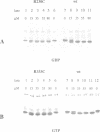
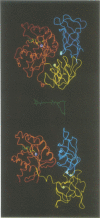
Abstract
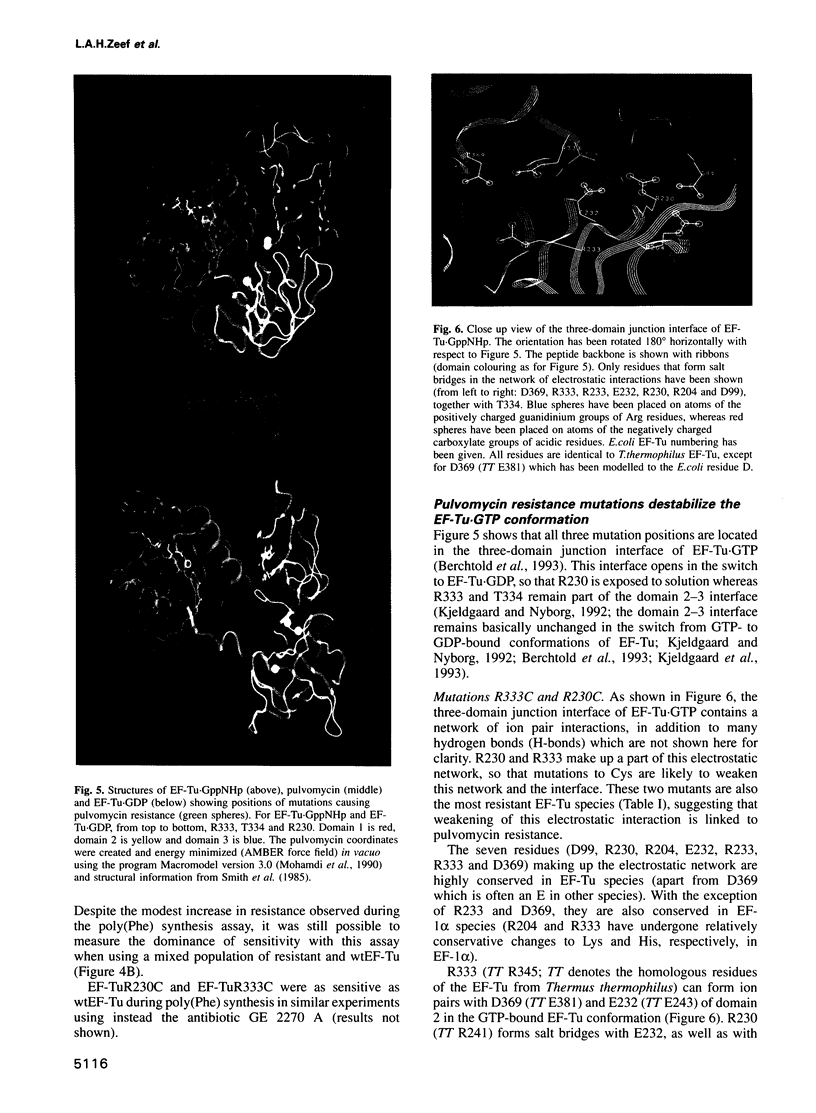
This paper reports the generation of Escherichia coli mutants resistant to pulvomycin. Together with targeted mutagenesis of the tufA gene, conditions were found to overcome membrane impermeability, thereby allowing the selection of three mutants harbouring elongation factor (EF)-Tu Arg230-->Cys, Arg333-->Cys or Thr334-->Ala which confer pulvomycin resistance. These mutations are clustered in the three-domain junction interface of the crystal structure of the GTP form of Thermus thermophilus EF-Tu. This result shares similarities with kirromycin resistance; kirromycin-resistant mutations cluster in the domain 1-3 interface. Since both interface regions are involved in the EF-Tu switch mechanism, we propose that pulvomycin and kirromycin both act by specifically disturbing the allosteric changes required for the switch from EF-Tu-GTP to EF-Tu-GDP. The three-domain junction changes dramatically in the switch to EF-Tu.GDP; in EF-Tu.GDP this region forms an open hole. Structural analysis of the mutation positions in EF-Tu.GTP indicated that the two most highly resistant mutants, R230C and R333C, are part of an electrostatic network involving numerous residues. All three mutations appear to destabilize the EF-Tu.GTP conformation. Genetic and protein characterizations show that sensitivity to pulvomycin is dominant over resistance. This appears to contradict the currently accepted model of protein synthesis inhibition by pulvomycin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AKITA E., MAEDA K., UMEZAWA H. CHEMISTRY OF LABILOMYCIN. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1964 Sep;17:200–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AKITA E., MAEDA K., UMEZAWA H. ILOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF LABILOMYCIN, A NEW ANTIBIOTIC. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1963 Jul;16:147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams J. P., van Raaij M. J., Ott G., Kraal B., Bosch L. Kirromycin drastically reduces the affinity of Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu for aminoacyl-tRNA. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 9;30(27):6705–6710. doi: 10.1021/bi00241a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anborgh P. H., Parmeggiani A., Jonák J. Site-directed mutagenesis of elongation factor Tu. The functional and structural role of residue Cys81. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 1;208(2):251–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anborgh P. H., Parmeggiani A. New antibiotic that acts specifically on the GTP-bound form of elongation factor Tu. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):779–784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anborgh P. H., Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin-induced modifications facilitate the separation of EF-Tu species and reveal intermolecular interactions. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):126–132. doi: 10.1038/365126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Model P., Zinder N. D. Effects of bacteriophage f1 gene III protein on the host cell membrane. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(2):185–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00331849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G., Wolf H., Parmeggiani A. Effect of kirromycin on elongation factor Tu. Location of the catalytic center for ribosome-elongation-factor-Tu GTPase activity on the elongation factor. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):55–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousineau B., Cerpa C., Lefebvre J., Cedergren R. The sequence of the gene encoding elongation factor Tu from Chlamydia trachomatis compared with those of other organisms. Gene. 1992 Oct 12;120(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90006-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg M., Rojas A. M., Weiser J., Kurland C. G. How many EF-Tu molecules participate in aminoacyl-tRNA binding and peptide bond formation in Escherichia coli translation? J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90074-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Sanchez A., Miller D. L. Mutagenesis of bacterial elongation factor Tu at lysine 136. A conserved amino acid in GTP regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8304–8309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivell R., Sander G., Parmeggiani A. Modulation by monovalent and divalent cations of the guanosine-5'-triphosphatase activity dependent on elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6852–6859. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Thirup S., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. Refined structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):721–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90986-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushiro M., Shimizu M., Tomita K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of the tuf gene coding for the elongation factor Tu of Thermus thermophilus HB8. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landini P., Bandera M., Soffientini A., Goldstein B. P. Sensitivity of elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) from different bacterial species to the antibiotics efrotomycin, pulvomycin and MDL 62879. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Apr;139(4):769–774. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-4-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei P., Sanz J. L., Altamura S., Hummel H., Cammarano P., Amils R., Böck A., Wolf H. Unique antibiotic sensitivity of archaebacterial polypeptide elongation factors. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):265–271. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.265-271.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesters J. R., Zeef L. A., Hilgenfeld R., de Graaf J. M., Kraal B., Bosch L. The structural and functional basis for the kirromycin resistance of mutant EF-Tu species in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4877–4885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ner S. S., Travers A. A., Churchill M. E. Harnessing the writhe: a role for DNA chaperones in nucleoprotein-complex formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):185–187. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Sander G. Properties and regulation of the GTPase activities of elongation factors Tu and G, and of initiation factor 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Mar 27;35(3):129–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02357085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Swart G. W. Mechanism of action of kirromycin-like antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:557–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S., Bloch P. L., Reeh S., Neidhardt F. C. Patterns of protein synthesis in E. coli: a catalog of the amount of 140 individual proteins at different growth rates. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingoud A., Block W., Wittinghofer A., Wolf H., Fischer E. The elongation factor Tu binds aminoacyl-tRNA in the presence of GDP. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11261–11267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingoud A., Urbanke C., Krauss G., Peters F., Maass G. Ternary complex formation between elongation factor Tu, GTP and aminoacyl-tRNA: an equilibrium study. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer R., Block W., Pingoud A., Wolf H. A 1H NMR study of the Escherichia coli elongation-factor Tu with guanine nucleotides and the antibiotic kirromycin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80231-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubulekas I., Hughes D. Growth and translation elongation rate are sensitive to the concentration of EF-Tu. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(4):761–770. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Klundert J. A., Van der Meide P. H., Van de Putte P., Bosch L. Mutants of Escherichia coli altered in both genes coding for the elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4470–4473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Vink T., Kraal B., Bosch L. Mutants of the elongation factor EF-Tu, a new class of nonsense suppressors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1049–1052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio R., Vaara M. The lipid A biosynthesis mutation lpxA2 of Escherichia coli results in drastic antibiotic supersusceptibility. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):826–829. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weijland A., Parmeggiani A. Toward a model for the interaction between elongation factor Tu and the ribosome. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1311–1314. doi: 10.1126/science.8446899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Assmann D., Fischer E. Pulvomycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis preventing ternary complex formation between elongation factor Tu, GTP, and aminoacyl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5324–5328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Sugisaki H., Takanami M., Kaziro Y. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned tufA gene of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C. C., Bernlohr R. W. Elongation factor Tu is methylated in response to nutrient deprivation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3096–3100. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3096-3100.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeef L. A., Bosch L. A technique for targeted mutagenesis of the EF-Tu chromosomal gene by M13-mediated gene replacement. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(1-2):252–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00279554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Vijgenboom E., Dicke M., Bosch L. Regulation of the expression of tufA and tufB, the two genes coding for the elongation factor EF-Tu in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]