The DNA binding specificities of four of the FREAC proteins were determined by selection of binding sites from random sequence oligonucleotides. The binding sites for all four FREAC proteins share a core sequence, RTAAAYA, but differ in the positions flanking the core. Domain swaps between two FREAC proteins identified two subregions within the forkhead domain as responsible for creating differences in DNA binding specificity. Applying a circular permutation assay, we show that binding of FREAC proteins to their cognate sites results in bending of the DNA at an angle of 80-90 degrees.
Full text
PDF

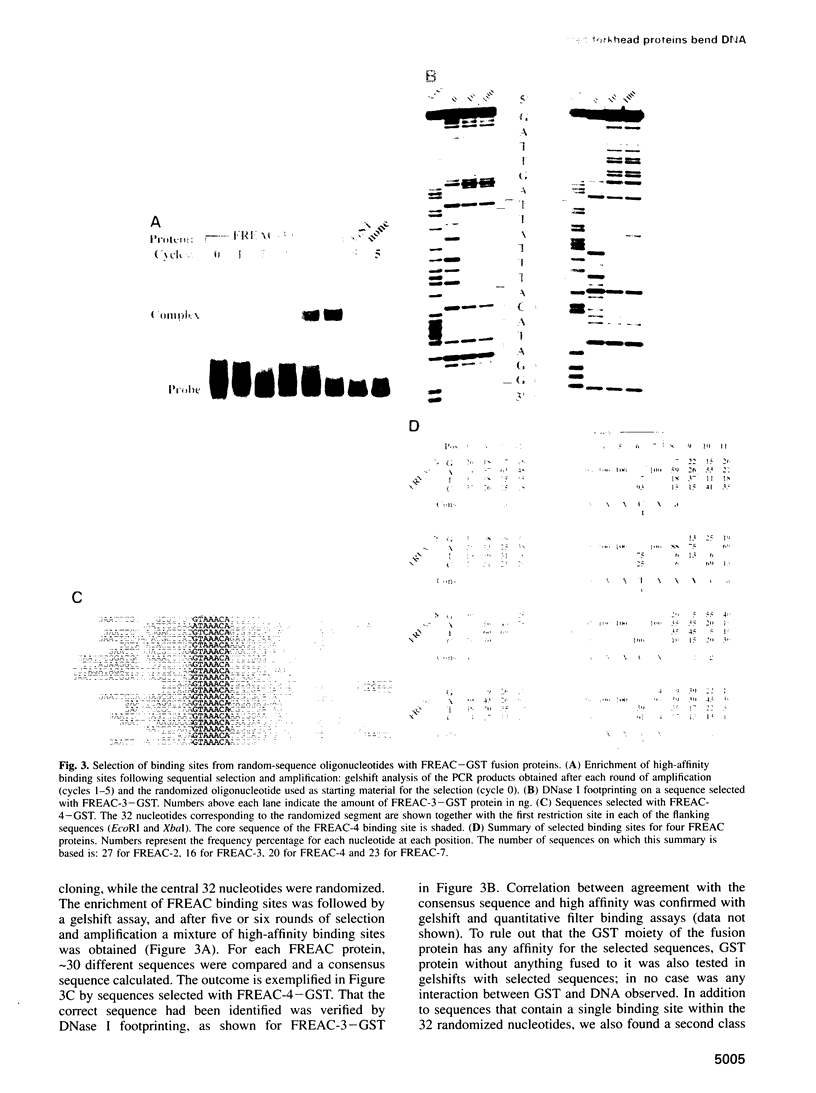







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bork P., Ouzounis C., Sander C., Scharf M., Schneider R., Sonnhammer E. Comprehensive sequence analysis of the 182 predicted open reading frames of yeast chromosome III. Protein Sci. 1992 Dec;1(12):1677–1690. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. G. The winged-helix DNA-binding motif: another helix-turn-helix takeoff. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):773–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Waterman M. L., Jones K. A. The hLEF/TCF-1 alpha HMG protein contains a context-dependent transcriptional activation domain that induces the TCR alpha enhancer in T cells. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2418–2430. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catron K. M., Iler N., Abate C. Nucleotides flanking a conserved TAAT core dictate the DNA binding specificity of three murine homeodomain proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2354–2365. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Halay E. D., Lai E., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):412–420. doi: 10.1038/364412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevidence D. E., Overdier D. G., Tao W., Qian X., Pani L., Lai E., Costa R. H. Identification of nine tissue-specific transcription factors of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead DNA-binding-domain family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3948–3952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen M. L., Jamrich M. A novel, activin-inducible, blastopore lip-specific gene of Xenopus laevis contains a fork head DNA-binding domain. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):599–608. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echelard Y., Epstein D. J., St-Jacques B., Shen L., Mohler J., McMahon J. A., McMahon A. P. Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1417–1430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Differential DNA sequence recognition is a determinant of specificity in homeotic gene action. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4059–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck S., Ohlsson B. G., Samuelsson L., Bjursell G. Characterization of the human lipoprotein lipase (LPL) promoter: evidence of two cis-regulatory regions, LP-alpha and LP-beta, of importance for the differentiation-linked induction of the LPL gene during adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4622–4633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Grosschedl R. LEF-1 contains an activation domain that stimulates transcription only in a specific context of factor-binding sites. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4667–4676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Giese K., Pagel J. HMG domain proteins: architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. The Drosophila sloppy paired locus encodes two proteins involved in segmentation that show homology to mammalian transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):1030–1051. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grueneberg D. A., Natesan S., Alexandre C., Gilman M. Z. Human and Drosophila homeodomain proteins that enhance the DNA-binding activity of serum response factor. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1089–1095. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Johnson F. B. Synergism in transcriptional activation: a kinetic view. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):173–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häcker U., Grossniklaus U., Gehring W. J., Jäckle H. Developmentally regulated Drosophila gene family encoding the fork head domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8754–8758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Luciw P. A., Duchange N. Structural arrangements of transcription control domains within the 5'-untranslated leader regions of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoters. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1101–1114. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Hiemisch H., Luckow B., Schütz G. The HNF-3 gene family of transcription factors in mice: gene structure, cDNA sequence, and mRNA distribution. Genomics. 1994 Apr;20(3):377–385. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Lee K. H., Schlöndorff J., Hiemisch H., Monaghan A. P., Schütz G. Six members of the mouse forkhead gene family are developmentally regulated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7628–7631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kain K. C., Orlandi P. A., Lanar D. E. Universal promoter for gene expression without cloning: expression-PCR. Biotechniques. 1991 Mar;10(3):366–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Clark K. L., Burley S. K., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/fork head or "winged helix" proteins: a family of transcription factors of diverse biologic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10421–10423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb P., McKnight S. L. Diversity and specificity in transcriptional regulation: the benefits of heterotypic dimerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90167-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Lai C. F., Sigman D. S., Gaynor R. B. Cloning of a cellular factor, interleukin binding factor, that binds to NFAT-like motifs in the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7739–7743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Lusis A. J., Sparkes R., Nirula A., Gaynor R. Characterization and chromosomal mapping of the gene encoding the cellular DNA binding protein ILF. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):665–671. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90139-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Lusis A. J., Sparkes R., Tran S. M., Gaynor R. Characterization and chromosomal mapping of the gene encoding the cellular DNA binding protein HTLF. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):658–664. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90138-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M., Ptashne M., Green M. R. How different eukaryotic transcriptional activators can cooperate promiscuously. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):359–361. doi: 10.1038/345359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. M., Gallegos M. E., Morisseau B. A., Kim S. K. lin-31, a Caenorhabditis elegans HNF-3/fork head transcription factor homolog, specifies three alternative cell fates in vulval development. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):933–947. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moitoso de Vargas L., Kim S., Landy A. DNA looping generated by DNA bending protein IHF and the two domains of lambda integrase. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1457–1461. doi: 10.1126/science.2544029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natesan S., Gilman M. Z. DNA bending and orientation-dependent function of YY1 in the c-fos promoter. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2497–2509. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. M., Long G. L. A general method of site-specific mutagenesis using a modification of the Thermus aquaticus polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jul;180(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overdier D. G., Porcella A., Costa R. H. The DNA-binding specificity of the hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/forkhead domain is influenced by amino-acid residues adjacent to the recognition helix. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2755–2766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Pham M. H., Galas D. J. Plasmid permutation vectors to monitor DNA bending. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10060–10060. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle R. D., Johnson R. L., Laufer E., Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1401–1416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Cox C., Jessell T. M., Klar A. Ectopic neural expression of a floor plate marker in frog embryos injected with the midline transcription factor Pintallavis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8268–8272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hogan B. L. Differential expression of multiple fork head related genes during gastrulation and axial pattern formation in the mouse embryo. Development. 1993 May;118(1):47–59. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Hogan B. L. HNF-3 beta as a regulator of floor plate development. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Blader P., Henrique D., Ingham P. W. Axial, a zebrafish gene expressed along the developing body axis, shows altered expression in cyclops mutant embryos. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1436–1446. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya S., Yamabe M., Yamaguchi Y., Kobayashi Y., Konno T., Tada K. Establishment and characterization of a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line (THP-1). Int J Cancer. 1980 Aug;26(2):171–176. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Fischer W. H., Jones K. A. A thymus-specific member of the HMG protein family regulates the human T cell receptor C alpha enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):656–669. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jäckle H. The fork head domain: a novel DNA binding motif of eukaryotic transcription factors? Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):455–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90439-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel D., Jürgens G., Küttner F., Seifert E., Jäckle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):645–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu G., Muller E. G., Amacher S. L., Northrop J. L., Davis T. N. A dosage-dependent suppressor of a temperature-sensitive calmodulin mutant encodes a protein related to the fork head family of DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1779–1787. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Catabolite activator protein-induced DNA bending in transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90562-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]