Abstract
The biological effects of the testes and testosterone are known since antiquity. Aristotle knew the effects of castration and his hypothesis on fertilization is one of the first scientific encounters in reproductive biology. Over centuries, castration has been performed as punishment and to produce obedient slaves, but also to preserve the soprano voices of prepubertal boys. The Chinese imperial (and other oriental) courts employed castrates as overseers in harems who often obtained high-ranking political positions. The era of testis transplantation and organotherapy was initiated by John Hunter in London who transplanted testes into capons in 1786. The intention of his experiments was to prove the ‘vital principle’ as the basis for modern transplantation medicine, but Hunter did not consider endocrine aspects. Arnold Adolph Berthold postulated internal secretion from his testicular transplantation experiments in 1849 in Göttingen and is thus considered the father of endocrinology. Following his observations, testicular preparations were used for therapy, popularized by self-experiments by Charles-Edouard Brown-Séquard in Paris (1889), which can at best have placebo effects. In the 1920s Sergio Voronoff transplanted testes from animals to men, but their effectiveness was disproved. Today testicular transplantation is being refined by stem cell research and germ cell transplantation. Modern androgen therapy started in 1935 when Enrest Lacquer isolated testosterone from bull testes in Amsterdam. In the same year testosterone was chemically synthesized independently by Adolf Butenandt in Göttingen and Leopold Ruzicka in Basel. Since testosterone was ineffective orally it was either compressed into subcutaneous pellets or was used orally as 17α-methyl testosterone, now obsolete because of liver toxicity. The early phases of testosterone treatment coincide with the first description of the most prominent syndromes of hypogonadism by Klinefelter, by Kallmann, DelCastillo and Pasqualini. In the 1950s longer-acting injectable testosterone enanthate became the preferred therapeutic modality. In the 1950s and 1960s, research concentrated on the chemical modification of androgens in order to emphasize their anabolic effects. Although anabolic steroids have largely disappeared from clinical medicine, they continue to live an illegal life for doping in athletics. In the 1970s the orally effective testosterone undecanoate was added to the spectrum of preparations. Recent transdermal gels and long-acting injectable preparations provide options for physiological testosterone substitution therapy.
Keywords: castration, testosteron, testosterone deficiency
INTRODUCTION
Testosterone is the hormone that turns males into men and is responsible for major differences between men and women. Testosterone has a tremendous impact on phenotype, physiology and psychology of the individual, it is the driving force for reproduction and has an impact on society, culture and politics.
Unlike other endocrine organs, well-hidden within the body, the testes, as the source of testosterone, have an exposed position and are thus quite vulnerable and also easily accessible for external manipulation, including forceful removal. Therefore, quite early in the history of mankind, the effects of testosterone or rather their lack, became known and history is full of examples how this knowledge was applied.
This article reviews some of these events and gives an account of the first descriptions of testosterone deficiency syndromes as well as the eventual identification of testosterone as a chemical entity and its application in clinical medicine over the past 80 years. In parts, this review is based on the introductory chapter to the 4th edition of our book on ‘Testosterone: action, deficiency, substitution’.1
TESTOSTERONE DEFICIENCY PRODUCED BY CASTRATION
Castration has been practised for socio-cultural and political purposes since antiquity. Its major purpose was to generate obedient slaves who were loyal to their masters or rulers and, being infertile, could not create competing offspring. Set to guarding harems, they also, and in larger numbers, obtained influential administrative and political positions as in China2,3 and formed elite troops in Islamic countries.4 In different cultures and over centuries ‘wealthy women preferred intercourse (or rather other sexual pleasures) with castrated slaves for a good reason: there was no risk of pregnancy’.5
The earliest documentation of creating eunuchs in China dates back to about 1300 BC. The Chinese eunuch system, with several thousand's existing at a time, continued until the end of the imperial period in 1912. The last Chinese eunuch, Sun Yaoting, died at the age of 94 in 1996. Only the fact that imperial eunuchs could obtain high-ranking positions and considerable power as well as wealth makes it plausible that adult men underwent this gruesome operation. It was performed by ‘licensed surgeons’ just outside the imperial court in Beijing by cutting off testes and penis. About 25% of the volunteers did not survive this bloody operation. The severed genitals were kept in a box, as shown vividly in the film ‘The Last Emperor’6, and were eventually buried with their owner.
During the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644) eunuchs attained outstanding influence and wealth. The prime example is represented by Liu Jin (1451–1510) who is counted among the richest persons in history; he accumulated 449 750 kg of gold and 9 000 000 kg of silver, but eventually his criminal intrigues led to his execution. In the nineteenth century there were still about 2000 eunuchs at the imperial court in Beijing. The impact of peri- and postpubertal castration on the phenotype of these men was described extensively by Wagenseil7 who in 1922 established an Anatomical Institute at the Chinese–German Tung-Chi University in Shanghai where he examined a series of 31 Chinese eunuchs aged 45–57 years. These eunuchs had no beard growth and sparse body hair and 21 of the 31 had developed kyphosis as a clear sign of osteoporosis.
In Greek mythology, castration already occurred among the first generation of gods. Gaea, mother earth, grew out of the chaos and produced Uranos by parthenogenesis with whom she then generated the titan Chronos. When Uranos prevented Gaea from creating children with their son Chronos, she induced Chronos to castrate his father. Uranos’ testes, thrown into the sea, caused the water to foam and out of these bubbles the foam-born goddess of love Aphrodite (Venus) was born. Quite extraordinary events in terms of reproductive physiology! This episode has been depicted beautifully in a fresco by Giorgio Vasari (1511–1574) in the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence.
Eunuchs probably already existed in ancient Egypt. From the times of the legendary Queen Semiramis (about 800 BC) eunuchs were reported from Assyria and the system developed and continued into the Islamic world in the Middle - East and North Africa. Over centuries, slaves were deported from Sub-Saharan Africa to the Islamic cities and courts and many of the slaves who survived the exhausting march through the desert were then castrated to serve as laborers, guards, administrators and even soldiers.8 It is astonishing that these tasks could be fulfilled without the anabolic effects of testosterone.
It has been estimated that the transatlantic deportation of Africans to the Americas between 1450 and 1870 comprised about 11.5 million people while the entire Islamic deportation of slaves from Africa between 650 and 1920 amounted to 17 million people and several million of these African slaves were castrated. This constant drain of manpower effectively prevented economic and cultural development of Sub-Saharan Africa. In medieval times, slaves were also exported from Europe to the Islamic countries. These slaves were mainly from Eastern European (Slavic) and Central Asian countries. There were well-established slave routes through Europe and Verdun in France enjoys the questionable historical fame of having been the European center for castration of slaves on their way from the East to the South at those times.4
Castration has also been practised as lawful punishment. In medieval Scandinavia, castration combined with blinding was administered for high treason, especially when the insurgent was a close relative whom one did not want to kill directly. As told in the Islendinga Saga, Sturla of the Sturlungar Clan in Iceland castrated and blinded his rebelling relative Oraekja Snorrason in 1236 (personal communication from U. Ebel, Chair of Scandinavian Sciences, University of Münster, 2007). When the Normans migrated south, they also introduced this penal practice in the areas they invaded. When he established his reign in Britain after 1066, William the Conqueror abolished the Anglo-Saxon death penalty and replaced it by castration and blinding: ‘I also forbid that anyone shall be slain or hanged for any fault, but let his eyes be put out and let him be castrated’.9 As a further example, when the Normans invaded Sicily, King William III was castrated and blinded in 1194 after a rebellion against Emperor Henry VI. This episode forms the historical background for Klingsor's castration in the Parsifal epos.10 The Toulouse Law Codex of 1296 describes (and depicts) castration for high treason.
Throughout the centuries castration was applied to beaten enemies by victorious soldiers for revenge and as a measure to eliminate the enemies without outright killing. This continues into recent times. When Italian troops invaded Ethiopia and lost the battle of Aduwa in 1896 supposedly 7000 Italian soldiers were castrated.11 As reported by Babtschenko,12 this still happened on both sides during the Chechen War in the Caucasus in 1996.
Castration has also been reported as self-mutilation for religious reasons since ancient times in order to make a life in chastity easier. The early church father Origines (186–254) is one of the most prominent examples. In the eleventh to fourteenth centuries, the sect of the Catharers with their strongholds in Southern France promulgated self-castration as part of a ‘pure’ life. More recently, castration was practised in Southern Russia among members of the Scoptic sect founded in the eighteenth century and the medical consequences were documented.13 The largest contemporary group of castrates is among the hijras in India who also comprise persons with disorders of sexual development (DSD). They function as professional well-wishers at birth rites and weddings and receive considerable financial rewards. Several thousand of them exist.
Castration has also been used as revenge for seduction and adultery through the centuries. For example, Paris – presumably in the twelfth century BC and preceding the Trojan War – has been reported to have castrated Peritanos after he had seduced his famous wife Helena.14 The case of the great medieval theologian and philosopher Peter Abaelard (1079–1142) has been celebrated in history and literature. As master of the cathedral school in Paris he seduced one of his disciples, Heloise (1100–1164), whose uncle in revenge then had Abaelard castrated by paid criminals. Despite the lack of testosterone, one of the most romantic love stories documented by literature developed. This type of revenge continues into most recent times as demonstrated by an incident in Germany in 2011 when the father of a 17-year-old girl castrated her 57-year-old lover.15 These people had migrated to Germany from Kazakhstan and obviously brought their rules of self-justice with them. The German court sentenced the father to 6 years imprisonment and € 80,000 penalty!
Castration before puberty maintains the high voice of boys so that soprano and alto voices with the acoustic volume of an adult male result. Such high-pitched voices were considered desirable among music lovers, especially at times when women were not allowed to sing in church or in operatic performances. Prepubertal castrates belonged to casts of operas in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries; in the Vatican choirs these voices could be heard until the early twentieth century. Some of these castrates became famous soloists, such as Carlo Farinelli (1705–1782) or Domenico Annibaldi (1705–1779).16,17,18 The middle Italian cities of Norcia and Preci were a center for the operation on young boys. In the solitude of this hidden Apennine valley, a surgical school had already been established in the thirteenth century and the 30 family dynasties monopolizing the trade there guarantied utmost secrecy concerning this illegal operation.19 Strangely enough, while castration was forbidden in the Vatican state, which extended over most of middle Italy, it was not forbidden to employ castrated singers. However, most of the thousands of prepubertal castrates lost their virility in vain as they did not achieve the promised career as a singer, developed only mediocre voices and were ridiculed by their contemporaries. An impression of the castrato voice, although of very low recording quality, is preserved from the last Vatican castrato Alessandro Moreschi (1858–1922) in one of the earliest gramophone recordings, made in 1902 (available today on CD). Today countertenors applying a trained falsetto sing the castrato roles in, for example, Händel operas, but their head voices only approximate those of seventeenth century castrati. Another impression of the castratos’ enormous artistic talents is provided by the recordings of the mezzo-soprano Cecilia Bartoli who trained her voice to sing the extremely demanding arias by Nicola Porpora (1686–1768), Georg Friedrich Händel (1685–1759) and others.20
Prepubertal castration provides an involuntary experiment on the influence of testosterone on longevity. A retrospective comparison of the life expectancy of singers born between 1580 and 1858 and castrated before puberty, in order to preserve their high voices, to intact singers born at the same time did not reveal a significant difference between the lifespan of castrated intact singers (65.5 ± 13.8 vs. 64.4 ± 14.1, mean ± SD) (Figure 1).21 This would imply that the presence or absence of normal male testosterone levels at and after the age of puberty has no influence on life expectancy
Figure 1.
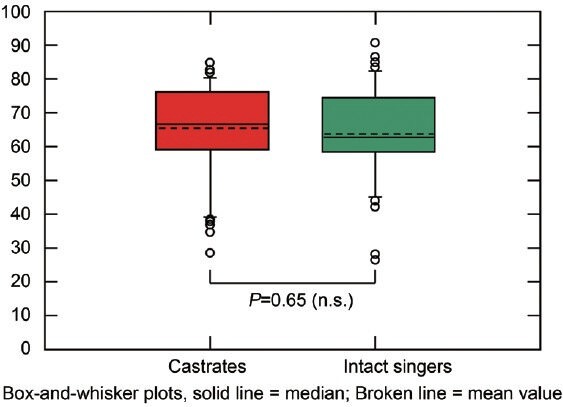
Age at death of castrated (n = 50) and intact singers (n = 50) born 1580–1859 (matched pairs). Reproduced with permission from Nieschlag et al.21
THE TESTES AS A MEDICINAL PRODUCT: ORGANOTHERAPY
As it was known that removal of the testes caused the clinically evidenced symptoms of hypogonadism including impotence, prescribing ingestion of testes to remedy the symptoms was a medical reflex inherent in organotherapy, practised since antiquity. Thus the Roman Gaius Plinius Secundus recommended the consumption of animal testes to treat symptoms of testosterone deficiency. Slightly more refined was the prescription of testicular extracts for the same purpose in Arabic medicine, for example, by Mensue the Elder (777–837) in Baghdad. Also in China, raw and desiccated testes were prescribed, documented at least in the twelfth century by Hsue Shu-Wei. Around the same time Albertus Magnus (1193–1280) in Cologne, better known as a philosopher, recommended powdered hog testes, but refined his recipe by offering the powder in wine.22
Since early documentation, these potions continued to be prescribed and consumed up into the twentieth century. In the 1920s, Testifortan® became a financially successful drug for treatment of impotence.23 Its main constituent was testis extracts and yohimbin; after the war 17α-methyl testosterone was added without changing the name. Another famous preparation from the 1920s and marketed until today is Okasa®, which, among other components, also contains testis sicca and thereby small amounts of testosterone, as we could determine in the 1970s (unpublished). However, as the testes synthesize testosterone but do not store their products in contrast to other endocrine organs such as the thyroid and the pancreas, the daily production by an adult man of about 6–8 mg is contained in roughly 1 kg of (bull) testes and even if this amount of testosterone were to be consumed, the testosterone taken orally would be inactivated by the first-pass effect in the liver.24 Therefore, all testicular organ therapy administered orally can only be considered as a placebo medication, which, however, may not be without its own effects.25 Ultimately this type of testicular organotherapy was terminated by the advent of phosphodiesterase inhibitors.
However, organotherapy literally had exploded at the end of the nineteenth century when Charles E. Brown-Séquard (1847–1894), who until then was a well-reputed scientist and member of several scientific academies, published the results of his famous self-experimentation in the Lancet.26 He gave himself 1-ml injections of a mixture of one part testicular vein blood, one part semen and one part juice extracted from dog or guinea-pig testes daily, and after 20 days made astonishing observations on himself: ‘A radical change took place in me. I had regained at least all the strength I possessed a good many years ago. I was able to make experiments for several hours. After dinner I was able to write a paper on a difficult subject. My limbs, tested with a dynamometer, gained 6 to 7 kg in strength. The jet of urine and the power of defecation became stronger’.
Certainly all these were placebo effects, but the world had obviously waited for such quackery, because in no time the ‘extracts of animal organs by the Brown–Séquard method’ were sold all over the (Western) world and factories sprang forth in Europe as well as in America, for example, next to Central Park in New York.27 There must have been a real craze for these products and physicians concerned about the image of the young field of endocrinology started worrying. The famous neurosurgeon Harvey W. Cushing (1869–1939) and the president of the Association of the Study of Internal Secretions, Edward H. Rynearson even talked about ‘endocriminology’ in the context of this organotherapy.28 This assessment of the medical scene at the time is also reflected in contemporary cartoons and comic songs from the early twentieth century. Eventually, this type of quackery stimulated science and decent pharmaceutical companies to search for real hormones.
TESTIS TRANSPLANTATION
Next to organotherapy there was another sad approach to treat hypogonadism and bring about rejuvenation and treatment for all sorts of disorders: the transplantation of testes. G. Frank Lydston (1858–1923) in Chicago was one of the first to perform human testicular transplantation from donors after experimentation in animals.29,30 Lespinase31 published his experience with transplanting human testes to patients for rejuvenation and Leo Stanley32 reported 20 cases of transplantation of testes from executed prisoners to other inmates who reported signs of revitalization. Later on he turned to animals as sources for his testicular grafts and reported satisfaction on the part of the patients including 13 physicians.33
In Vienna, Eugen Steinach (1861–1944) performed vasoligation for rejuvenation34 and one of his followers, Serge Voronoff (1866–1951) turned to xenotransplantation and used monkey testes to be transplanted for rejuvenation.35,36 He first offered his surgery in Paris, but after some scandals continued his questionable operations in Algiers, where he was obviously visited by patients all from over the world. Voronoff had followers in many countries who xenotransplanted animal testes or pieces thereof to patients in need of rejuvenation, also in the USA, where this type of treatment caused great interest among the laymen and the media.37 As unrest among the medical profession continued to grow, in 1927 the Royal Society of Medicine (London) sent an international committee to Voronoff in Algiers, which concluded that Voronoff's claims were all poppycock.38
These surgeons had followers in many parts of the world, for example, even in Iceland where, in 1929, the surgeon Jonas Sveinsson transplanted testis slices from a poor farmer in need of money to a rich Norwegian businessman who, he then claimed, satisfied his 23-year-old wife so that he even had three children with her.39 In the Soviet Union experimentation with human testicular transplantation continued at least into the 1980s.40 The only testicular transplantation resulting in fertility of the recipient was performed by Silber41 between twin brothers.
The idea of transplanting tissues and cells continued in a transformed fashion as ‘cellular therapy’ by injecting suspensions of fresh cells of sheep embryos including testis cells, also for rejuvenation and revitalization, well into the second half of the twentieth century.42 Meanwhile, however, science has progressed and, in the age of cell biology, testicular transplantation continues with the aim of inducing fertility, but now uses isolated germ cells43, and fertility has indeed been restored by this method in gamma-irradiated cocks.44 Whether this may become a method to treat male infertility, for example, in Klinefelter patients45 remains to be seen, but at least it is pursued on a rational scientific basis – as far as our present knowledge goes.
SCIENTIFIC EXPLORATION OF THE TESTES AND THEIR ENDOCRINE FUNCTION
The declaration of the Netherlands as an independent state during the 30 Years War (1618–1648), and legalized at the Westphalian Peace Treaty in Münster in 1648, resulted in an enormous upswing in economy, culture and science in this country. The medical sciences also boomed, based on proper research, especially in anatomy, as shown in Rembrandt's contemporary painting ‘Anatomy of Dr. Tulp’ (1632).
The reproductive sciences benefited from this boom as well. It was Regnier de Graaf (1641–1673), who not only described the Graafian follicle (1672), but also published a book about the anatomy of the male reproductive tract as well as the treatment of its disorders.46 He produced very detailed drawings and descriptions of the male genital organs and was the first to discover that the testes were composed of a ‘collection of minute vessels or tubules, which confect semen; if these tubules were disentangled without being broken and tied to one another, they would far exceed 20 Dutch ells in length’ (about 13 m). Having first described this in the edible dormouse, he then went on to the human: a classical case of translational medicine. Unfortunately, de Graaf became involved in a quarrel with his contemporary Jan Swammerdam (1637–1680) about the question of who had first described the ovarian follicles and during that phase he died under nebulous circumstances at the young age of 32.47
A few years after Regnier de Graaf's early and mysterious death, his friend Antoni A. Leeuwenhoek (1632–1723), together with the student Johan Hamm, used his newly invented prototype of a microscope and described the ‘little animals of the sperm’ in a letter to the Royal Society in London in 1677 (Collected Letters 1948). Considering the primitive appearance of his microscope, the details of his morphological descriptions of sperm are amazing and it is even more amazing that 300 years later we are still quarreling about normal and abnormal sperm morphology.48
But it took another century until Lazzaro Spallanzani (1729–1799), a priest and scientist in Modena, artificially inseminated frogs and dogs and demonstrated the real function of sperm.49 By using sperm that he had preserved on ice he also became the father of cryopreservation without which modern reproductive medicine and medicine in general would be unthinkable. He was a very systemic investigator and insisted – quite in contrast to others at the time – that experiments needed to be repeated before results could be accepted50, a principle that prevails until today.
The anatomist Franz Leydig (1821–1908) in Würzburg described the interstitial cells of the testes in 1850.51 Although he did not know their function, they still carry his name.52 Finally in Milano, in 1865 Enrico Sertoli (1842–1910) discovered the supporting cells in the seminiferous tubules53, also carrying his name until today.54
Thus, over roughly two centuries, the basic morphological elements of the testes had been described, as well as the one major product of the testes, the sperm. Even the function of sperm and fertilization had been elucidated so that the time had come to explore the basis of testicular endocrine function.
Although the endocrine function of the testes was known through their physiological and clinical effects, their nature remained completely obscure. Although William Harvey (1578–1657) had discovered the role of the heart and blood circulation in 1628, in some medical schools Galen's (129–216) concept of the four bodily humors prevailed well into the nineteenth century. Against this background it is not surprising that the idea of a hormone working as a signal transduced by circulating blood took so long to be born.
John Hunter (1728–1793) is considered by some to be the father of endocrinology, as he transplanted testes in chickens. However, his outstanding achievement as a scientist notwithstanding, he transplanted testes in order to demonstrate the ‘vital principle’ of living organs. As a surgeon in the Seven Years’ War (1756–1763) he saw the need for transplantation of organs and limbs, and this is what stimulated his research. He never described his testis transplantations himself, but we learn about them through a scholar, Dr. W. Irvine, in a letter to Prof. Th. Hamilton in Glasgow in 1771: ‘…Nay more, he has many hens just now into whose abdomen when young, he has put the testes of a cock just separated from his body and his testis has got blood vessels and nerves from the part of the abdomen or viscera to which it is applied…’. Far from any endocrine thought the goal was to demonstrate the survival of the transplant due to nerve growth.55
Such thoughts were precipitated by Arnold Adolph Berthold's (1803–1861) experiments, which also concerned transplanting chicken testes. As published in 1849, he castrated four cocks, two received an ectopic transplantation of one testis, the two others remained untreated and he observed: ‘They (the transplanted roosters) crowed quite considerably, often fought among themselves and with other young roosters and showed a normal inclination to hens …Since the testes can no longer remain in connection with their original nerves after being transplanted to a strange place … it follows that the consensus in question must be affected through the productive relationship of the testes, that is to say, through their action on the blood, and then through the suitable ensuing action of the blood on the organism as a whole’.56 The paper describes only four animals and comprises only four pages – in contrast to the extensive style of the time, but was epochal. However, Berthold's rival at the University of Göttingen, Rudolf Wagner (1805-1864) was jealous, tried to repeat the experiments, but failed and declared them as rubbish.57 And as he became the full professor of physiology, his opinion prevailed. Berthold's personality did not allow him to fight for recognition of his findings, which fell into oblivion.58,59
THE HOMESTRETCH TO ARRIVE AT TESTOSTERONE AS A CHEMICAL ENTITY
Berthold's unique discovery was superseded by organotherapy as described previously, but it was not permanently forgotten: Moritz Nussbaum (1850–1915), professor of anatomy in Bonn, repeated Berthold's experiments at the beginning of the twentieth century and confirmed the results in frogs60, as did Eugen Steinach in rats.61 Finally, A. Pézard confirmed Berthold's original results in cocks62, and the search for the active androgenic substance in the testes began.
From observation of the cock's comb growing under the influence of transplanted testes first described by Berthold, in 1929 Moore and coworkers established the standardized capon comb's test measuring androgenic activity in square cm of comb surface.63 This first bioassay facilitated determination of androgenic activity in body products as well as in chemical solutions. Loewe and Voss64 used the biological effects of androgens on the accessory sex organs and developed the ‘cytological regeneration test’, which was based on regrowth of the seminal vesicle epithelium under androgenic substances (Loewe–Voss-Test). The then still hypothetical male hormone was called ‘Androkinin’.
Simultaneously steroid biochemistry emerged and the great breakthroughs were the discovery of the ring structure of steroids and bile acids at the National Institute of Medical Research in London65 and at the Bavarian Academy of Sciences in Munich.66 A heated discussion started about whether there were three of four rings in the steroid structure and, if four rings, whether the fourth had five or six C-atoms. Under the sponsorship of the Health Organization of the League of Nations (the predecessor of WHO) famous chemists including Edmund A. Doisy, Adolf Butenandt and Guy Marrian assembled at University College London in 1932 and reached the consensus that steroids had four rings and the fourth ring had five C-atoms.67 Shortly before, these eminent researchers, including Ernest Laqueur, had isolated pregnandiol and estrone from pregnant mare urine provided by various drug companies cooperating with scientists in order to replace the miscredited organotherapy and to bring proper hormone substitution to patients.68
In 1931, Butenandt isolated the androgenic steroid androsterone (androstan-3α-ol-17-one) from urine for which he required 15 000 liters provided by young policemen from Berlin, which was then processed by Schering to obtain 15 mg of this first androgen.69 In 1935, Ernst Laqueur (1866–1947) and his group in Amsterdam extracted and isolated 10 mg testosterone (androsten-17α-ol-3-one) from 100 kg of bull testes, which they found more active than androsterone and named it ‘testosterone’.70 In the same year Butenandt and Hanisch in Göttingen71 as well as Ruzicka and Wettstein in Basel72 published the chemical synthesis of testosterone. This marked the beginning of modern clinical pharmacology and endocrinology of testosterone and male reproductive physiology.73
DEVELOPMENT OF TESTOSTERONE PREPARATIONS
Soon after its synthesis testosterone became clinically available, first in the form of pellets41,74 and then as injectable esters, that is, testosterone propionate with a short half-life and, from the mid-1950s on, the longer-acting testosterone enanthate75 appeared, which remained the major testosterone preparation for half a century.76,77 Also in 1935, 17α-methyl-testosterone was synthesized and its oral effectiveness was demonstrated.78 However, due to its 17α-structure it turned out to be liver toxic79, a fact that gave testosterone in general a bad name among physicians, as this toxicity was also suspected for testosterone without reason; eventually in the 1980s this androgen became obsolete for clinical use in Europe. In the late 1970s the orally effective testosterone undecanoate, absorbed from the gut via the lymph to avoid the first-pass effect in the liver, was added to the spectrum of testosterone preparations used clinically.77,80,81
In the 1950s and 1960s, the pharmaceutical industry became more interested in new androgens than in testosterone itself and concentrated its androgen research on the chemical modification of steroid molecules in order to disentangle the various effects of testosterone and produce predominantly erythropoietic or anabolic steroids.82 In 1956, contemporary textbooks on androgens had already described 256 androgenic steroids83 and by 1976 the number had increased to more than 1000.84
However, it proved impossible to produce androgens with only one effect out of the spectrum of testosterone activities; at best, one of these effects could be emphasized, but the other effects remained. The steroid with pure anabolic effects on muscles or bones to treat cachexia, osteoporosis or small stature, or pure erythropoietic effect for the treatment of anemia without androgenisation could not be found. Nevertheless, anabolic and similar steroids were clinically used, but disappeared again in the wake of evidence-based medicine. However, they continued their existence for illegal use and abuse for doping in sports and bodybuilding85 potentially causing considerable undesired effects.86 Regrettably, at that time the pharmaceutical industry neglected the chance to develop testosterone preparations better suited for the substitution of hypogonadal patients than the existing testosterone esters. It remains to be seen whether the current search for SARMs will take a more rewarding course than did anabolic steroids.87
From the 1970s, the newly developed testosterone immunoassays made serial testosterone determinations in blood possible and, when applied to pharmacokinetic studies, it turned out that all available testosterone preparations resulted in unphysiologically high or low serum levels, which were undesirable in substitution therapy. Clinicians assembled at a workshop on androgen therapy sponsored by WHO, NIH and FDA in 1990 came to the conclusion: ‘The consensus view was that the major goal of therapy is to replace testosterone levels at as close to physiologic concentrations as is possible’88 and demanded that new testosterone preparations better suited for clinical use be manufactured.
In the mid-1990s, transdermal testosterone patches applied to the scrotal skin became the first transdermal testosterone preparation in clinical use.89 They had been invented by Virgil Place at ALZA in Palo Alto, a company specializing in new forms of delivery of known drugs.90 However, although clinical results with this preparation were excellent91 and for the first time physiological serum levels could be achieved under testosterone substitution, physicians were reluctant to prescribe a medication to be applied to the scrotum and preferred a subsequently developed nonscrotal system.92 This, however, caused unpleasant skin reactions as it required an enhancer to drive testosterone through the skin. For this reason, the advent of the first transdermal testosterone gel was welcome. This gel became available in 2000 for the treatment of male hypogonadism, first in the US and later also in other countries.93 Since then, several other gels have been developed and brought to the market, differing slightly in composition and concentrations. The one with the highest testosterone concentration (2.5% Testotop®) has also been tested for scrotal application and because of the high absorptive capacity of the scrotal skin only 20% of the gel needed for nonscrotal application is required, making this form of application economically and ecologically more desirable.94 Finally in 2004, the intramuscular testosterone undecaonate preparation entered the market and soon achieved great popularity as a real testosterone depot preparation.77,95,96
Testosterone undecanoate had originally been used in oral capsules (see description earlier), but had been turned into an injectible preparation by Chinese investigators using tea seed oil as a vehicle.97 When the author came across it at an exhibition accompanying an andrology symposium in Beijing in 1993, samples were brought to Germany, injected into monkeys and showed a surprisingly long half-life.98 A long half-life could be confirmed in volunteering hypogonadal men who all showed serum levels in the normal range.95,96 When finally a company could be interested in this fascinating preparation, it was ‘Europeanised’ by using castor oil as vehicle and was developed as Nebido® (or Reandron®) for clinical use77,99 and is licensed today in 97 countries.
EARLY DESCRIPTIONS OF SYNDROMES OF HYPOGONADISM
It may not have been a coincidence, but a sign of heightened interest in the clinics of hypogonadism that at the same time when testosterone became available for clinical use, that is, when rational treatment became possible, that the major syndromes of primary and secondary hypogonadism were first described, that is, the Klinefelter syndrome in 1942100 and the Kallmann syndrome in 1944.101 As recent epidemiologic figures show, Klinefelter et al.,100 identified the most frequent syndrome of male hypogonadism and their case description could almost be written today. Nevertheless, pathophysiology and management of this syndrome have significantly advanced, as displayed graphically in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
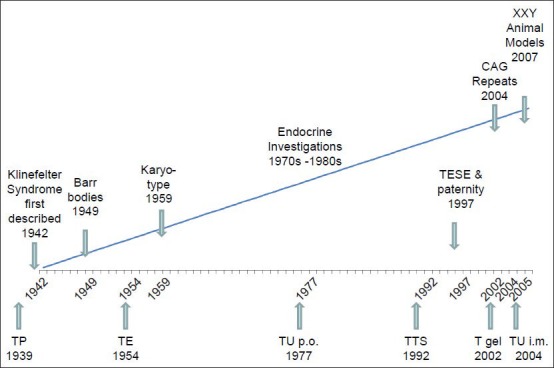
Historical landmarks in the development of diagnosis (upper line) and treatment (lower line) of the Klinefelter syndrome. (T = testosterone; TP = testosterone pellets; TE = testosterone enanthate; TU = testosterone undecanoate; TTS = testosterone therapeutic system).
In 1950, Pasqualini and Bur102 described the first case of the fertile-eunuch syndrome, characterized by all symptoms of lack of testosterone, but with active spermatogenesis; Del Castillo et al.,103 published the first five cases suffering from Sertoli-cell-only syndrome in 1947. Also in 1945, the symptoms of the aging male were first described systematically, but unfortunately wrongly termed as ‘male climacteric’104, starting a controversial discussion that continues until today.105
Also at that time, the first cases of DSD were described properly: in 1947, Reifenstein106 first described a syndrome with partial androgen insensitivity (PAIS) that carried his name for a long time and in 1953, Morris107 published the first cases of complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS) as ‘testicular feminisation in male pseudo-hermaphroditism’ – of course without knowing anything about the androgen receptor or androgen receptor mutations.
The description of the various syndromes soon required a systematic classification of male hypogonadism, which was always complicated by the fact that the testes have dual functions, each of which may develop failure independently or they may become dysfunctional together. Even in the early deliberations in 1941 about the classification of hypogonadism Fuller Albright, when describing ‘hypoleydigism’, was clear about hypogonadism, which might refer to either of the two functions of the male gonad or both.108 Heller and Nelson109 in 1948 and Hellinga110 in 1957, who further developed the classification over half a century ago, took the two compartments well into account as well as the period of life when hypogonadism starts. Heller and Nelson109 summarized their findings by saying ‘The age at onset of the defect (before, at or after puberty) and its exact location (indicating which function of the pituitary or testes is involved) determines the diagnosis as well as the treatment’ and they provided a table similar to those seen today, although much less detailed111, reflecting the state of knowledge. At the time Hellinga110 takes Leydig cell and tubular function clearly into consideration, and comes up with nine gross entities of hypogonadism and, in addition, differentiates between onset before and after puberty. Although many other syndromes and disease entities have been added since those early days and endocrinology and more recently, molecular genetics have yielded a wealth of pathophysiological explanations, this definition of hypogonadism signifying an impaired function of the testes, either as testosterone deficiency or infertility or both, continues as the major nosologic guideline up to most recent textbooks.111
Also in 1941, Huggins posted his warning about testosterone influencing prostate carcinoma112, which prevailed and led to castration (euphemistically called ‘orchiectomy’) as the major treatment of prostate carcinoma, until quite recently when androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) by GnRH analogues or antiandrogens was introduced instead of or in addition to castration (maximal androgen blockade = MAB). Huggins’ statement ‘Cancer of the prostate is activated by androgen injections’ induced a general fear of testosterone, especially among urologists, that prevented testosterone treatment in many patients who might have needed it. Only recently, it became clear that neither endogenous serum testosterone levels113 nor testosterone treatment114 have an impact on prostate carcinogenesis. As the deleterious effects of ADT become evident and documented115, now testosterone treatment under careful supervision is even considered for patients after radical prostatectomy suffering from testosterone deficiency.116,117 However, in the foreseeable future orchiectomy may continue to remain an option for treatment of prostate carcinoma.118 Thus, castration continues to be recommended for therapeutic purposes, as it had already been promulgated during Greek–Roman times and the Middle Ages for the treatment of leprosy, epilepsy, gout, priapism, excessive masturbation and insanity11, reflecting the knowledge or rather the lack of knowledge of the respective period. There remains the hope that research will eventually result in more humane and patient-friendly methods of treatment, as we have witnessed the transition from castration to ADT for treating sexual offenders.119
COMPETING INTERESTS
Nothing to declare.
REFERENCES
- 1.Nieschlag E, Nieschlag S. The medical and cultural history of testosterone and the testes. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Nieschlag S, editors. Testosterone: Action, deficiency, substitution. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012. pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anderson MM. Buffalo NY: Prometheus; 1990. Hidden power: the palace eunuchs of imperial China; pp. 307–11. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mitamura T. Rutland, Vermont: Charles E. Tuttle; 1992. Chinese eunuchs: the structure of intimate politics. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Flaig E. München: Verlag CH Beck; 2009. Weltgeschichte der Sklaverei. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dettenhofer MH. Eunuchs, women and imperial courts. In: Scheidel W, editor. Rome and China: comparative perspectives on ancient world empires. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2009. pp. 83–127. [Google Scholar]
- 6.The Last Emperor. Film by B. Bertolucci, Columbia Pictures. 1987 [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wagenseil F. Chinese eunuchs. A report on the sequelae of castration as well as on the importance of race and body composition for anthropomorphic characteristics. Ztschr Morphol Anthropol. 1933;32:415–68. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barth H. Gotha: Justus Pertes; 1857. Travels and discoveries in North and Central Africa from 1849 to 1855. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Van Eickels K. Gendered violence: Castration and blinding as punishment for treason in Normandy and Anglo-Norman England. Gender History. 2004;16:588–602. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tuchel S. Droste-Verlag: Droste-Verlag; 1998. Castration in the middle ages. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Melicow MM. Castration down the ages. N Y State J Med. 1977;77:804–08. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Babtschenko A. Rowohlt; 2008. The colour of war Hamburg. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wilson JD, Roehrborn C. Long-term consequences of castration in men: lessons from the Skoptzy and the eunuchs of the Chinese and Ottoman courts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84:4324–31. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.12.6206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lehrs On the representation of Helena in Greek mythology and literature. In: historische und literarische Abhandlungen der Königlichen deutschen Gesellschaft zu Königsberg. Second Collection. 1832:108. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Holzhaider H. Vol. 31.3. Süddeutsche Zeitung; 2011. Forbidden love; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Melicow MM. Castrati singers and the lost “cords”. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1983;59:744–64. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ortkemper H. Berlin: Henschel-Verlag; 1993. Unwilling angels: the world of the castrato. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jenkins JS. The voice of the castrato. Lancet. 1998;351:1877–81. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(97)10198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fabbi A. Spoleto; 1974. The surgical schools of Preci, Panetto and Petrelli. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bartoli C. London: Decca Music Group; 2009. Sacrificium: The school for castratos, CD and booklet. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nieschlag E, Nieschlag S, Behre HM. Life expectancy and testosterone. Nature. 1993;366:215. doi: 10.1038/366215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Medvei VC. Carnforth UK and Pearl River NY Parthenon Publishing Group; 1993. The history of clinical endocrinology. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hirschfeld M. Berlin: Institute for Sex Research; 1927. The treatment of impotence in medical practice. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nieschlag E, Cüppers EJ, Wickings EJ. Influence of sex, testicular development and liver function on the bioavailability of oral testosterone. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977;7:145–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bundesärztekammer, editor. Cologne: Deutscher Aerzteverlag; 2011. The placebo in medicine. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brown-Séquard E. The effects produced on man by subcutaneous injections of a liquid obtained from the testicles of animals. Lancet. 1889;20:105–7. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Borell M. Brown-Séquard's organotherpay and its appearance in America at the end of the nineteenth century. Bull Hist Med. 1976;50:309–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hamblen EC. Endocrinology or endocriminology! Some abuses of endocrine therapy. Southern Med J. 1950;43:506–9. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lydston GF. Sex gland implantation. N Y Med J. 1915;51:601–8. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schultheiss D, Engel RM. G. Frank Lydston (1858–1923) revisited: therapy by testicular implantation in the early twentieth century. World J Urol. 2003;21:356–63. doi: 10.1007/s00345-003-0370-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lespinase VD. Transplantation of the testicle. J Am Med Assoc. 1913;18:251–3. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stanley LL. Experiences in testicle transplantation. Cal State J Med. 1920;18:251–3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Stanley LL. An analysis of one thousand testicular substance implantations. Endocrinol. 1923;7:787–94. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Steinach E. Berlin: J Springer Verlag; 1920. Rejuvenation by experimental reactivation of the aging pubertal gland. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Voronoff S. London: Brentanos Ltd; 1920. Testicular grafting from ape to man. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Voronoff S. Milano: Quintieri Editore; 1923. Transplantation of the testes. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Gayton B. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 1922. The gland stealers. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Parkes AS. The rise of reproductive endocrinology. 1926-1940 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sveinsson H. J Endocrinol. Vol. 34. Iceland: Helgafell; 1969; 1966. Lifid er dásamlegt (autobiography) pp. XX–XXXii. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shumakov VI, Gotsiridze OA. Surgical technique for testes transplantation. Vestn Khir Im II Grek. 1978;121:77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Silber SJ, Rodriguez-Rigau LJ. Pregnancy after testicular transplant: importance of treating the couple. Fertil Steril. 1980;33:454–5. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)44667-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Niehans P. New York: Pageant; 1960. Introduction to cellular therapy. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brinster RL, Zimmermann JW. Spermatogenesis following male germ-cell transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:11287–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Trefil P, Micakova A, Mucksova J, Hejnar J, Poplstein M, et al. Restoration of spermatogenesis and male fertility by transplantation of dispersed testicular cells in the chicken. Biol Reprod. 2006;75:575–81. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.105.050278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wistuba J. Animal models for Klinefelter's syndrome and their relevance for the clinic. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010;16:375–85. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaq024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.De Graaf R. Leyden and Rotterdam: ex officina Hackiana; 1668. On disorders of male reproductive organs, on clysters and the use of siphons in anatomy. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Setchell BP. The contributions of Reinier de Graaf to reproductive biology. Eur J Obstet Gynec Reprod Biol. 1974;4:1–13. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(74)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kremer J. The significance of Antoni van Leeuwenhoek for the early development of andrology. Andrologia. 1979;11:243–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.1979.tb02195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Spallanzani L. Siena: Prodomo Della Nuova Encyclopedia Italiana; 1779. Artificial fertilization. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gaeto M. The bicentennial of a forgotten giant: Lazzaro Spallanzani (1729-1799) Int Microbiol. 1999;2:273–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Leydig F. On the anatomy of the male sexual organs and anal glands of mammals. Ztschr Wiss Zool. 1850;2:1–57. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Christensen AK. A history of studies on testicular Leydig cells: the first century. In: Payne AH, Hardy M, Russel LD, editors. The Leydig cell. Vienna IL: Cache River Press; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sertoli E. The existence of particular branched cells in the seminiferous tubules of the human testicle. Il Morgagni. 1865;7:31–40. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Virdis R. Historical milestones in endocrinology. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005;28:944–8. doi: 10.1007/BF03345329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jorgensen CB, John Hunter, A.A. Berthold and the origins of endocrinology. Acta Hist Sci Nat Med. 1971;24:7–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Berthold AA. On the transplantation of the testes. Arch Anat Physiol Wiss Med. 1849:42–6. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wagner R. Göttingen: Nachr Königl Ges Wiss; 1852. Report of a simple method in experiments on the morphological and chemical alterations of animal tissue; pp. 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Simmer H, Simmer I. Arnold Adolph Berthold (1803-1861). In memory of the 100 th anniversary of the death of the founder of experimental endocrinology. Dtsch med Wschr. 1961;86:2186–92. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Simmer HH. Arnold Adolph Berthold (1803-1861) - Forerunner or founder of experimental endocrinology? Endokrinol Inform. 1980;3:101–11. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nussbaum M. Testes and rutting organs of the brown frog (Rana fusca) Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol. 1909;126:519–77. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Steinach E. Sexual drive and true secondary sexual characteristics as a result of internal secretory functions of the gonads. Zbl Physiol. 1910;24:551–66. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pézard A. On the determination of secondary sexual characteristics in poultry. Cpt Rend Scienc. 1911;153:1027. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Moore CR, Gallagher TF, Koch FC. The effects of extracts of testis in correcting the castrated condition in the fowl and in the mammal. Endocrinol. 1929;13:367–74. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Loewe S, Voss HE. Update on the male sex hormone [androkinins] Klin Wschr. 1930;9:481–7. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Rosenheim SO, King H. The ring-system of steroids and bile acids. Nature. 1932;130:315. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wieland HO, Dane E. Investigations on the constitution of bile acids. Hoppe-Syler's Ztschr Physiol Chem. 1932;210:268–81. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Butenandt A. History of the discovery of oestrone. Endokrinol Inform. 1980;4:160–3. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Simmer H. Biosynthesis of steroid hormones. Endokrinol Inform. 1982;2:80–92. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Butenandt A. The chemical investigation of the sex hormone. Z Angew Chem. 1931;44:905–8. [Google Scholar]
- 70.David K, Dingemanse E, Freud J, Laquer E. Crystalline male hormone from the testes (Testosterone) is more effective than androsterone derived from urine or cholesterin. Hoppe-Seyler's Z physiol Chem. 1935;233:281–2. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Butenandt A, Hanisch G. Testosterone. The transformation of dehydroandrosterone into androstendiol and testosterone; a method for producing testosterone from cholesterin. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem. 1935;237:89–98. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ruzicka L, Wettstein A. Synthesis of the testicular hormone (testosterone) (androstene 3-on-17-ol) Helv chim Acta. 1935;18:1264–75. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ratmoko C. Zürich. Chronos-Verlag; 2010. Making the chemistry right. The beginnings of industrial production of female and male sexual hormones 1914–1938. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Deansley R, Parkes AS. Factors influencing effectiveness of administered hormones. Proc R Soc London. 1937;124:279–98. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Junkmann K. Long-acting steroids in reproduction. Rec Progr Horm Res. 1957;13:389–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nieschlag E, Behre HM. Clinical uses of testosterone in hypogonadism and other conditions. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Nieschlag S, editors. Testosterone: action, deficiency, substitution. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012. pp. 292–308. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Behre HM, Nieschlag E. Testosterone preparations for clinical use in males. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Nieschlag S, editors. Testosterone: action, deficiency, substitution. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012. pp. 309–35. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ruzicka L, Goldberg MW, Rosenberg HR. Production of 17alpha-methyl-testosterone and other androstene and androstane derivatives. Connections between chemical constitution and male hormone effect. Helv Chim Acta. 1935;18:1487–98. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Nieschlag E. Is the use of methyltestosterone obsolete? Dtsch med Wschr. 1981;106:1123–5. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1070466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Coert A, Geelen J, de Visser J, van der Vies J. The pharmacology and metabolism of testosterone undecanoate (TU), a new orally active androgen. Acta Endocrinol. 1975;79:789–800. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0790789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Nieschlag E, Mauss J, Coert A, Kicovic P. Plasma androgen levels in men after oral administration of testosterone or testosterone undecanoate. Acta Endocrinol. 1975;79:366–74. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0790366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kopera H. Eikelboom FA, van der Vies J, editors. The history of anabolic steroids and a review of clinical experience with anabolic steroids. Anabolics in the ‘80s. Acta endocrinol. 1985;271(Suppl):11–8. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.109s00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Dorfman RL, Shipley RA. New York: Wiley and Sons; 1956. Androgens: biochemistry, physiology and clinical significance. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kochakian CD, editor. Heidelberg: Springer; 1976. Anabolic-androgenic steroids. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Schänzer W, Thevis M. Detection of illegal use of androgens and SARMs. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Nieschlag S, editors. Testosterone: action, deficiency, substitution. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012. pp. 517–34. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Vorona E, Nieschlag E. Sequelae of doping with anabolic steroids. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Nieschlag S, editors. Testosterone: action, deficiency, substitution. 4th edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012. pp. 535–546. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Jasuja R, Zacharov MN, Bhasin S. The state-of-the-art in the development of selective androgen receptor modulators. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Nieschlag S, editors. Testosterone: action, deficiency, substitution. 4th edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2012. pp. 459–469. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Nieschlag E, Wang C, Handelsman DJ, Swerdloff RS, Wu F, Einer-Jensen N, Waites G. World Health Organization. Geneva: WHO; 1992. Guidelines for the use of androgens. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Bals-Pratsch M, Knuth UA, Yoon YD, Nieschlag E. Transdermal testosterone substitution therapy for male hypogonadism. Lancet. 1986;ii:943–46. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90600-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Atkinson LE, Chang YL, Snyder PJ. Long-term experience with testosterone replacement through scrotal skin. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, editors. Testosterone: action, deficiency, substitution. 2nd ed. Heidelberg: Springer; 1998. pp. 365–88. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Behre HM, von Eckardstein S, Kliesch S, Nieschlag E. Long-term substitution therapy of hypogonadal men with transscrotal testosterone over 7-10 years. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1999;50:629–35. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1999.00705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Meikle AW, Mazer NA, Moellmer JF, Stringham JD, Tolman KG, et al. Enhanced transdermal delivery of testosterone across nonscrotal skin produces physiological concentrations of testosterone and its metabolites in hypogonadal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992;74:623–8. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.3.1740497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wang C, Berman N, Longstreth JA, Chuapoco B, Hull L, et al. Pharmacokinetics of transdermal testosterone gel in hypogonadal men: application of gel at one site versus four sites: a general clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:964–9. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.3.6437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Kühnert B, Byrne M, Simoni M, Köpcke W, Gerss J, et al. Testosterone substitution with a new transdermal, hydroalcoholic gel applied to scrotal or non-scrotal skin: a multicentre trial. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005;153:317–26. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.01964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Nieschlag E, Büchter D, von Eckardstein S, Abshagen K, Simoni M, et al. Repeated intramuscular injections of testosterone undecanoate for substitution therapy in hypogonadal men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1999;51:757–63. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1999.00881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Behre HM, Abshagen K, Oettel M, Hubler D, Nieschlag E. Intramuscular injection of testosterone undecanoate for the treatment of male hypogonadism: phase I studies. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999;140:414–9. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1400414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Wang L, Shi DC, Lu SY, Fang RY. The therapeutic effect of domestically produced testosterone undecanoate in Klinefelter syndrome. New Drug Mark. 1991;8:28–32. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Partsch CJ, Weinbauer GF, Fang R, Nieschlag E. Injectable testosterone undecanoate has more favourable pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics than testosterone enanthate. Eur J Endocrinol. 1995;132:514–9. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1320514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Nieschlag E. Testosterone treatment comes of age: new options for hypogonadal men. Clin Endocrinol. 2006;65:275–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Klinefelter HF, Reifenstein EC, Albright F. Syndrome characterized by gynecomastia, aspermatogenesis, without A-Leydigism, and increased excretion of follicle-stimulating hormone. J Clin Endocrinol. 1942;2:615–27. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kallmann FJ, Schoenfeld WA, Barrera SE. The genetic aspects of primary eunuchoidism. Am J Ment Def. 1944;158:203–36. [Google Scholar]
- 102.Pasqualini RQ, Bur GE. Hypoandrogenic syndrome with gametogenesis. Classification of testicular insufficiency. Rev Asoc Med Argent. 1950;64:6–10. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Del Castillo EB, Trabucco A, de la Balze FA. Syndrome produced by absence of the germinal epithelium without impairment of the Sertoli or Leydig cells. J Clin Endocrinol. 1950;7:493–502. doi: 10.1210/jcem-7-7-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Werner AA. The male climacteric. J Am Med Assoc. 1945;127:705–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.1946.02870390004002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Nieschlag E, Swerdloff R, Behre HM, Gooren LJ, Kaufman JM, et al. Investigation, treatment and monitoring of late–onset hypogonadism in males: ISA, ISSAM, and EAU recommendations. Int J Androl. 2005;28:125–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2005.00553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Reifenstein EC., Jr Hereditary familial hypogonadism. Proc Am Fed Clin Res. 1947;3:86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Morris JM. The syndrome of testicular feminization in male pseudohermaphrodites. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1953;65:1192–211. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(53)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Albright F, Forbes AF, Fraser R, Miller B, Reifenstein EC. A classification of the causes of hypoleydigism. Trans Assoc Am Phys. 1941;56:43–54. [Google Scholar]
- 109.Heller CG, Nelson WO. Classification of male hypogonadism and a discussion of the pathologic physiology, diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1948;8:345–66. doi: 10.1210/jcem-8-5-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Hellinga G. Classification of male hypogonadism. Acta Endocrinol. 1957;24(Suppl 31):148–80. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.024s148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Tüttelmann F, Nieschlag E. Classification of andrological disorders. In: Nieschlag E, Behre HM, Nieschlag S, editors. Andrology: male reproductive health and dysfunction. 3rd ed. Heidelberg: Springer; 2010. pp. 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Huggins C, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer: i. The effect of castration, of estrogen and of androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res. 1941:293–7. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.22.4.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Endogenous Hormones and Prostate Cancer Collaborative Group. Endogenous sex hormones and prostate cancer: a collaborative analysis of 18 prospective studies. J Ntl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:170–83. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djm323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Raynaud JP. Prostate cancer risk in testosterone-treated men. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2006. 2006;102:261–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.09.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Levine GN, D’Amico AV, Berger P, Clark PE, Eckel RH, et al. American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, the American Cancer Society, and the American Urological Association. Androgen-deprivation therapy in prostate cancer and cardiovascular risk: a science advisory from the American Heart Association, American Cancer Society, and American Urological Association: endorsed by the American Society for Radiation Oncology. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:194–201. doi: 10.3322/caac.20061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Morgenthaler A. Testosterone deficiency and prostate cancer: emerging recognition of an important and troubling relationship. Eur Urol. 2007;52:623–5. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.EAU Guideline on male hypogonadism. [Last accessed on 2013 Nov 7]. Available from: www.uroweb.org .
- 118.Damber JE. Prostate cancer. Lancet. 2008;371:1710–21. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60729-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Gooren L. Ethical and medical considerations of androgen deprivation treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:3628–37. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


