Abstract
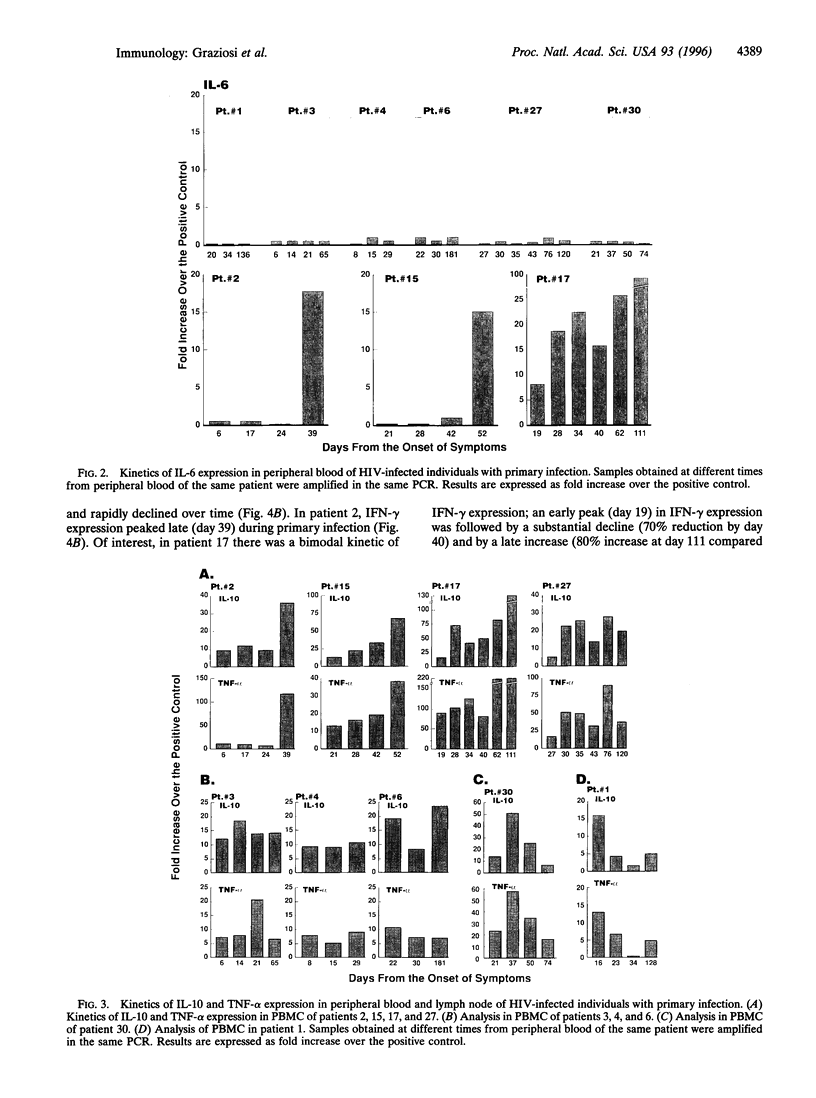
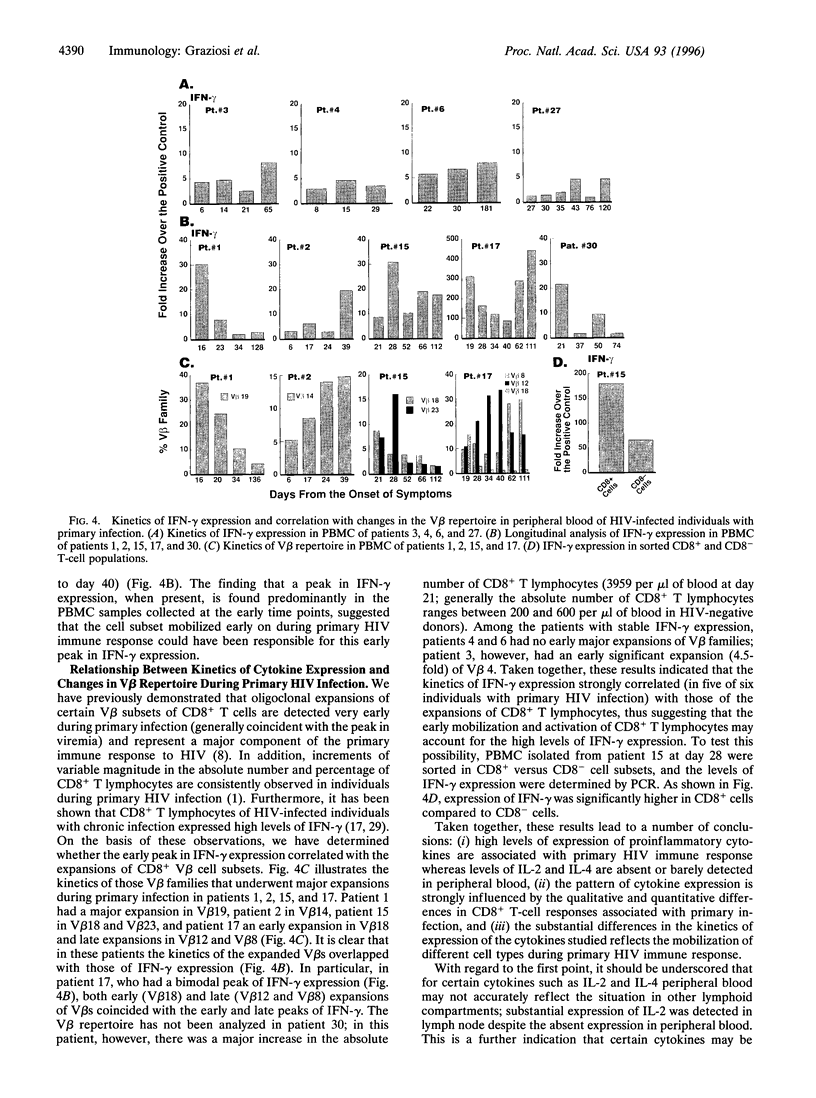
In the present study, we have determined the kinetics of constitutive expression of a panel of cytokines [interleukin (IL) 2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)] in sequential peripheral blood mononuclear cell samples from nine individuals with primary human immunodeficiency virus infection. Expression of IL-2 and IL-4 was barely detected in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. However, substantial levels of IL-2 expression were found in mononuclear cells isolated from lymph node. Expression of IL-6 was detected in only three of nine patients, and IL-6 expression was observed when transition from the acute to the chronic phase had already occurred. Expression of IL-10 and TNF-alpha was consistently observed in all patients tested, and levels of both cytokines were either stable or progressively increased over time. Similar to IL-10 and TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma expression was detected in all patients; however, in five of nine patients, IFN-gamma expression peaked very early during primary infection. The early peak in IFN-gamma expression coincided with oligoclonal expansions of CD8+ T cells in five of six patients, and CD8+ T cells mostly accounted for the expression of this cytokine. These results indicate that high levels of expression of proinflammatory cytokines are associated with primary infection and that the cytokine response during this phase of infection is strongly influenced by oligoclonal expansions of CD8+ T cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Autran B., Legac E., Blanc C., Debré P. A Th0/Th2-like function of CD4+CD7- T helper cells from normal donors and HIV-infected patients. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 1;154(3):1408–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baier M., Werner A., Bannert N., Metzner K., Kurth R. HIV suppression by interleukin-16. Nature. 1995 Dec 7;378(6557):563–563. doi: 10.1038/378563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrow P., Lewicki H., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Oldstone M. B. Virus-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity associated with control of viremia in primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):6103–6110. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.6103-6110.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. W., Kou Z. C., Lekutis C., Shen L., Zhou D., Halloran M., Li J., Sodroski J., Lee-Parritz D., Letvin N. L. T cell receptor V beta repertoire in an acute infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency viruses and a chimeric simian-human immunodeficiency virus. J Exp Med. 1995 Jul 1;182(1):21–31. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Saag M. S., Decker W. D., Campbell-Hill S., Roberson J. L., Veldkamp P. J., Kappes J. C., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. High titers of cytopathic virus in plasma of patients with symptomatic primary HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):954–960. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Shearer G. M. A TH1-->TH2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi F., DeVico A. L., Garzino-Demo A., Arya S. K., Gallo R. C., Lusso P. Identification of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MIP-1 beta as the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T cells. Science. 1995 Dec 15;270(5243):1811–1815. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5243.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar E. S., Moudgil T., Meyer R. D., Ho D. D. Transient high levels of viremia in patients with primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):961–964. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwart E. L., Shpaer E. G., Louwagie J., McCutchan F. E., Grez M., Rübsamen-Waigmann H., Mullins J. I. Genetic relationships determined by a DNA heteroduplex mobility assay: analysis of HIV-1 env genes. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1257–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.8235655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J., Bass H. Z., Fahey J. L. Elevated IFN-gamma and decreased IL-2 gene expression are associated with HIV infection. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):5031–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziosi C., Pantaleo G., Gantt K. R., Fortin J. P., Demarest J. F., Cohen O. J., Sékaly R. P., Fauci A. S. Lack of evidence for the dichotomy of TH1 and TH2 predominance in HIV-infected individuals. Science. 1994 Jul 8;265(5169):248–252. doi: 10.1126/science.8023143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Panka D. J., Cui H., Ettinger R., el-Khatib M., Sherr D. H., Stanger B. Z., Marshak-Rothstein A. Fas(CD95)/FasL interactions required for programmed cell death after T-cell activation. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):444–448. doi: 10.1038/373444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koup R. A., Safrit J. T., Cao Y., Andrews C. A., McLeod G., Borkowsky W., Farthing C., Ho D. D. Temporal association of cellular immune responses with the initial control of viremia in primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 syndrome. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4650–4655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4650-4655.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrecque N., McGrath H., Subramanyam M., Huber B. T., Sékaly R. P. Human T cells respond to mouse mammary tumor virus-encoded superantigen: V beta restriction and conserved evolutionary features. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1735–1743. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackewicz C. E., Yang L. C., Lifson J. D., Levy J. A. Non-cytolytic CD8 T-cell anti-HIV responses in primary HIV-1 infection. Lancet. 1994 Dec 17;344(8938):1671–1673. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90459-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi E., Mazzetti M., Ravina A., Annunziato F., de Carli M., Piccinni M. P., Manetti R., Carbonari M., Pesce A. M., del Prete G. Ability of HIV to promote a TH1 to TH0 shift and to replicate preferentially in TH2 and TH0 cells. Science. 1994 Jul 8;265(5169):244–248. doi: 10.1126/science.8023142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyaard L., Otto S. A., Keet I. P., van Lier R. A., Miedema F. Changes in cytokine secretion patterns of CD4+ T-cell clones in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 1994 Dec 15;84(12):4262–4268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Cao Y., Ho D. D., Koup R. A. Development of the anti-gp120 antibody response during seroconversion to human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1994 Aug;68(8):5142–5155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.5142-5155.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Demarest J. F., Soudeyns H., Graziosi C., Denis F., Adelsberger J. W., Borrow P., Saag M. S., Shaw G. M., Sekaly R. P. Major expansion of CD8+ T cells with a predominant V beta usage during the primary immune response to HIV. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):463–467. doi: 10.1038/370463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Fauci A. S. New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of HIV infection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:487–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Butini L., Pizzo P. A., Schnittman S. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. Lymphoid organs function as major reservoirs for human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9838–9842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Demarest J. F., Butini L., Montroni M., Fox C. H., Orenstein J. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):355–358. doi: 10.1038/362355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Demarest J. F., Cohen O. J., Vaccarezza M., Gantt K., Muro-Cacho C., Fauci A. S. Role of lymphoid organs in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Immunol Rev. 1994 Aug;140:105–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Fauci A. S. New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 4;328(5):327–335. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302043280508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Koenig S., Baseler M., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Defective clonogenic potential of CD8+ T lymphocytes in patients with AIDS. Expansion in vivo of a nonclonogenic CD3+CD8+DR+CD25- T cell population. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1696–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Seder R. A. Lymphocyte responses and cytokines. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Fauci A. S. The effect of cytokines and pharmacologic agents on chronic HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Feb;8(2):191–197. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebai N., Pantaleo G., Demarest J. F., Ciurli C., Soudeyns H., Adelsberger J. W., Vaccarezza M., Walker R. E., Sekaly R. P., Fauci A. S. Analysis of the T-cell receptor beta-chain variable-region (V beta) repertoire in monozygotic twins discordant for human immunodeficiency virus: evidence for perturbations of specific V beta segments in CD4+ T cells of the virus-positive twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1529–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinicco A., Biglino A., Sciandra M., Forno B., Pollono A. M., Raiteri R., Gioannini P. Cytokine network and acute primary HIV-1 infection. AIDS. 1993 Sep;7(9):1167–1172. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199309000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall B., Cooper D. A. Primary HIV infection: host responses and intervention strategies. AIDS. 1991 Jan;5(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]