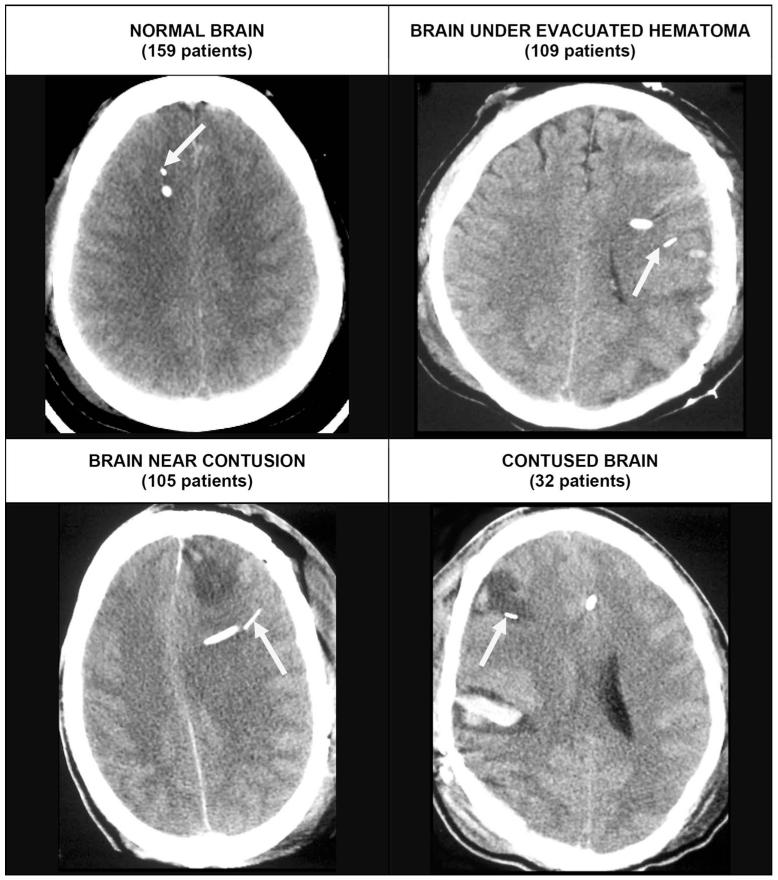
FIGURE 2.
Computed tomography scans illustrate typical appearance of the different catheter positions. The arrow identifies the brain tissue PO2 (PbtO2) probe in each case. Top left, the PbtO2 probe in normal-appearing right frontal lobe in a patient with a diffuse brain injury. Top right, the PbtO2 probe in brain after evacuation of a subdural hematoma. The probe was placed at the time of surgery in brain tissue. The brain appears normal but has been compressed by the subdural hematoma. Bottom left, a PbtO2 probe in the left frontal lobe near a contusion. If the contusion expands, this tissue is likely to become involved or to be compressed. Bottom right, a PbtO2 within a contusion in the right frontal lobe.