Abstract
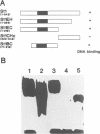
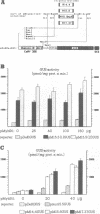
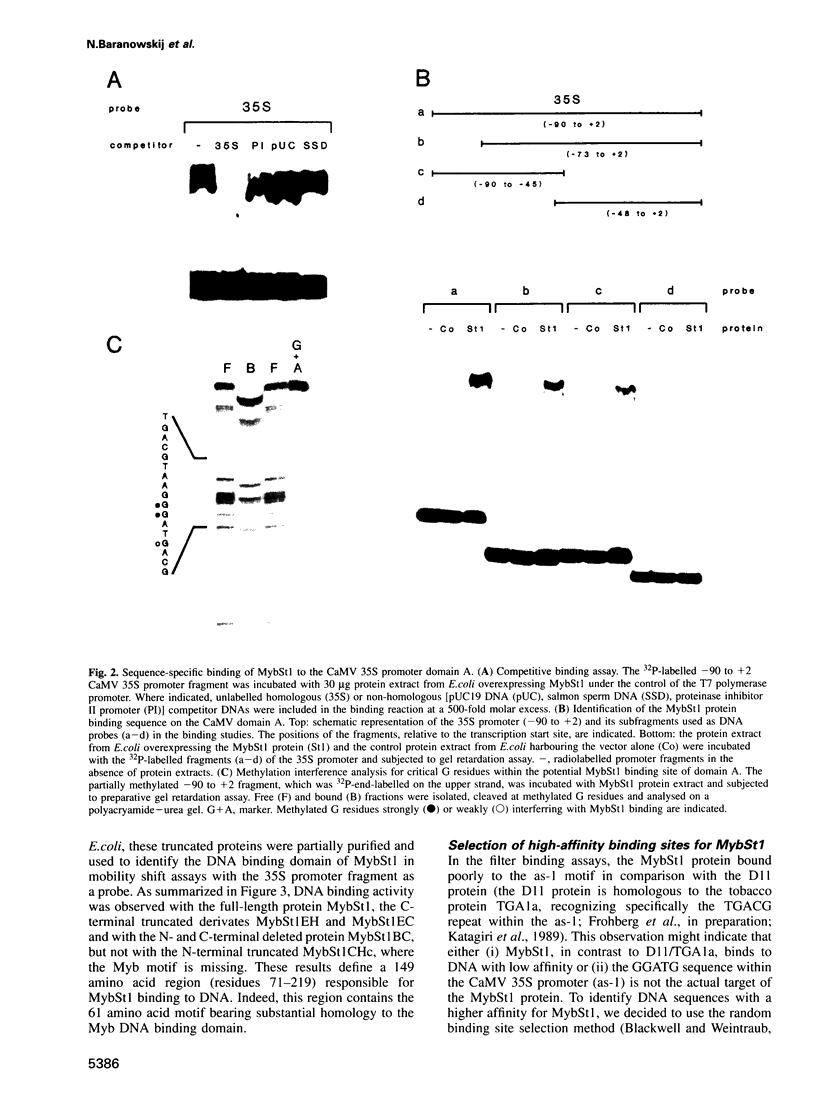
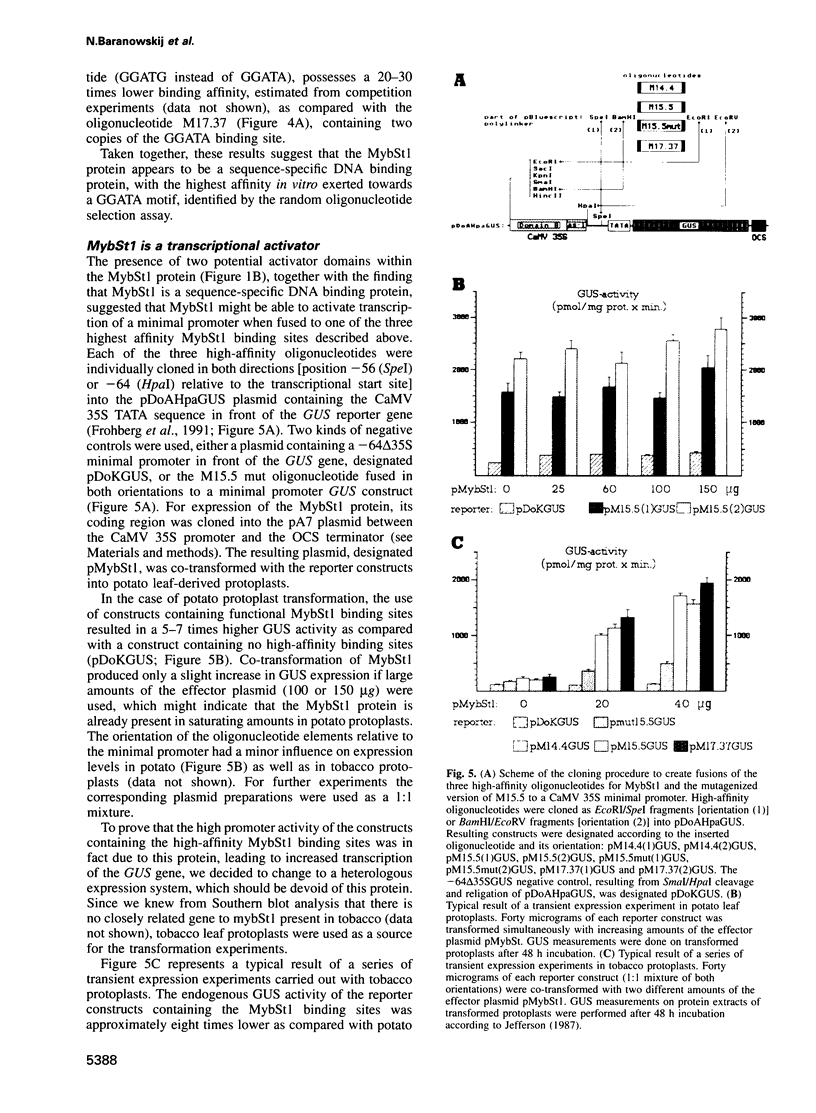
A cDNA clone encoding a novel Myb-related protein, designated MybSt1, was isolated from a potato cDNA expression library by South Western screening using the CaMV 35S promoter domain A as a probe. Sequence comparison shows a small region with some homology to the highly conserved DNA binding domain of the c-myb proto-oncogene consisting of three imperfect repeats. The Myb motif of the MybSt1 protein is distinct from the plant Myb DNA binding domain described so far. In contrast to the known plant Myb proteins, with two repeats required for the DNA binding activity, the clone mybSt1 contains only one such repeat. Nevertheless, the Myb-related protein MybSt1 is able to bind to DNA in a sequence-specific manner. In addition to the Myb-like region, the protein MybSt1 contains an acidic segment in its central region as well as a proline-rich region near the C-terminus. Applying the random binding site selection technique, high-affinity DNA binding sites for MybSt1 were identified, sharing the core motif GGATA. In transient expression assays using plant protoplasts, clear evidence was obtained for this myb clone functioning as a transcriptional activator.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaravadi L., King M. W. Characterization and expression of the Xenopus c-Myb homolog. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):971–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anton I. A., Frampton J. Tryptophans in myb proteins. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):719–719. doi: 10.1038/336719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J., Nieto C., Cañas L., Benito M. J., Paz-Ares J. Petunia hybrida genes related to the maize regulatory C1 gene and to animal myb proto-oncogenes. Plant J. 1993 Apr;3(4):553–562. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.03040553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Ren L., Chua N. H. The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue-specific expression patterns. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2195–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm B., Schmidt R., Willmitzer L. Efficient transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using direct gene transfer to protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):6–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00330935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England B. P., Admon A., Tjian R. Cloning of Drosophila transcription factor Adf-1 reveals homology to Myb oncoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):683–687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Gibson T. J., Ness S. A., Döderlein G., Graf T. Proposed structure for the DNA-binding domain of the Myb oncoprotein based on model building and mutational analysis. Protein Eng. 1991 Dec;4(8):891–901. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.8.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Leutz A., Gibson T., Graf T. DNA-binding domain ancestry. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):134–134. doi: 10.1038/342134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohberg C., Heins L., Gatz C. Characterization of the interaction of plant transcription factors using a bacterial repressor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10470–10474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamborg O. L., Miller R. A., Ojima K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Apr;50(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Cone K. C., Fromm M. E. Identification of functional domains in the maize transcriptional activator C1: comparison of wild-type and dominant inhibitor proteins. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):298–309. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotewold E., Athma P., Peterson T. Alternatively spliced products of the maize P gene encode proteins with homology to the DNA-binding domain of myb-like transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4587–4591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotewold E., Drummond B. J., Bowen B., Peterson T. The myb-homologous P gene controls phlobaphene pigmentation in maize floral organs by directly activating a flavonoid biosynthetic gene subset. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Reakes C. F., Watson R. J. Characterization of the sequence-specific interaction of mouse c-myb protein with DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):161–169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D., Culianez-Macia F., Prescott A. G., Roberts K., Martin C. Expression patterns of myb genes from Antirrhinum flowers. Plant Cell. 1991 Feb;3(2):115–125. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.2.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju Q. D., Morrow B. E., Warner J. R. REB1, a yeast DNA-binding protein with many targets, is essential for growth and bears some resemblance to the oncogene myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5226–5234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkbrenner F., Guehmann S., Moelling K. Transcriptional activation by human c-myb and v-myb genes. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):657–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri F., Lam E., Chua N. H. Two tobacco DNA-binding proteins with homology to the nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):727–730. doi: 10.1038/340727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen A. L., Kornberg T. B., Bishop J. M. Isolation of the proto-oncogene c-myb from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):449–456. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kispert A., Herrmann B. G. The Brachyury gene encodes a novel DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3211–3220. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the retroviral transforming gene v-myb is a truncated version of the protein encoded by the cellular oncogene c-myb. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Benfey P. N., Gilmartin P. M., Fang R. X., Chua N. H. Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7890–7894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech M. J., Kammerer W., Cove D. J., Martin C., Wang T. L. Expression of myb-related genes in the moss, Physcomitrella patens. Plant J. 1993 Jan;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.t01-3-00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmer S., Maddaloni M., Motto M., Salamini F., Thompson R. D. Translation of the mRNA of the maize transcriptional activator Opaque-2 is inhibited by upstream open reading frames present in the leader sequence. Plant Cell. 1993 Jan;5(1):65–73. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Christenson E., Litchfield D. W., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myb DNA binding inhibited by phosphorylation at a site deleted during oncogenic activation. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):517–522. doi: 10.1038/344517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part II. Myb. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2235–2241. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Kenyon L. C., Dalla-Favera R. Human c-myb protooncogene: nucleotide sequence of cDNA and organization of the genomic locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9636–9640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marocco A., Wissenbach M., Becker D., Paz-Ares J., Saedler H., Salamini F., Rohde W. Multiple genes are transcribed in Hordeum vulgare and Zea mays that carry the DNA binding domain of the myb oncoproteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00334354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. The proline-rich transcriptional activator of CTF/NF-I is distinct from the replication and DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):741–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow B. E., Ju Q., Warner J. R. A bipartite DNA-binding domain in yeast Reb1p. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1173–1182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucenski M. L., McLain K., Kier A. B., Swerdlow S. H., Schreiner C. M., Miller T. A., Pietryga D. W., Scott W. J., Jr, Potter S. S. A functional c-myb gene is required for normal murine fetal hepatic hematopoiesis. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):677–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90099-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Marknell A., Graf T. The v-myb oncogene product binds to and activates the promyelocyte-specific mim-1 gene. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1115–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura N., Takahashi M., Matsui M., Ishii S., Date T., Sasamoto S., Ishizaki R. Isolation of human cDNA clones of myb-related genes, A-myb and B-myb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11075–11089. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Hojo H., Aimoto S., Nakai T., Nakamura H., Sarai A., Ishii S., Nishimura Y. Solution structure of a DNA-binding unit of Myb: a helix-turn-helix-related motif with conserved tryptophans forming a hydrophobic core. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6428–6432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohi R., McCollum D., Hirani B., Den Haese G. J., Zhang X., Burke J. D., Turner K., Gould K. L. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc5+ gene encodes an essential protein with homology to c-Myb. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):471–483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. G., Herman P. L., Sivakumaran S., Esch J., Marks M. D. A myb gene required for leaf trichome differentiation in Arabidopsis is expressed in stipules. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90523-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares J., Ghosal D., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3553–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat S., Willmitzer L., Sánchez-Serrano J. J. Nuclear proteins binding to a cauliflower mosaic virus 35S truncated promoter. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):209–214. doi: 10.1007/BF02464883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sablowski R. W., Moyano E., Culianez-Macia F. A., Schuch W., Martin C., Bevan M. A flower-specific Myb protein activates transcription of phenylpropanoid biosynthetic genes. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):128–137. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06242.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikumar P., Murali R., Reddy E. P. Role of tryptophan repeats and flanking amino acids in Myb-DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8452–8456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Nagase T., Nakagoshi H., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Delineation of three functional domains of the transcriptional activator encoded by the c-myb protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5758–5762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Terzaghi W., Beckmann H., Kadesch T., Cashmore A. R. DNA binding site preferences and transcriptional activation properties of the Arabidopsis transcription factor GBF1. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1275–1289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Urao T., Koizumi M. Nucleotide sequence of a gene from Arabidopsis thaliana encoding a myb homologue. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jun;19(3):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00023398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Helix-turn-helix, zinc-finger, and leucine-zipper motifs for eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90145-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Serrano J. J., Peña-Cortés H., Willmitzer L., Prat S. Identification of potato nuclear proteins binding to the distal promoter region of the proteinase inhibitor II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7205–7209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanikawa J., Yasukawa T., Enari M., Ogata K., Nishimura Y., Ishii S., Sarai A. Recognition of specific DNA sequences by the c-myb protooncogene product: role of three repeat units in the DNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9320–9324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bach C. Target Detection Assay (TDA): a versatile procedure to determine DNA binding sites as demonstrated on SP1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3203–3209. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tice-Baldwin K., Fink G. R., Arndt K. T. BAS1 has a Myb motif and activates HIS4 transcription only in combination with BAS2. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):931–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2683089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urao T., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Urao S., Shinozaki K. An Arabidopsis myb homolog is induced by dehydration stress and its gene product binds to the conserved MYB recognition sequence. Plant Cell. 1993 Nov;5(11):1529–1539. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.11.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Bishop J. M. Transcriptional activation by the v-myb oncogene and its cellular progenitor, c-myb. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]