Abstract
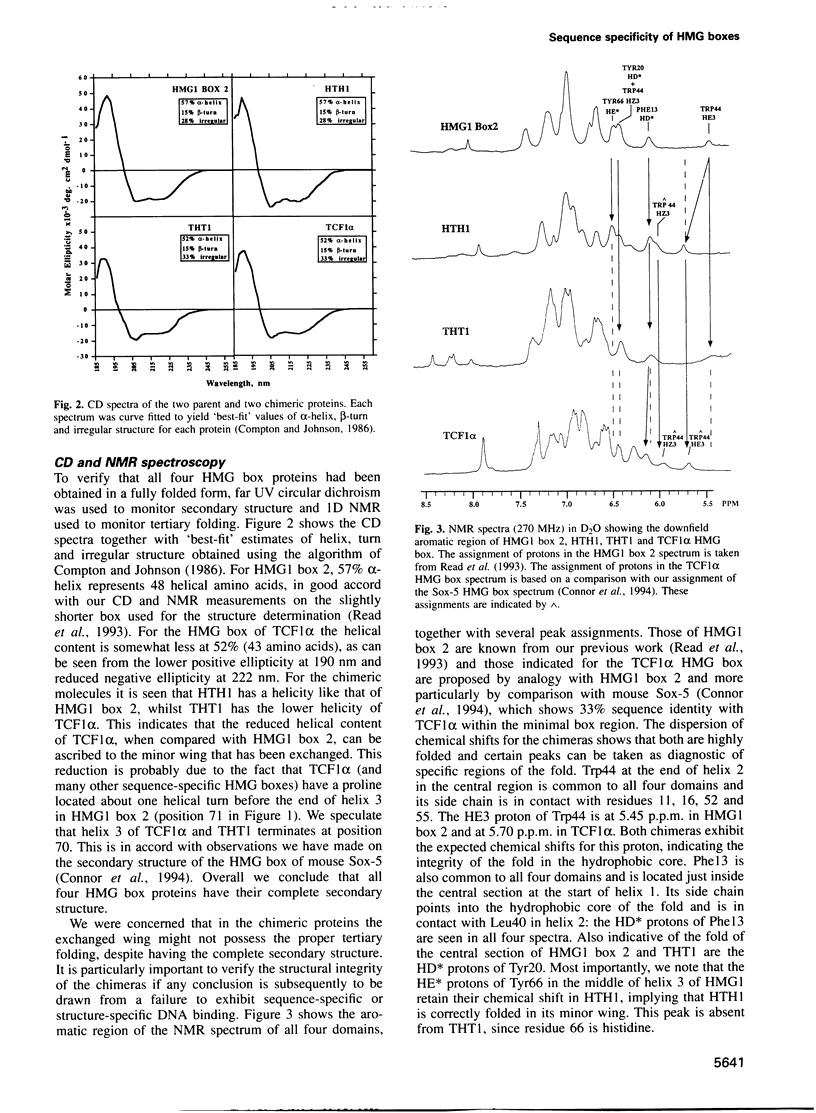
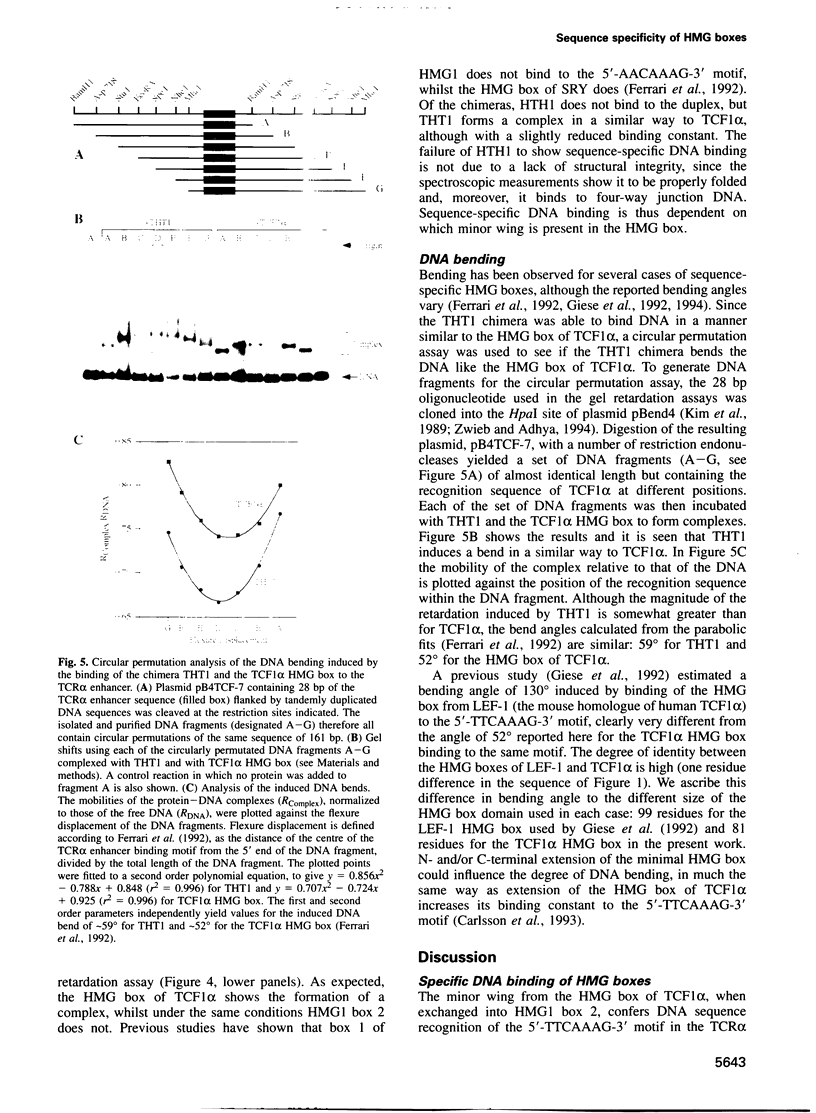
To establish the basis of sequence-specific DNA recognition by HMG boxes we separately transferred the minor and major wings from the sequence-specific HMG box of TCF1 alpha into their equivalent position in the non-sequence-specific box 2 of HMG1. Thus chimera THT1 contains the minor wing (of 11 N-terminal and 25 C-terminal residues) from the HMG box of TCF1 alpha and the major wing (the 45 residue central section) from HMG1 box 2, whilst the situation is reversed in chimera HTH1. The structural integrity of the two chimeric proteins was established by CD, NMR and their binding to four-way junction DNA. Gel retardation and circular permutation assays showed that only chimera THT1, containing the TCF1 alpha minor wing, formed a sequence-specific complex and bent the DNA. The bend angle was estimated to be 59 degrees for chimera THT1 and 52 degrees for the HMG box of TCF1 alpha. Our results, in combination with mutagenesis and other data, suggests a model for the DNA binding of HMG boxes in which the N-terminal residues and part of helix 1 contact the minor groove on the outside of a bent DNA duplex.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachvarov D., Moss T. The RNA polymerase I transcription factor xUBF contains 5 tandemly repeated HMG homology boxes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2331–2335. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon S. F., Coleman J. H., Lippard S. J. DNA unwinding produced by site-specific intrastrand cross-links of the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):8026–8035. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Pitts J. E., Tickle I. J., Wood S. P., Wu C. W. X-ray analysis (1. 4-A resolution) of avian pancreatic polypeptide: Small globular protein hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4175–4179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn S. L., Pil P. M., Essigmann J. M., Housman D. E., Lippard S. J. Isolation and characterization of human cDNA clones encoding a high mobility group box protein that recognizes structural distortions to DNA caused by binding of the anticancer agent cisplatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Waterman M. L., Jones K. A. The hLEF/TCF-1 alpha HMG protein contains a context-dependent transcriptional activation domain that induces the TCR alpha enhancer in T cells. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2418–2430. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Turner C. H., Mayes E., Crane-Robinson C. Conformation and domain structure of the non-histone chromosomal proteins, HMG 1 and 2. Isolation of two folded fragments from HMG 1 and 2. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 15;131(2):367–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton L. A., Johnson W. C., Jr Analysis of protein circular dichroism spectra for secondary structure using a simple matrix multiplication. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor F., Cary P. D., Read C. M., Preston N. S., Driscoll P. C., Denny P., Crane-Robinson C., Ashworth A. DNA binding and bending properties of the post-meiotically expressed Sry-related protein Sox-5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 25;22(16):3339–3346. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.16.3339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Connor F., Ashworth A. An SRY-related gene expressed during spermatogenesis in the mouse encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falciola L., Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M., Bianchi M. Mutational analysis of the DNA binding domain A of chromosomal protein HMG1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):285–292. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Harley V. R., Pontiggia A., Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R., Bianchi M. E. SRY, like HMG1, recognizes sharp angles in DNA. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4497–4506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Amsterdam A., Grosschedl R. DNA-binding properties of the HMG domain of the lymphoid-specific transcriptional regulator LEF-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2567–2578. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Cox J., Grosschedl R. The HMG domain of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 bends DNA and facilitates assembly of functional nucleoprotein structures. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90129-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Pagel J., Grosschedl R. Distinct DNA-binding properties of the high mobility group domain of murine and human SRY sex-determining factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3368–3372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R. SRY and sex determination in mammals. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:71–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Giese K., Pagel J. HMG domain proteins: architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Jackson D. I., Hextall P. J., Hawkins J. R., Berkovitz G. D., Sockanathan S., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. DNA binding activity of recombinant SRY from normal males and XY females. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):453–456. doi: 10.1126/science.1734522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. Definition of a consensus DNA binding site for SRY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1500–1501. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. Y., Weiss M. A. The SRY high-mobility-group box recognizes DNA by partial intercalation in the minor groove: a topological mechanism of sequence specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11990–11994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Stehelin D., Clevers H. Ancestry and diversity of the HMG box superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2493–2501. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasrin N., Buggs C., Kong X. F., Carnazza J., Goebl M., Alexander-Bridges M. DNA-binding properties of the product of the testis-determining gene and a related protein. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):317–320. doi: 10.1038/354317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ner S. S. HMGs everywhere. Curr Biol. 1992 Apr;2(4):208–210. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90541-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paull T. T., Haykinson M. J., Johnson R. C. The nonspecific DNA-binding and -bending proteins HMG1 and HMG2 promote the assembly of complex nucleoprotein structures. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1521–1534. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Chow C. S., Lippard S. J. High-mobility-group 1 protein mediates DNA bending as determined by ring closures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9465–9469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Lippard S. J. Specific binding of chromosomal protein HMG1 to DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1566071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read C. M., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Driscoll P. C., Norman D. G. Solution structure of a DNA-binding domain from HMG1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3427–3436. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeck G. R., Isackson P. J., Teller D. C. Domain structure in high molecular weight high mobility group nonhistone chromatin proteins. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):76–78. doi: 10.1038/300076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stros M., Stokrová J., Thomas J. O. DNA looping by the HMG-box domains of HMG1 and modulation of DNA binding by the acidic C-terminal domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1044–1051. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Use of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme to improve an inducible T7 expression system. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 5;219(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90855-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto A., Iino Y., Maeda T., Watanabe Y., Yamamoto M. Schizosaccharomyces pombe ste11+ encodes a transcription factor with an HMG motif that is a critical regulator of sexual development. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):1990–1999. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.1990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Fischer W. H., Jones K. A. A thymus-specific member of the HMG protein family regulates the human T cell receptor C alpha enhancer. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):656–669. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Kraulis P. J., Hill C. S., Raine A. R., Laue E. D., Thomas J. O. Structure of the HMG box motif in the B-domain of HMG1. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen L., Huang J. K., Johnson B. H., Reeck G. R. A human placental cDNA clone that encodes nonhistone chromosomal protein HMG-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1197–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwieb C., Adhya S. Improved plasmid vectors for the analysis of protein-induced DNA bending. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;30:281–294. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-256-6:281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., Dooijes D., Clevers H. Identification and cloning of TCF-1, a T lymphocyte-specific transcription factor containing a sequence-specific HMG box. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]