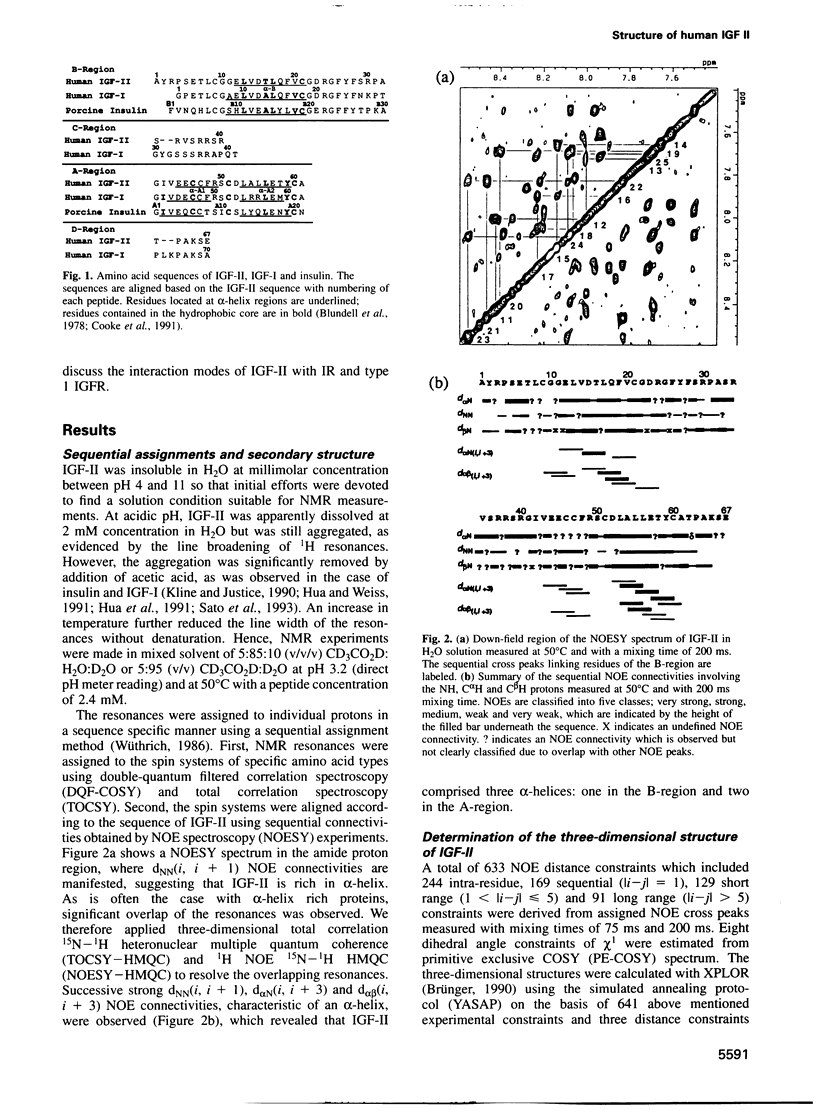
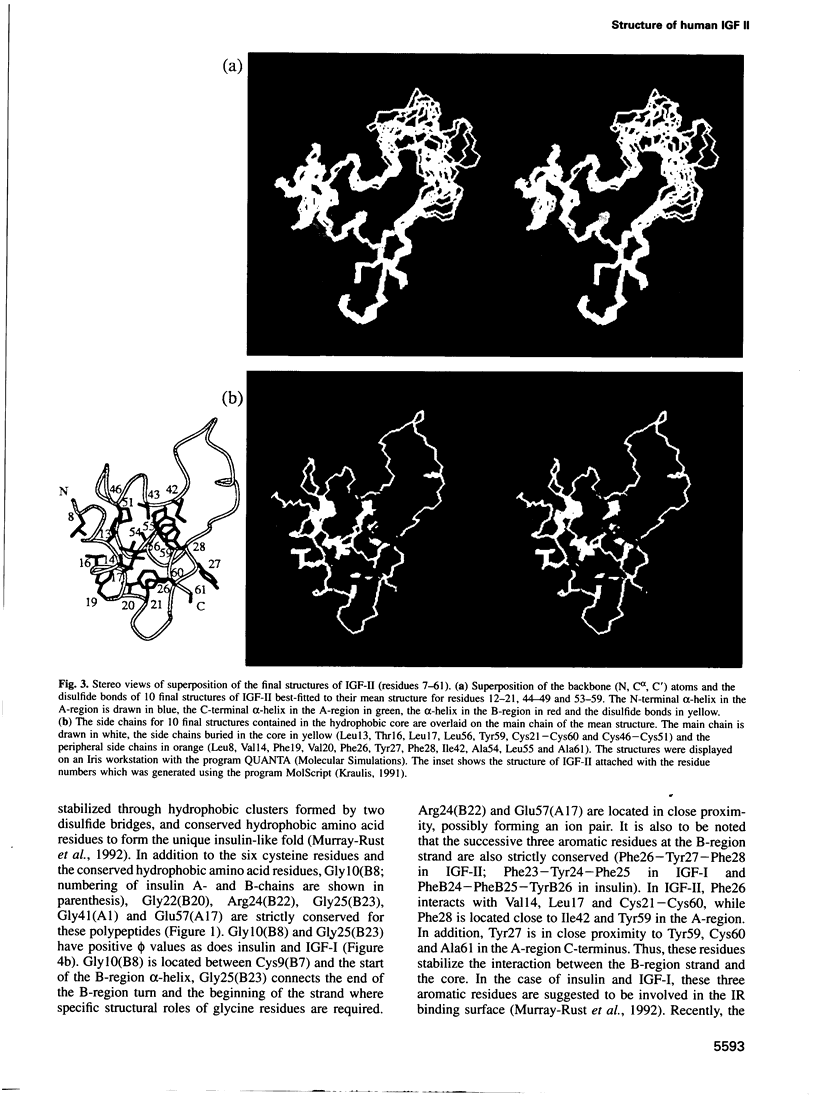
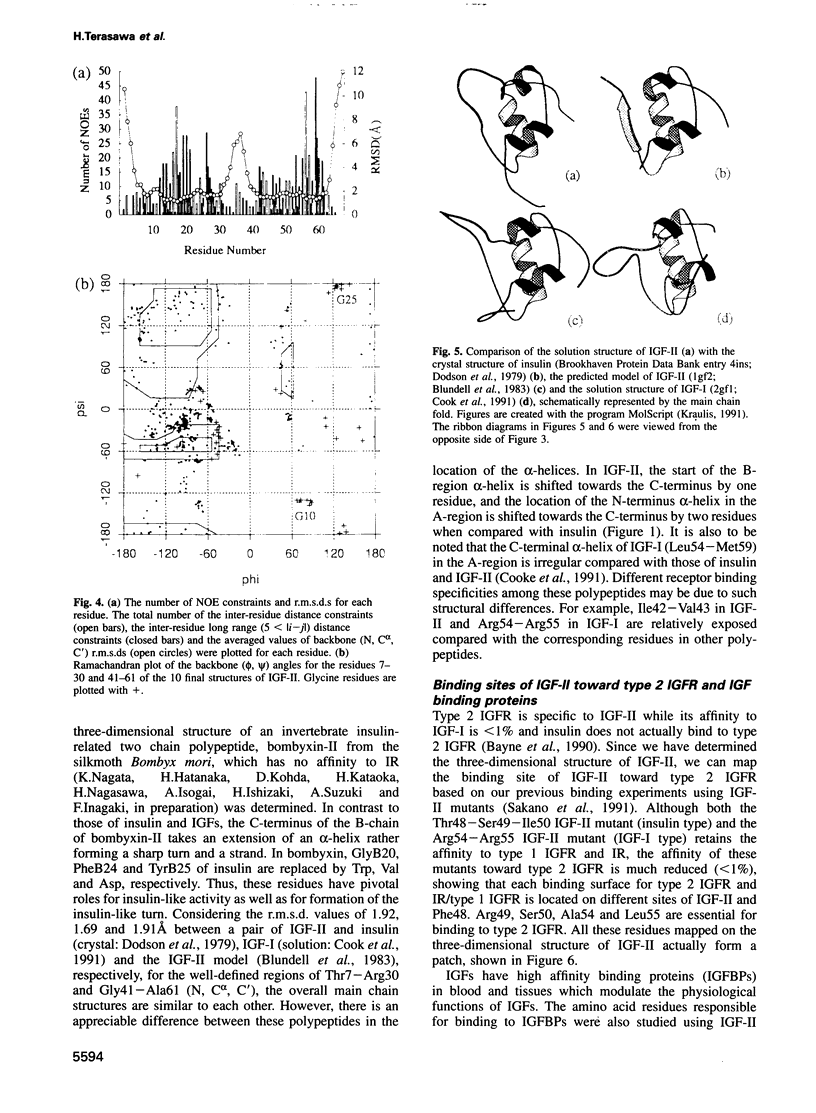
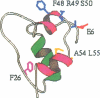Abstract
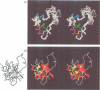
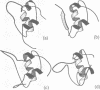
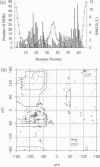
The three-dimensional structure of human insulin-like growth factor II was determined at high resolution in aqueous solution by NMR and simulated annealing based calculations. The structure is quite similar to those of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I, which consists of an alpha-helix followed by a turn and a strand in the B-region and two antiparallel alpha-helices in the A-region. However, the regions of Ala1-Glu6, Pro31-Arg40 and Thr62-Glu67 are not well-defined for lack of distance constraints, possibly due to motional flexibility. Based on the resultant structure and the results of structure-activity relationships, we propose the interaction sites of insulin-like growth factor II with the type 2 insulin-like growth factor receptor and the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. These sites partially overlap with each other at the opposite side of the putative binding surface to the insulin receptor and the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. We also discuss the interaction modes of insulin-like growth factor II with the insulin receptor and the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach L. A., Hsieh S., Sakano K., Fujiwara H., Perdue J. F., Rechler M. M. Binding of mutants of human insulin-like growth factor II to insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 1-6. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9246–9254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors: structure, regulation and function. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne M. L., Applebaum J., Chicchi G. G., Miller R. E., Cascieri M. A. The roles of tyrosines 24, 31, and 60 in the high affinity binding of insulin-like growth factor-I to the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15648–15652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayne M. L., Applebaum J., Underwood D., Chicchi G. G., Green B. G., Hayes N. S., Cascieri M. A. The C region of human insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I is required for high affinity binding to the type 1 IGF receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11004–11008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Bedarkar S., Humbel R. E. Tertiary structures, receptor binding, and antigenicity of insulinlike growth factors. Fed Proc. 1983 Jun;42(9):2592–2597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Bedarkar S., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor: a model for tertiary structure accounting for immunoreactivity and receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):180–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella S. J., Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Insulin-like growth factor II binding to the type I somatomedin receptor. Evidence for two high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9268–9273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Naik P., Hanahan D. A second signal supplied by insulin-like growth factor II in oncogene-induced tumorigenesis. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):414–418. doi: 10.1038/369414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. IGF binding proteins: regulation of cellular actions. Growth Regul. 1992 Jun;2(2):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Driscoll P. C., Wingfield P. T., Gronenborn A. M. Low resolution structure of interleukin-1 beta in solution derived from 1H-15N heteronuclear three-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 20;214(4):811–817. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90336-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. M., Harvey T. S., Campbell I. D. Solution structure of human insulin-like growth factor 1: a nuclear magnetic resonance and restrained molecular dynamics study. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5484–5491. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):68–91. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Efstratiadis A., Robertson E. J. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):78–80. doi: 10.1038/345078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derewenda U., Derewenda Z., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Bing X., Markussen J. X-ray analysis of the single chain B29-A1 peptide-linked insulin molecule. A completely inactive analogue. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. C., Reynolds C. D. Structural relationships in the two-zinc insulin hexamer. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):469–479. doi: 10.1139/o79-060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hubbard R. E., Reynolds C. D. Insulin's structural behavior and its relation to activity. Biopolymers. 1983 Jan;22(1):281–291. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallicchio V. S., Hughes N. K., Tse K. F. Prevention of hematopoietic myeloid and megakaryocyte toxicity associated with zidovudine in vivo in mice with recombinant GM-CSF. Growth Regul. 1994 Jun;4(2):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka H., Oka M., Kohda D., Tate S., Suda A., Tamiya N., Inagaki F. Tertiary structure of erabutoxin b in aqueous solution as elucidated by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 8;240(2):155–166. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua Q. X., Kochoyan M., Weiss M. A. Structure and dynamics of des-pentapeptide-insulin in solution: the molten-globule hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2379–2383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua Q. X., Shoelson S. E., Kochoyan M., Weiss M. A. Receptor binding redefined by a structural switch in a mutant human insulin. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):238–241. doi: 10.1038/354238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua Q. X., Weiss M. A. Comparative 2D NMR studies of human insulin and des-pentapeptide insulin: sequential resonance assignment and implications for protein dynamics and receptor recognition. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5505–5515. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):445–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline A. D., Justice R. M., Jr Complete sequence-specific 1H NMR assignments for human insulin. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2906–2913. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Inagaki F. Three-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance structures of mouse epidermal growth factor in acidic and physiological pH solutions. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11928–11939. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraulis J., Clore G. M., Nilges M., Jones T. A., Pettersson G., Knowles J., Gronenborn A. M. Determination of the three-dimensional solution structure of the C-terminal domain of cellobiohydrolase I from Trichoderma reesei. A study using nuclear magnetic resonance and hybrid distance geometry-dynamical simulated annealing. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7241–7257. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthi C., Roth B. V., Humbel R. E. Mutants of human insulin-like growth factor II (IGF II). Expression and characterization of truncated IGF II and of two naturally occurring variants. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):483–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Driscoll P. C., Kay L. E., Wingfield P. T., Bax A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Overcoming the overlap problem in the assignment of 1H NMR spectra of larger proteins by use of three-dimensional heteronuclear 1H-15N Hartmann-Hahn-multiple quantum coherence and nuclear Overhauser-multiple quantum coherence spectroscopy: application to interleukin 1 beta. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6150–6156. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirmira R. G., Tager H. S. Role of the phenylalanine B24 side chain in directing insulin interaction with its receptor. Importance of main chain conformation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6349–6354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Short P. A., Rechler M. M., White R. M., Knight A. B., Higa O. Z. Increased levels of multiplication-stimulating activity, an insulin-like growth factor, in fetal rat serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3649–3653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray-Rust J., McLeod A. N., Blundell T. L., Wood S. P. Structure and evolution of insulins: implications for receptor binding. Bioessays. 1992 May;14(5):325–331. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilges M., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins from interproton distance data by hybrid distance geometry-dynamical simulated annealing calculations. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omichinski J. G., Clore G. M., Appella E., Sakaguchi K., Gronenborn A. M. High-resolution three-dimensional structure of a single zinc finger from a human enhancer binding protein in solution. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9324–9334. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance M., Sørensen O. W., Bodenhausen G., Wagner G., Ernst R. R., Wüthrich K. Improved spectral resolution in cosy 1H NMR spectra of proteins via double quantum filtering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Vitam Horm. 1993;47:1–114. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Kiess W. Insulin-like growth factor receptors: recent developments and new methodologies. Growth Regul. 1994 Feb;4 (Suppl 1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano K., Enjoh T., Numata F., Fujiwara H., Marumoto Y., Higashihashi N., Sato Y., Perdue J. F., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. The design, expression, and characterization of human insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) mutants specific for either the IGF-II/cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor or IGF-I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20626–20635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki N., Rees-Jones R. W., Zick Y., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated tyrosine kinase activity associated with the beta-subunit of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors of rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9793–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Nishimura S., Ohkubo T., Kyogoku Y., Koyama S., Kobayashi M., Yasuda T., Kobayashi Y. Three-dimensional structure of human insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) determined by 1H-NMR and distance geometry. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1993 May;41(5):433–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1993.tb00462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher R., Soos M. A., Schlessinger J., Brandenburg D., Siddle K., Ullrich A. Signaling-competent receptor chimeras allow mapping of major insulin receptor binding domain determinants. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1087–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]