Abstract
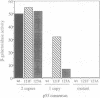
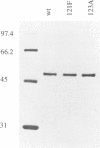
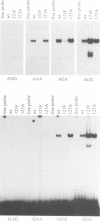
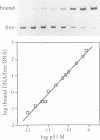
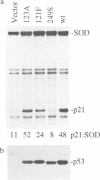
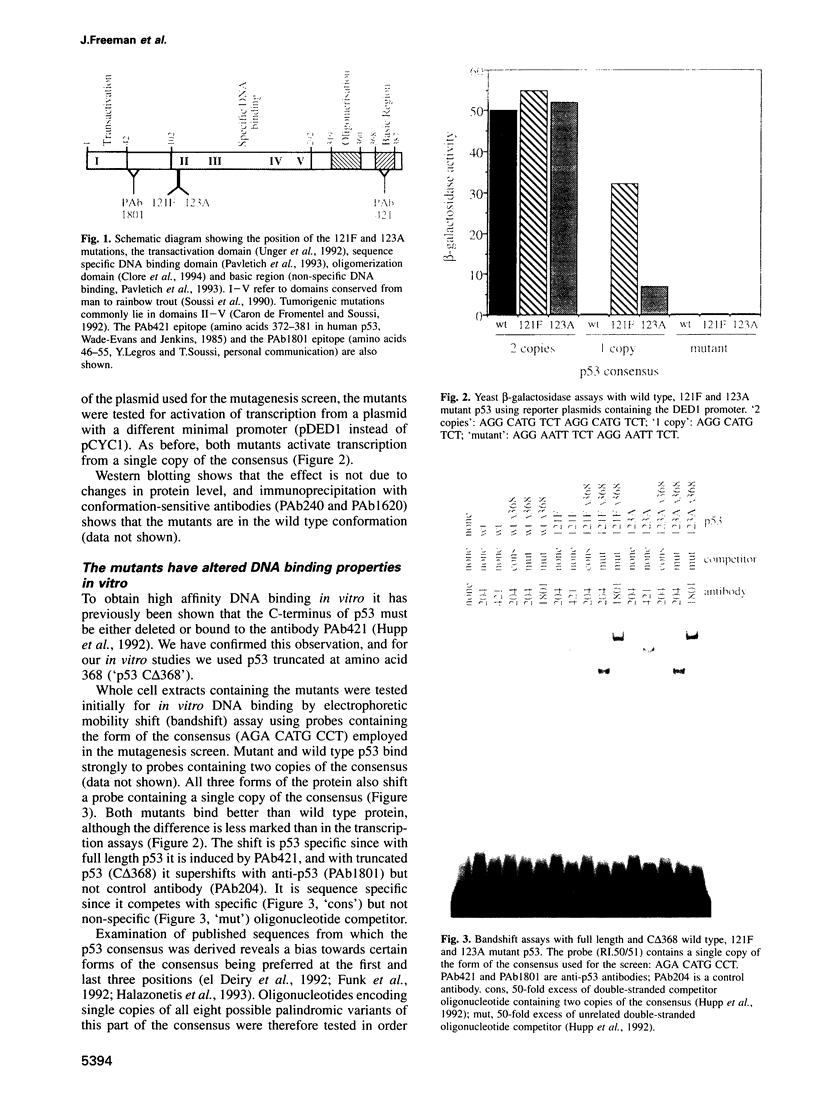
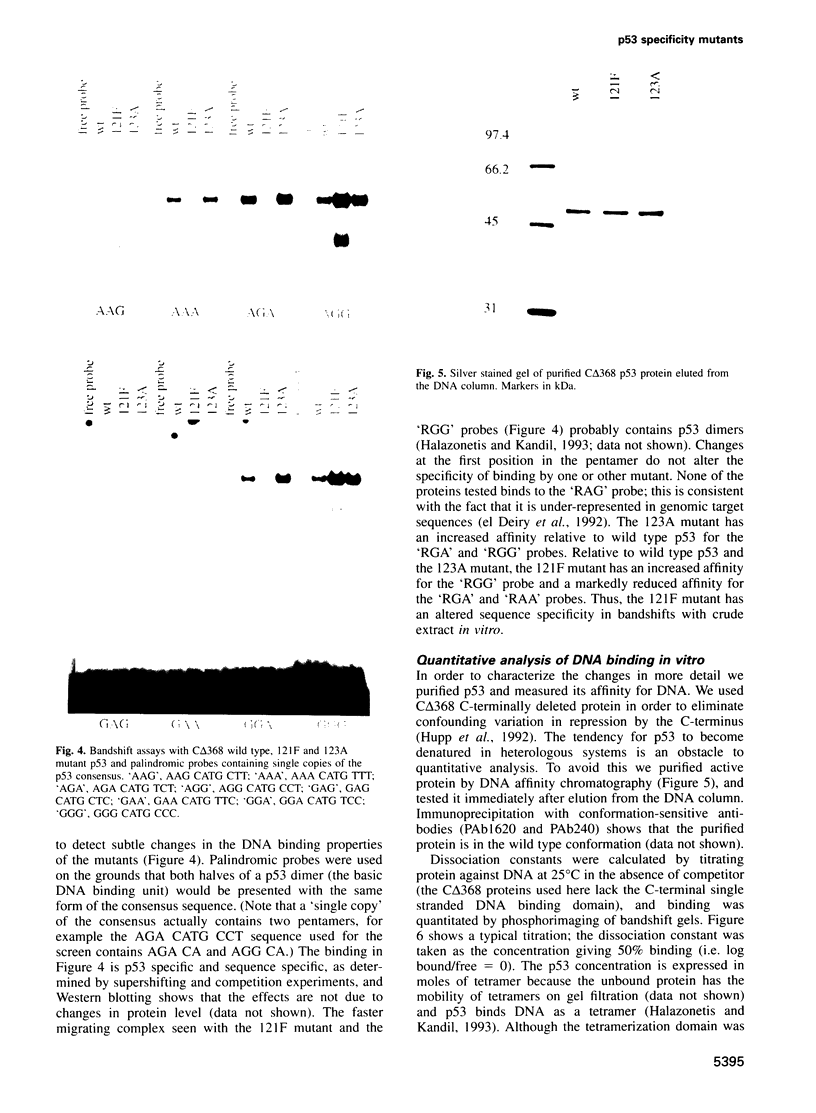
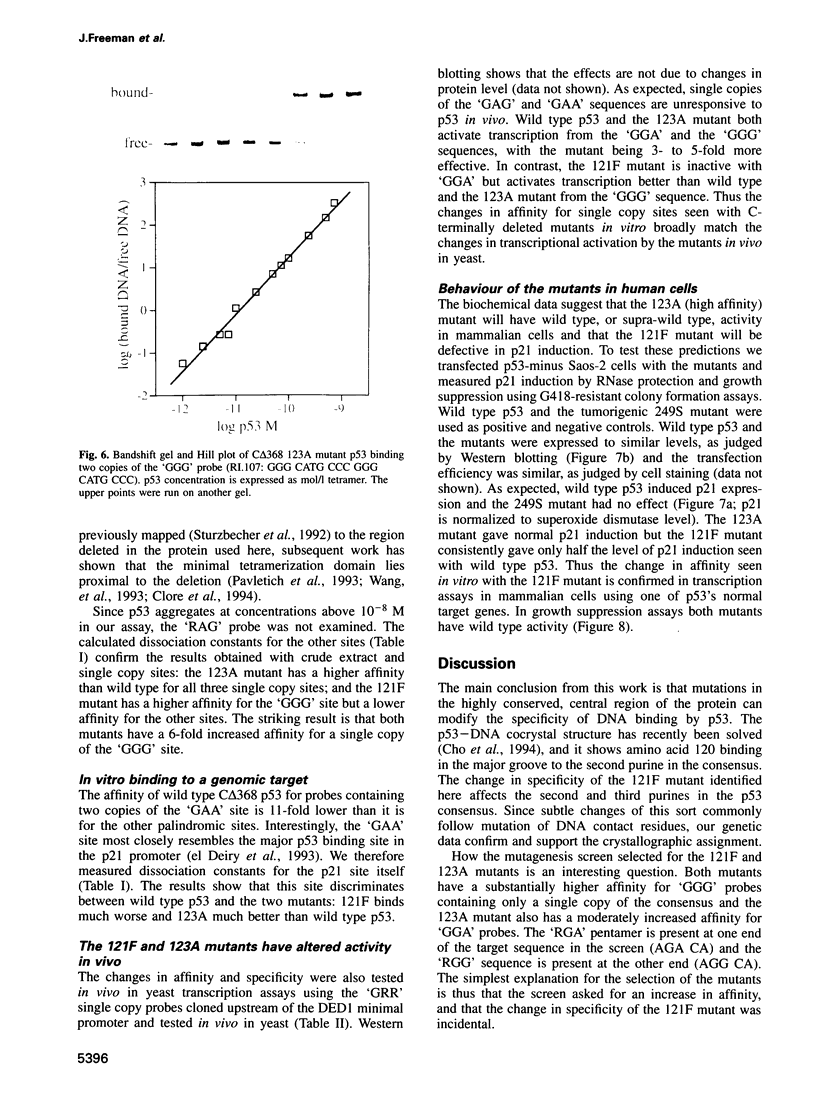
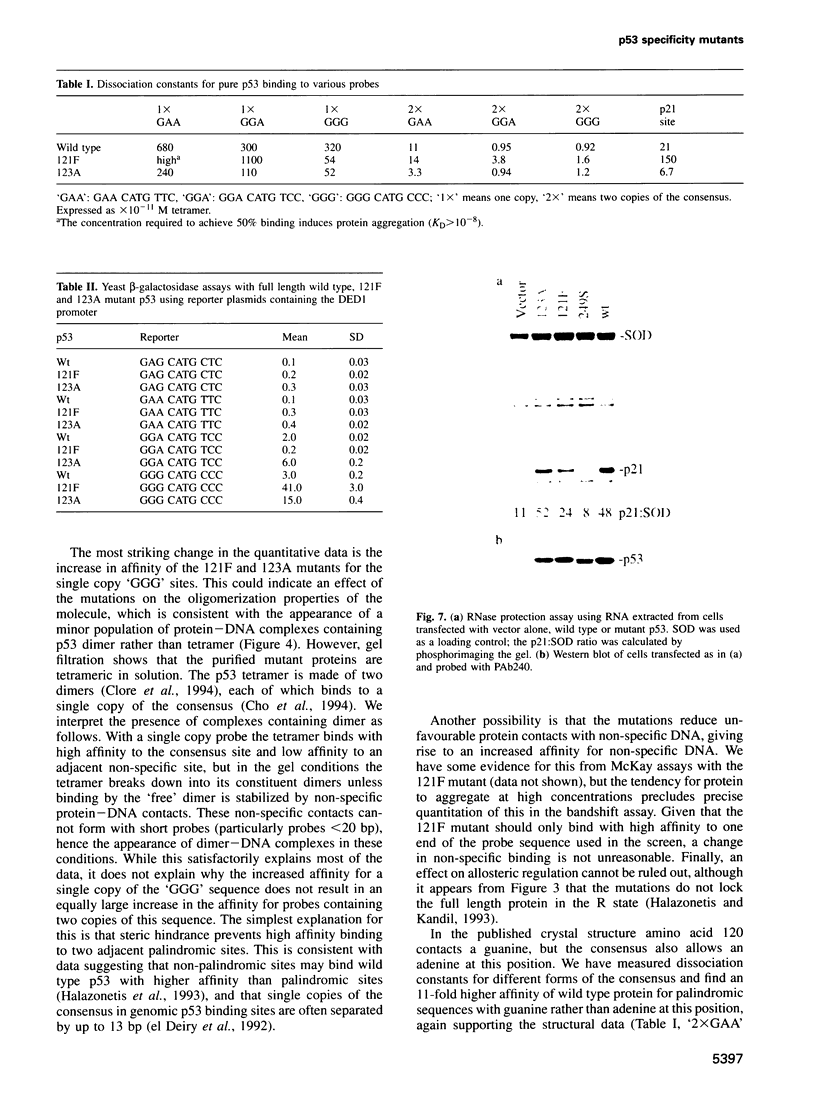
We have mutagenized human p53 expressed in yeast and selected two mutants, 121F and 123A, which activate transcription from one, rather than the normal two, copies of the consensus p53 DNA binding sequence. Both mutants have a 6-fold increase in affinity for a single copy of the sequence GGG CATG CCC. The 121F mutant has a decrease, and the 123A mutant an increase, in the affinity for the sequence GAA CATG TTC. This genetic and biochemical evidence supports the crystallographic finding that amino acid 120 contacts guanine in the major groove at the second position in the consensus. The major p53 binding site in the p21WAF1/CIP1 promoter resembles the GAA CATG TTC form of the consensus. Compared with wild type p53, the 121F mutant has a 7-fold lower affinity for the p21WAF1/CIP1 site in vitro, and the 121F mutant is defective in p21 induction in vivo. Mutants with subtly altered sequence specificity may facilitate dissection of downstream pathways activated by p53.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball R. K., Siegl B., Quellhorst S., Brandner G., Braun D. G. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 nuclear large T tumour antigen: epitope mapping, papova virus cross-reaction and cell surface staining. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1485–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Manfredi J. J., Chen X., Marshak D. R., Prives C. A proteolytic fragment from the central region of p53 has marked sequence-specific DNA-binding activity when generated from wild-type but not from oncogenic mutant p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2565–2574. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caelles C., Helmberg A., Karin M. p53-dependent apoptosis in the absence of transcriptional activation of p53-target genes. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):220–223. doi: 10.1038/370220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron de Fromentel C., Soussi T. TP53 tumor suppressor gene: a model for investigating human mutagenesis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Jan;4(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. Y., Funk W. D., Wright W. E., Shay J. W., Minna J. D. Heterogeneity of transcriptional activity of mutant p53 proteins and p53 DNA target sequences. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2159–2166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho Y., Gorina S., Jeffrey P. D., Pavletich N. P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):346–355. doi: 10.1126/science.8023157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov A. M., Miller C. W., Chen D. L., Koeffler H. P. Analysis of p53 transactivation through high-affinity binding sites. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):3005–3011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaramella M., Sacco M., Pulitzer J. F. Foreign transcriptional enhancers in yeast. I. Interactions of papovavirus transcriptional enhancers and a quiescent pseudopromoter on supercoiled plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8847–8868. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Omichinski J. G., Sakaguchi K., Zambrano N., Sakamoto H., Appella E., Gronenborn A. M. High-resolution structure of the oligomerization domain of p53 by multidimensional NMR. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):386–391. doi: 10.1126/science.8023159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frebourg T., Barbier N., Kassel J., Ng Y. S., Romero P., Friend S. H. A functional screen for germ line p53 mutations based on transcriptional activation. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 15;52(24):6976–6978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., Pak D. T., Karas R. H., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. A transcriptionally active DNA-binding site for human p53 protein complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2866–2871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Greaves R., Iggo R., Lane D. P. Activating mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect. A monoclonal antibody specific for the mutant form. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1595–1602. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Davis L. J., Kandil A. N. Wild-type p53 adopts a 'mutant'-like conformation when bound to DNA. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halazonetis T. D., Kandil A. N. Conformational shifts propagate from the oligomerization domain of p53 to its tetrameric DNA binding domain and restore DNA binding to select p53 mutants. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5057–5064. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebel M., Brandner G., Hochkeppel H. K., Braun D. G. Transformation-related cellular protein p53: increased level in untransformed rat cells following treatment with the tumorpromoter, tetradecanoylphorbol-acetate. Z Naturforsch C. 1986 Jan-Feb;41(1-2):94–99. doi: 10.1515/znc-1986-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Meek D. W., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. Regulation of the specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):875–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90562-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Hoeffler W. K. SV40 large T shares an antigenic determinant with a cellular protein of molecular weight 68,000. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):167–170. doi: 10.1038/288167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E. Stabilization of the p53 tumor suppressor is induced by adenovirus 5 E1A and accompanies apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):535–545. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Cook A., Sheldon M. A new anti-p53 monoclonal antibody, previously reported to be directed against the large T antigen of simian virus 40. Oncogene. 1987;1(4):453–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita T., Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Wang H. G., Lin H. K., Liebermann D. A., Hoffman B., Reed J. C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1799–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke R. W., Miller C. W., Kato G. J., Simon K. J., Chen D. L., Dang C. V., Koeffler H. P. A potential transcriptional activation element in the p53 protein. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1829–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Chambers K. A., Pabo C. O. The DNA-binding domain of p53 contains the four conserved regions and the major mutation hot spots. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2556–2564. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Tokino T., Thiagalingam S., el-Deiry W. S., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Sequence-specific transcriptional activation is essential for growth suppression by p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):1998–2002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schärer E., Iggo R. Mammalian p53 can function as a transcription factor in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1539–1545. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Dafni N., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Groner Y. Nucleotide sequence and expression of human chromosome 21-encoded superoxide dismutase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., May P. Structural aspects of the p53 protein in relation to gene evolution. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):945–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Addison C., Rudge K., Remm M., Grimaldi M., Keenan E., Jenkins J. R. A C-terminal alpha-helix plus basic region motif is the major structural determinant of p53 tetramerization. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1513–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger T., Nau M. M., Segal S., Minna J. D. p53: a transdominant regulator of transcription whose function is ablated by mutations occurring in human cancer. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1383–1390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade-Evans A., Jenkins J. R. Precise epitope mapping of the murine transformation-associated protein, p53. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):699–706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Reed M., Wang P., Stenger J. E., Mayr G., Anderson M. E., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. p53 domains: identification and characterization of two autonomous DNA-binding regions. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2575–2586. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Bayle J. H., Olson D., Levine A. J. The p53-mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1126–1132. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Funk W. D., Wright W. E., Shay J. W., Deisseroth A. B. Novel DNA binding of p53 mutants and their role in transcriptional activation. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2555–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]