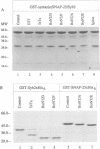
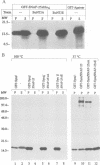
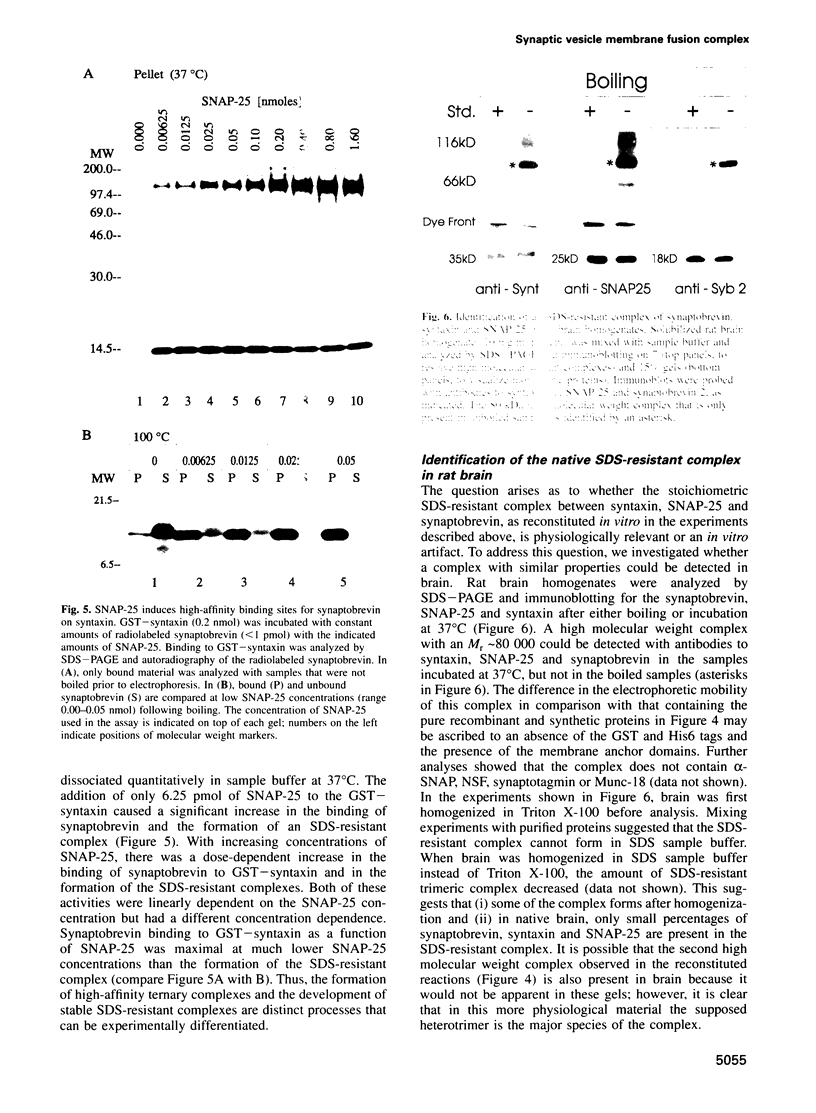
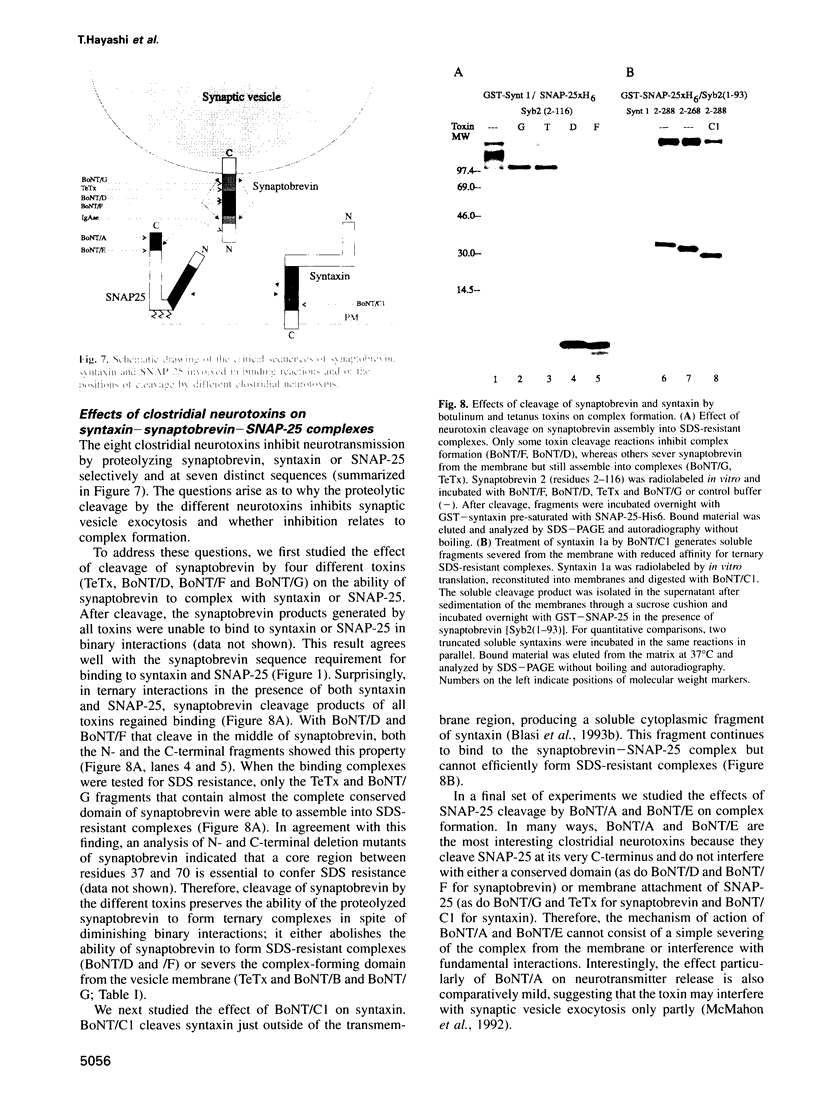
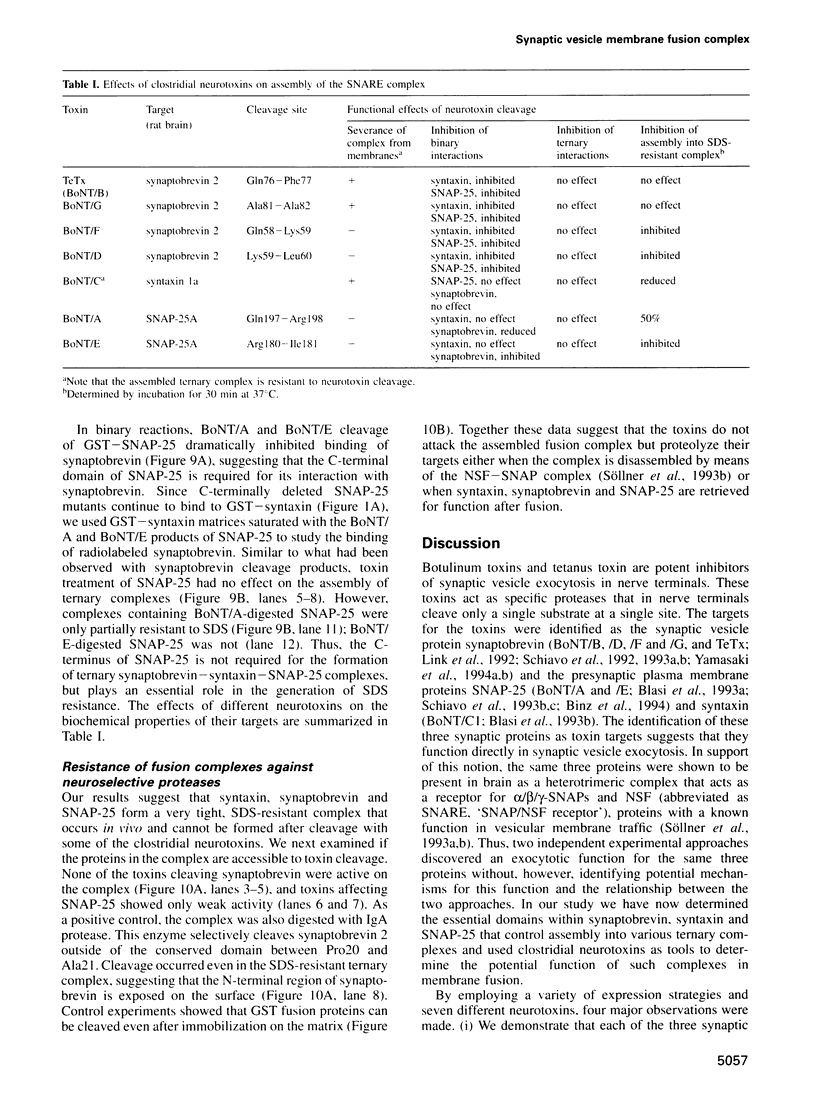
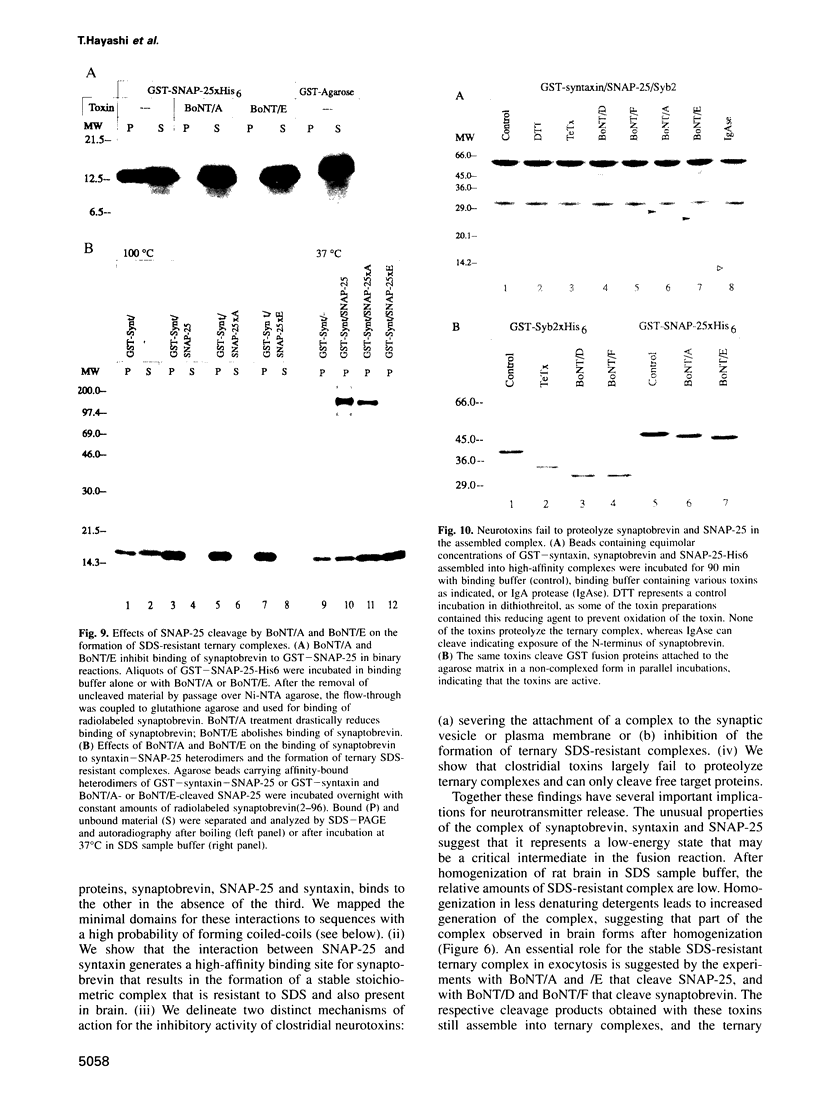
Abstract
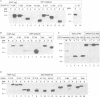
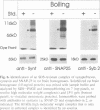
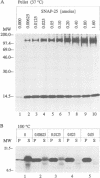
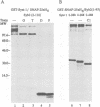
Clostridial neurotoxins inhibit neurotransmitter release by selective and specific intracellular proteolysis of synaptobrevin/VAMP, synaptosomal-associated protein of 25 kDa (SNAP-25) or syntaxin. Here we show that in binary reactions synaptobrevin binds weakly to both SNAP-25 and syntaxin, and SNAP-25 binds to syntaxin. In the presence of all three components, a dramatic increase in the interaction strengths occurs and a stable sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant complex forms. Mapping of the interacting sequences reveals that complex formation correlates with the presence of predicted alpha-helical structures, suggesting that membrane fusion involves intermolecular interactions via coiled-coil structures. Most toxins only attack the free, and not the complexed, proteins, and proteolysis of the proteins by different clostridial neurotoxins has distinct inhibitory effects on the formation of synaptobrevin-syntaxin-SNAP-25 complexes. Our data suggest that synaptobrevin, syntaxin and SNAP-25 associate into a unique stable complex that functions in synaptic vesicle exocytosis.
Full text
PDF
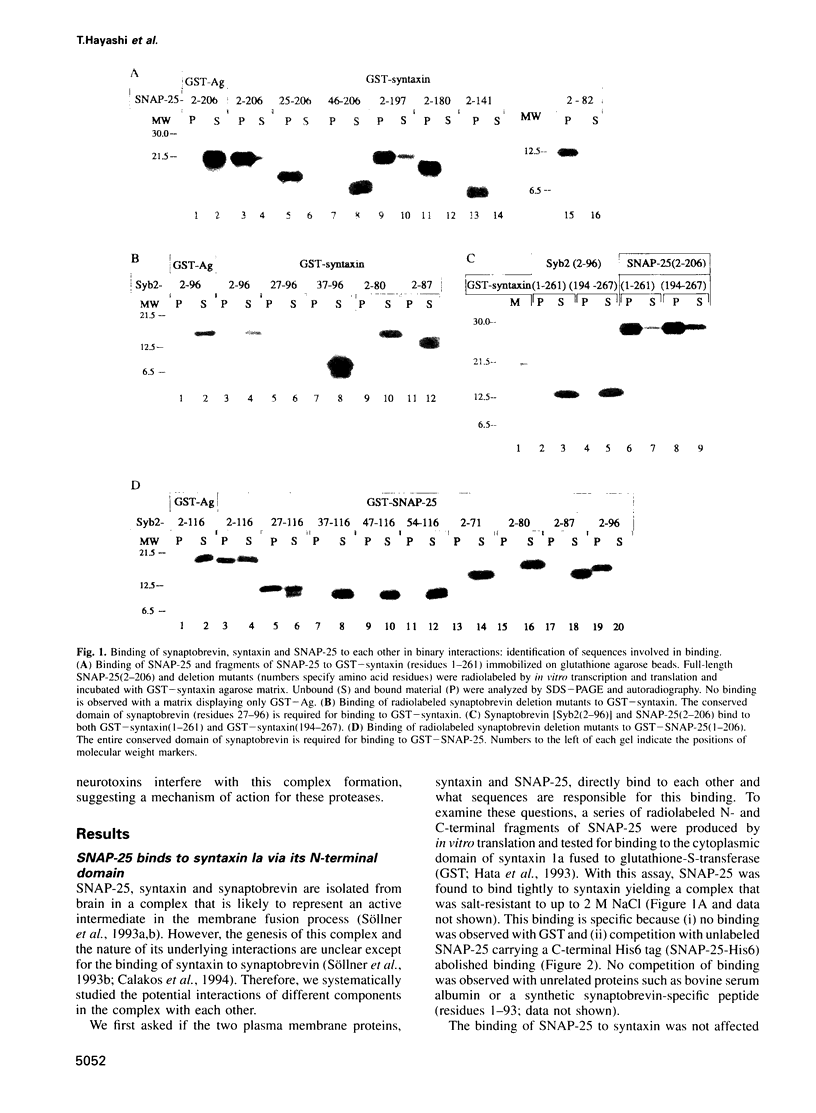





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer B. T., 3rd, Ozçelik T., Jahn R., Francke U., Südhof T. C. Structures and chromosomal localizations of two human genes encoding synaptobrevins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17267–17273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz T., Blasi J., Yamasaki S., Baumeister A., Link E., Südhof T. C., Jahn R., Niemann H. Proteolysis of SNAP-25 by types E and A botulinal neurotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1617–1620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi J., Chapman E. R., Yamasaki S., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R. Botulinum neurotoxin C1 blocks neurotransmitter release by means of cleaving HPC-1/syntaxin. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4821–4828. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Bennett M. K., Peterson K. E., Scheller R. H. Protein-protein interactions contributing to the specificity of intracellular vesicular trafficking. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1146–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.8108733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. M., Kim P. S. A spring-loaded mechanism for the conformational change of influenza hemagglutinin. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90260-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Parry D. A. Alpha-helical coiled coils and bundles: how to design an alpha-helical protein. Proteins. 1990;7(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata Y., Slaughter C. A., Südhof T. C. Synaptic vesicle fusion complex contains unc-18 homologue bound to syntaxin. Nature. 1993 Nov 25;366(6453):347–351. doi: 10.1038/366347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. M., Bommert K., Charlton M. P., Kistner A., Habermann E., Augustine G. J., Betz H. A post-docking role for synaptobrevin in synaptic vesicle fusion. Neuron. 1994 Jun;12(6):1269–1279. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Obata K., Akagawa K. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for a neuronal cell membrane antigen, HPC-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10613–10619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Synaptic vesicles and exocytosis. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:219–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link E., Edelmann L., Chou J. H., Binz T., Yamasaki S., Eisel U., Baumert M., Südhof T. C., Niemann H., Jahn R. Tetanus toxin action: inhibition of neurotransmitter release linked to synaptobrevin proteolysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92305-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Van Dyke M., Stock J. Predicting coiled coils from protein sequences. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1162–1164. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer T., Tamura T., Falk M., Niemann H. Membrane integration and intracellular transport of the coronavirus glycoprotein E1, a class III membrane glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14956–14963. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)68131-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Foran P., Dolly J. O., Verhage M., Wiegant V. M., Nicholls D. G. Tetanus toxin and botulinum toxins type A and B inhibit glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, aspartate, and met-enkephalin release from synaptosomes. Clues to the locus of action. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21338–21343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Ushkaryov Y. A., Edelmann L., Link E., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Cellubrevin is a ubiquitous tetanus-toxin substrate homologous to a putative synaptic vesicle fusion protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):346–349. doi: 10.1038/364346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Simons K. The Golgi complex: in vitro veritas? Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):829–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90027-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Blasi J., Jahn R. Clostridial neurotoxins: new tools for dissecting exocytosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Klemm J. D., Kim P. S., Alber T. X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.1948029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Molecular dissection of the secretory pathway. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):409–415. doi: 10.1038/355409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Benfenati F., Poulain B., Rossetto O., Polverino de Laureto P., DasGupta B. R., Montecucco C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):832–835. doi: 10.1038/359832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Rossetto O., Catsicas S., Polverino de Laureto P., DasGupta B. R., Benfenati F., Montecucco C. Identification of the nerve terminal targets of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A, D, and E. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23784–23787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Santucci A., Dasgupta B. R., Mehta P. P., Jontes J., Benfenati F., Wilson M. C., Montecucco C. Botulinum neurotoxins serotypes A and E cleave SNAP-25 at distinct COOH-terminal peptide bonds. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 29;335(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Shone C. C., Rossetto O., Alexander F. C., Montecucco C. Botulinum neurotoxin serotype F is a zinc endopeptidase specific for VAMP/synaptobrevin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11516–11519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring J., Kato M., Bernfield M. Epimorphin is related to a new class of neuronal and yeast vesicle targeting proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):124–125. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90018-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Bennett M. K., Whiteheart S. W., Scheller R. H., Rothman J. E. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki S., Baumeister A., Binz T., Blasi J., Link E., Cornille F., Roques B., Fykse E. M., Südhof T. C., Jahn R. Cleavage of members of the synaptobrevin/VAMP family by types D and F botulinal neurotoxins and tetanus toxin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12764–12772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki S., Binz T., Hayashi T., Szabo E., Yamasaki N., Eklund M., Jahn R., Niemann H. Botulinum neurotoxin type G proteolyses the Ala81-Ala82 bond of rat synaptobrevin 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 29;200(2):829–835. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]