Abstract
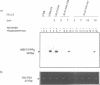
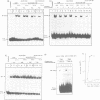
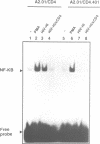
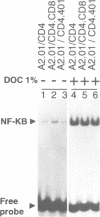
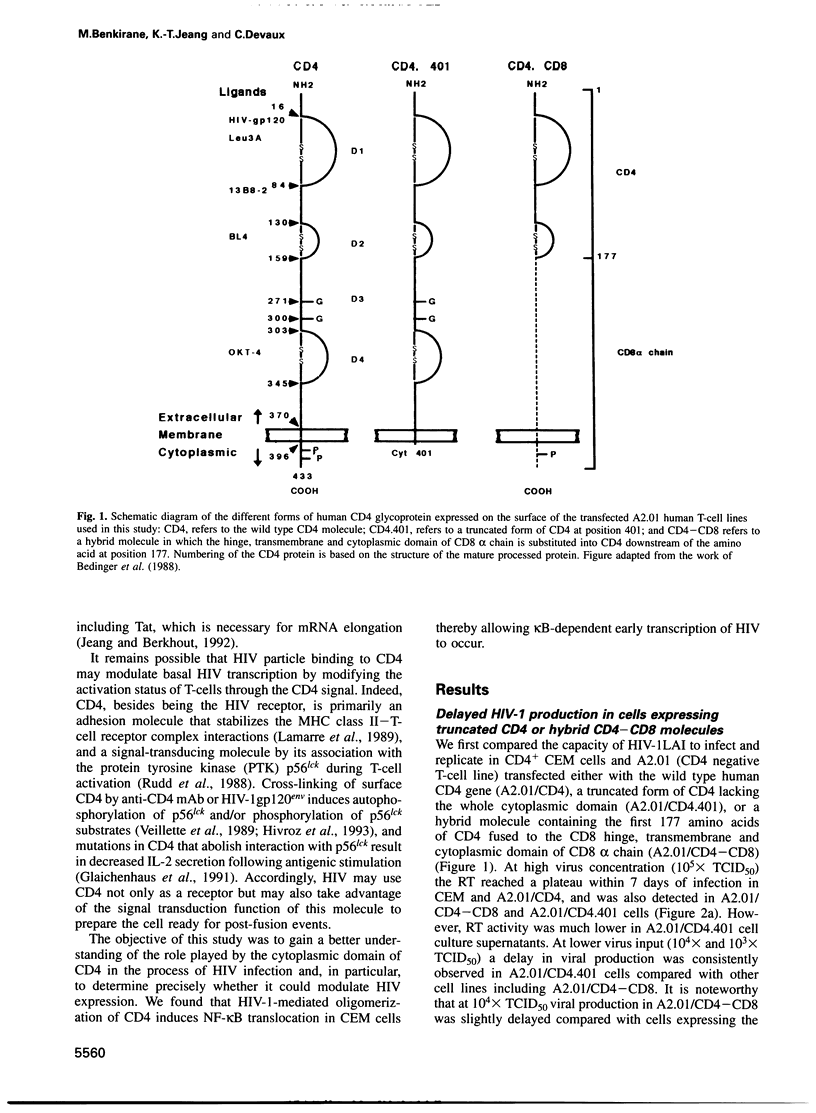
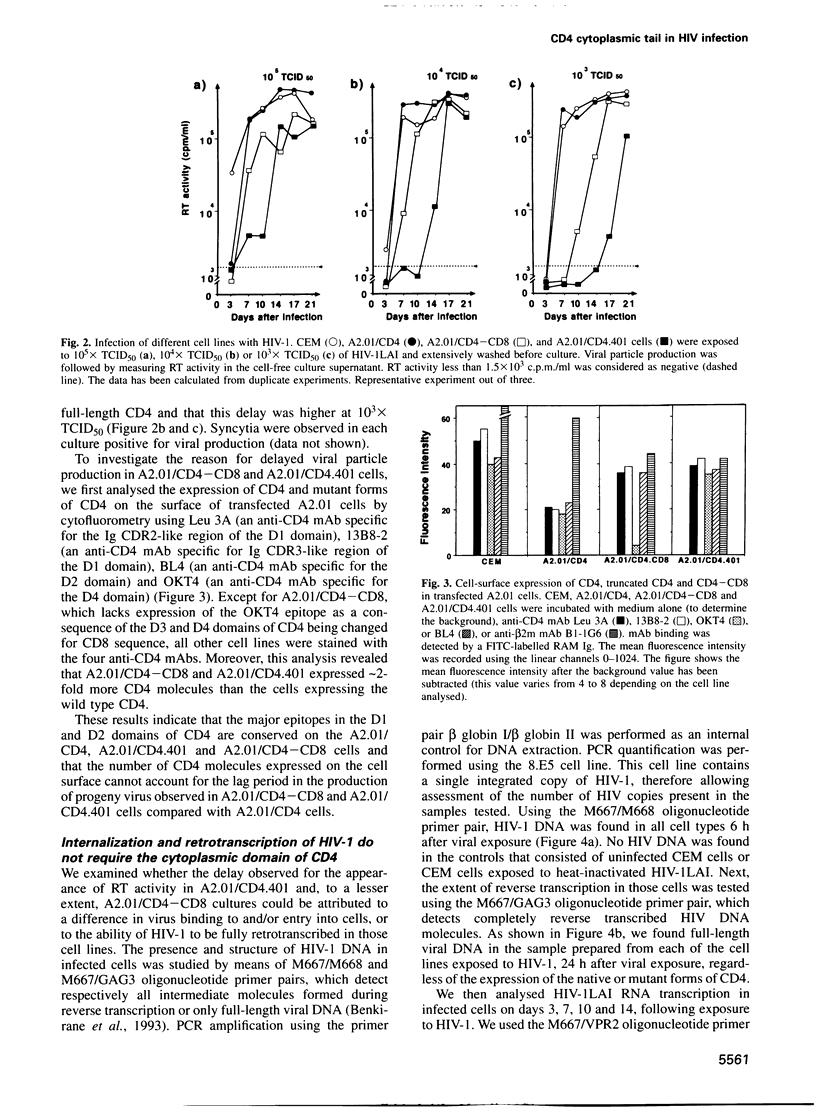
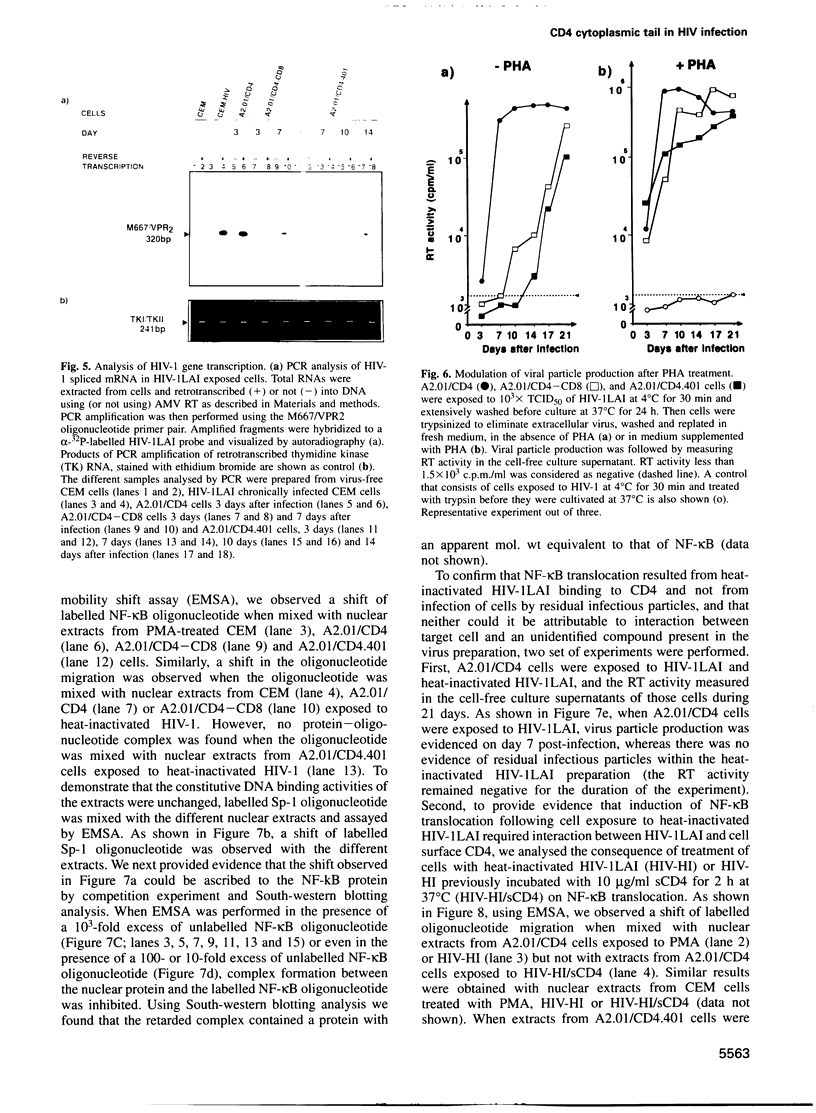
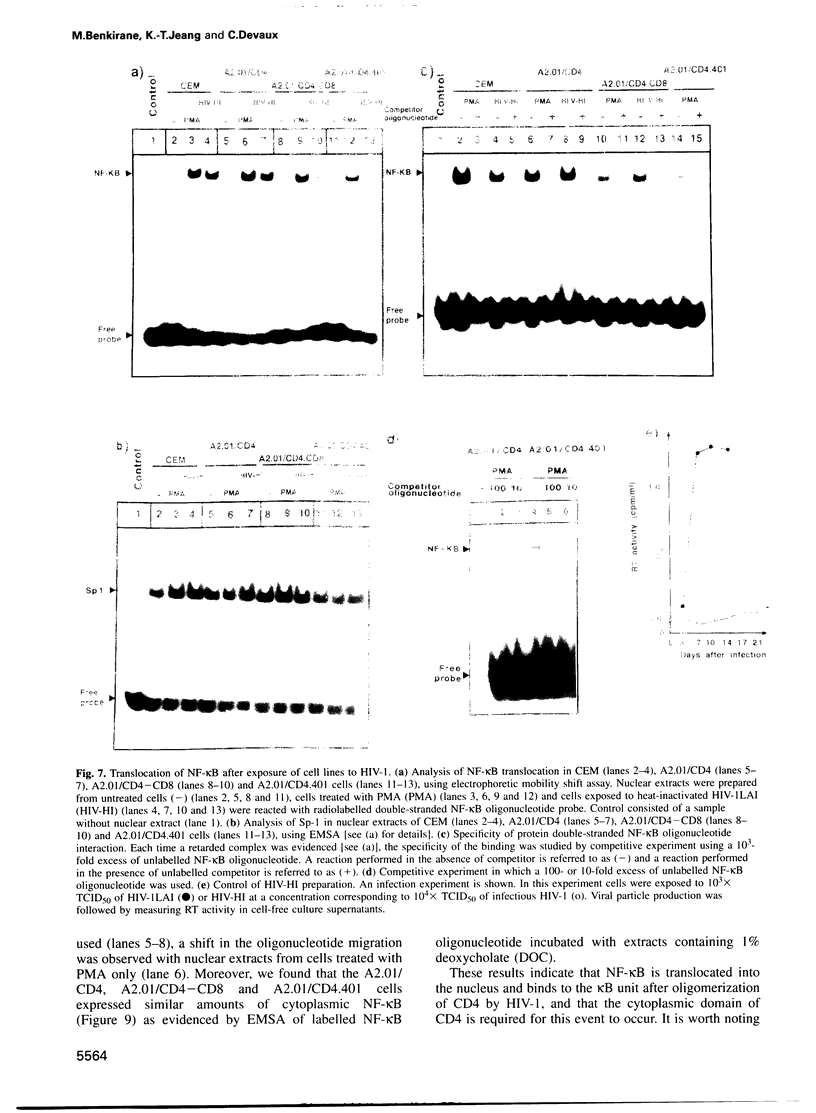
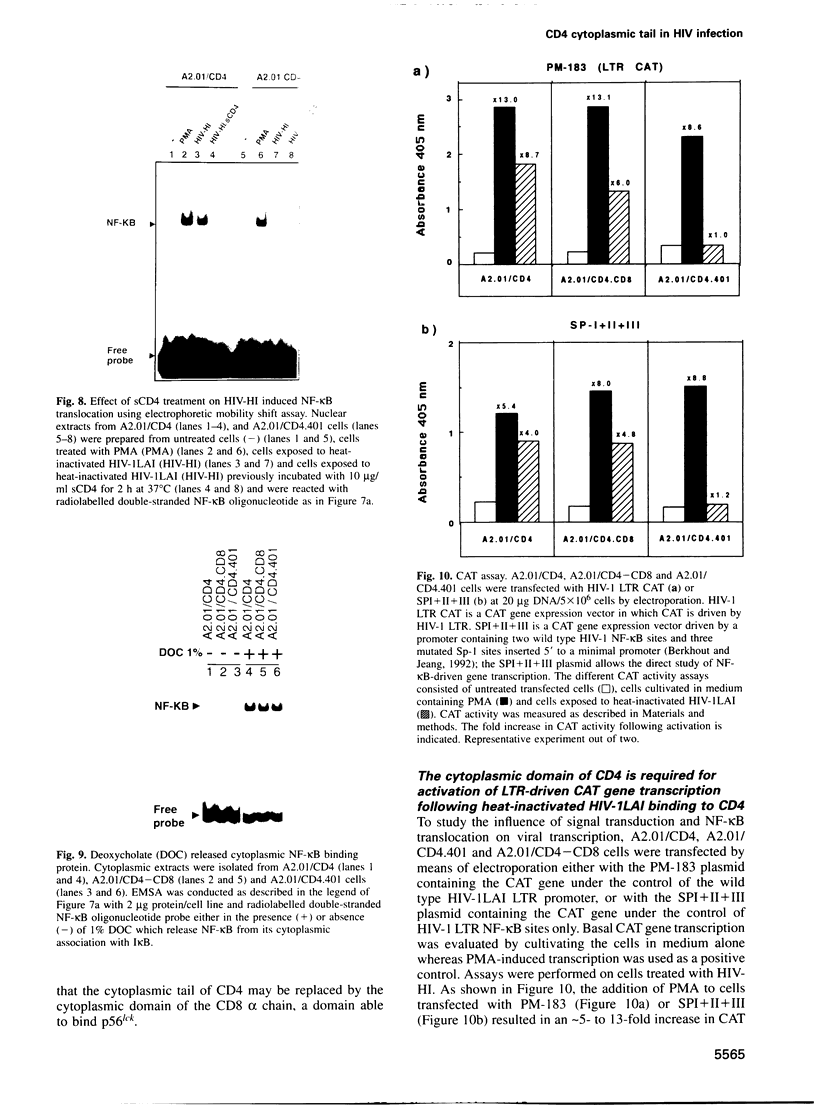
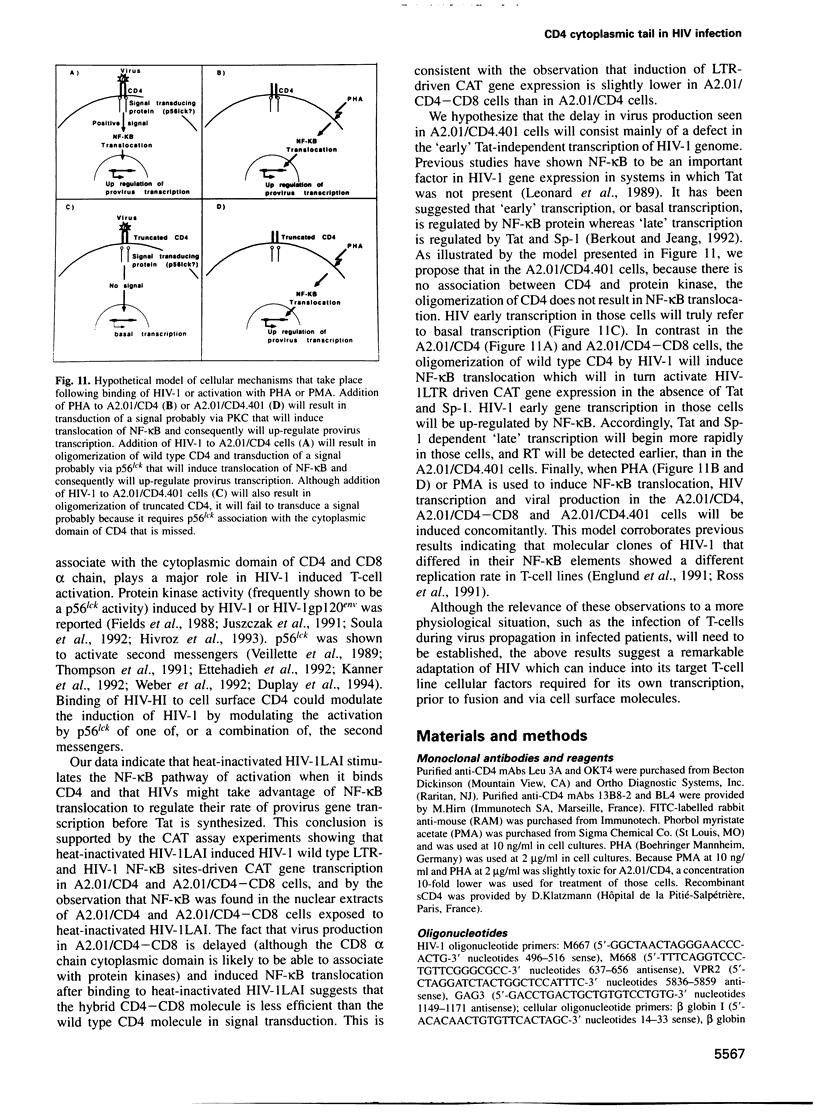
The role played by the cytoplasmic domain of the CD4 molecule in the process of HIV infection was investigated, using A2.01 cells which express different forms of the CD4 gene. A delay in HIV production was consistently observed in cells expressing a truncated CD4 which lacks the cytoplasmic domain (CD4.401) compared with cells expressing the wild type CD4. The delay was much less in cells expressing a hybrid CD4-CD8 molecule (amino acids 1-177 of CD4 fused to the hinge, transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of CD8). Yet the extent of viral entry and reverse transcription, monitored by semi-quantitative PCR, was similar in each cell type studied. For further study of the mechanism responsible for delayed HIV replication in the A2.01/CD4.401 cell line, cells were treated with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), 24 h after HIV infection. Under such experimental conditions HIV production was detected at the same time in the culture supernatants of A2.01/CD4 and A2.01/CD4.401 cells. Moreover, we found that CD4 oligomerization by HIV-1 induced NF-kappa B translocation in A2.01/CD4 and A2.01/CD4-CD8 but not in A2.01/CD4.401 cells. This was consistent with CAT assay experiments which provided evidence for Tat-independent NF-kappa B mediated activation of HIV-1 LTR promoter after HIV binding to CD4 in A2.01/CD4 and A2.01/CD4-CD8 but not in A2.01/CD4.401 cells. In contrast to results published recently by Tremblay et al. (1994, EMBO J., 13, 774-783), we propose that a positive cellular signal initiated following oligomerization of the CD4 by the virus itself is involved in NF-kappa B-dependent early HIV transcription in A2.01/CD4 cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Shatzman A., Truneh A., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. The genetic analysis of the HIV envelope binding domain on CD4. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;616:116–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedinger P., Moriarty A., von Borstel R. C., 2nd, Donovan N. J., Steimer K. S., Littman D. R. Internalization of the human immunodeficiency virus does not require the cytoplasmic domain of CD4. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):162–165. doi: 10.1038/334162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benkirane M., Blanc-Zouaoui D., Hirn M., Devaux C. Involvement of human leukocyte antigen class I molecules in human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-positive cells. J Virol. 1994 Oct;68(10):6332–6339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.10.6332-6339.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benkirane M., Corbeau P., Housset V., Devaux C. An antibody that binds the immunoglobulin CDR3-like region of the CD4 molecule inhibits provirus transcription in HIV-infected T cells. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):4909–4921. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Functional roles for the TATA promoter and enhancers in basal and Tat-induced expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):139–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.139-149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkly L. C., Olson D., Shapiro R., Winkler G., Rosa J. J., Thomas D. W., Williams C., Chisholm P. Inhibition of HIV infection by a novel CD4 domain 2-specific monoclonal antibody. Dissecting the basis for its inhibitory effect on HIV-induced cell fusion. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1779–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeau P., Benkirane M., Weil R., David C., Emiliani S., Olive D., Mawas C., Serre A., Devaux C. Ig CDR3-like region of the CD4 molecule is involved in HIV-induced syncytia formation but not in viral entry. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):290–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeau P., Olive D., Devaux C. Anti-HLA antigen class I heavy chain monoclonal antibodies inhibit human immunodeficiency virus production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):865–871. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello R., Lipcey C., Algarté M., Cerdan C., Baeuerle P. A., Olive D., Imbert J. Activation of primary human T-lymphocytes through CD2 plus CD28 adhesion molecules induces long-term nuclear expression of NF-kappa B. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Apr;4(4):329–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond D. C., Sleckman B. P., Gregory T., Lasky L. A., Greenstein J. L., Burakoff S. J. Inhibition of CD4+ T cell function by the HIV envelope protein, gp120. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3715–3717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duplay P., Thome M., Hervé F., Acuto O. p56lck interacts via its src homology 2 domain with the ZAP-70 kinase. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1163–1172. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund G., Hoggan M. D., Theodore T. S., Martin M. A. A novel HIV-1 isolate containing alterations affecting the NF-kappa B element. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90479-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettehadieh E., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L., Hess-Bienz D., Watts J., Shastri N., Aebersold R. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinases by p56lck. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.1311128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields A. P., Bednarik D. P., Hess A., May W. S. Human immunodeficiency virus induces phosphorylation of its cell surface receptor. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):278–280. doi: 10.1038/333278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Powell D., Lightfoote M., Koenig S., Fauci A. S., Benn S., Rabson A., Daugherty D., Gendelman H. E., Hoggan M. D. Biological and biochemical characterization of a cloned Leu-3- cell surviving infection with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):280–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. Cellular transcription factors involved in the regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. AIDS. 1992 Apr;6(4):347–363. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaichenhaus N., Shastri N., Littman D. R., Turner J. M. Requirement for association of p56lck with CD4 in antigen-specific signal transduction in T cells. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90235-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., Blumenthal R., Manischewitz J., Littman D. R., Dimitrov D. S. Cell fusion mediated by interaction of a hybrid CD4.CD8 molecule with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein does occur after a long lag time. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6469–6475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6469-6475.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Moran P. A., Smithgall M. D., Diegel M. L., Sridhar P., Ledbetter J. A., Zarling J. M., Hu S. L. Inhibition of virus production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1-seropositive donors by treatment with recombinant HIV-like particles. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4279–4287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4279-4287.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasunuma T., Tsubota H., Watanabe M., Chen Z. W., Lord C. I., Burkly L. C., Daley J. F., Letvin N. L. Regions of the CD4 molecule not involved in virus binding or syncytia formation are required for HIV-1 infection of lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1841–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hivroz C., Mazerolles F., Soula M., Fagard R., Graton S., Meloche S., Sekaly R. P., Fischer A. Human immunodeficiency virus gp120 and derived peptides activate protein tyrosine kinase p56lck in human CD4 T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Mar;23(3):600–607. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann B., Nishanian P., Baldwin R. L., Insixiengmay P., Nel A., Fahey J. L. HIV inhibits the early steps of lymphocyte activation, including initiation of inositol phospholipid metabolism. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3699–3705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann B., Nishanian P., Nguyen T., Insixiengmay P., Fahey J. L. Human immunodeficiency virus proteins induce the inhibitory cAMP/protein kinase A pathway in normal lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6676–6680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Popovic M., Horak E. M., Lucas P. J., Gress R. E., June C. H., Bolen J. B. No T-cell tyrosine protein kinase signalling or calcium mobilization after CD4 association with HIV-1 or HIV-1 gp120. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):557–560. doi: 10.1038/348557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Bottomly K. Signals and signs for lymphocyte responses. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Berkhout B. Kinetics of HIV-1 long terminal repeat trans-activation. Use of intragenic ribozyme to assess rate-limiting steps. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17891–17899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juszczak R. J., Turchin H., Truneh A., Culp J., Kassis S. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus gp120 glycoprotein on the association of the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck with CD4 in human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11176–11183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner S. B., Kavanagh T. J., Grossmann A., Hu S. L., Bolen J. B., Rabinovitch P. S., Ledbetter J. A. Sulfhydryl oxidation down-regulates T-cell signaling and inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Cruikshank W. W., Pyle S. W., Berman J. S., Center D. M. Lymphocyte activation by HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):445–448. doi: 10.1038/335445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre D., Capon D. J., Karp D. R., Gregory T., Long E. O., Sékaly R. P. Class II MHC molecules and the HIV gp 120 envelope protein interact with functionally distinct regions of the CD4 molecule. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3271–3277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08487.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Parrott C., Buckler-White A. J., Turner W., Ross E. K., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B. The NF-kappa B binding sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat are not required for virus infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4919–4924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4919-4924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Dalgleish A. G., Jamal S., Weiss R. A., Axel R. HIV infection does not require endocytosis of its receptor, CD4. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):865–874. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Lasane F., Popovic M., Arthur L. O., Robey W. G., Blattner W. A., Newman M. J. HTLV-III large envelope protein (gp120) suppresses PHA-induced lymphocyte blastogenesis. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2640–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Mawle A., Cort S. P., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Scheppler-Campbell J. A., Hicks D., Sligh J. Cellular tropism of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV. I. Role of T cell activation and expression of the T4 antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3151–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. B., Girard P., Grinstein S., Gelfand E. W. Interleukin-2 induces proliferation of T lymphocyte mutants lacking protein kinase C. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Huang Y. X., Ashkenazi A., Ho D. D. Virions of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates resistant to soluble CD4 (sCD4) neutralization differ in sCD4 binding and glycoprotein gp120 retention from sCD4-sensitive isolates. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):235–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.235-243.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neudorf S. M., Jones M. M., McCarthy B. M., Harmony J. A., Choi E. M. The CD4 molecule transmits biochemical information important in the regulation of T lymphocyte activity. Cell Immunol. 1990 Feb;125(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin L., Evans L. A., Tang S. B., Barboza A., Legg H., Littman D. R., Levy J. A. Several CD4 domains can play a role in human immunodeficiency virus infection in cells. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4893–4901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4893-4901.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieber E. P., Federle C., Reiter C., Krauss S., Gürtler L., Eberle J., Deinhardt F., Riethmüller G. The monoclonal CD4 antibody M-T413 inhibits cellular infection with human immunodeficiency virus after viral attachment to the cell membrane: an approach to postexposure prophylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10792–10796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. K., Buckler-White A. J., Rabson A. B., Englund G., Martin M. A. Contribution of NF-kappa B and Sp1 binding motifs to the replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: distinct patterns of viral growth are determined by T-cell types. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4350–4358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4350-4358.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. E., Kwong P. D., Truneh A., Porter T. G., Arthos J., Rosenberg M., Dai X. P., Xuong N. H., Axel R., Sweet R. W. Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):419–426. doi: 10.1038/348419a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Weiss R. A. The CD4 antigen: physiological ligand and HIV receptor. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):631–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Krowka J. F., Gregory T. J., Hirabayashi S. E., McCabe S. M., Kaufman D. S., Stites D. P., Ammann A. J. The effects of human immunodeficiency virus recombinant envelope glycoprotein on immune cell functions in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1987 Nov;110(1):140–148. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soula M., Fagard R., Fischer S. Interaction of human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein 160 with CD4 in Jurkat cells increases p56lck autophosphorylation and kinase activity. Int Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(2):295–299. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Haggerty S., Lamonica C. A., Meier C. M., Welch S. K., Wasiak A. J. Integration is not necessary for expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein products. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2421–2425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2421-2425.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Lamonica C. A. HIV-1 replication is controlled at the level of T cell activation and proviral integration. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1551–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzan M., Salaun D., Neuveut C., Spire B., Hirsch I., Le Bouteiller P., Querat G., Sire J. Induction of NF-KB during monocyte differentiation by HIV type 1 infection. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):377–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. A., Ledbetter J. A., Rapp U. R., Bolen J. B. The Raf-1 serine-threonine kinase is a substrate for the p56lck protein tyrosine kinase in human T-cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Dec;2(12):609–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starkesen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Signaling through T lymphocyte surface proteins, TCR/CD3 and CD28, activates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay M., Meloche S., Gratton S., Wainberg M. A., Sékaly R. P. Association of p56lck with the cytoplasmic domain of CD4 modulates HIV-1 expression. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):774–783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Yan Y. W., Garrett T. P., Liu J. H., Rodgers D. W., Garlick R. L., Tarr G. E., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L., Harrison S. C. Atomic structure of a fragment of human CD4 containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):411–418. doi: 10.1038/348411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. R., Bell G. M., Han M. Y., Pawson T., Imboden J. B. Association of the tyrosine kinase LCK with phospholipase C-gamma 1 after stimulation of the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):373–379. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Littman D. R. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Haislip A. M., Krogstad P., Chen I. S. Incompletely reverse-transcribed human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes in quiescent cells can function as intermediates in the retroviral life cycle. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1717–1725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1717-1725.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]