Abstract
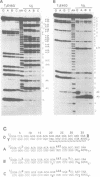
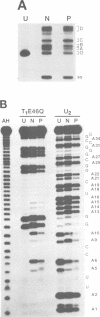
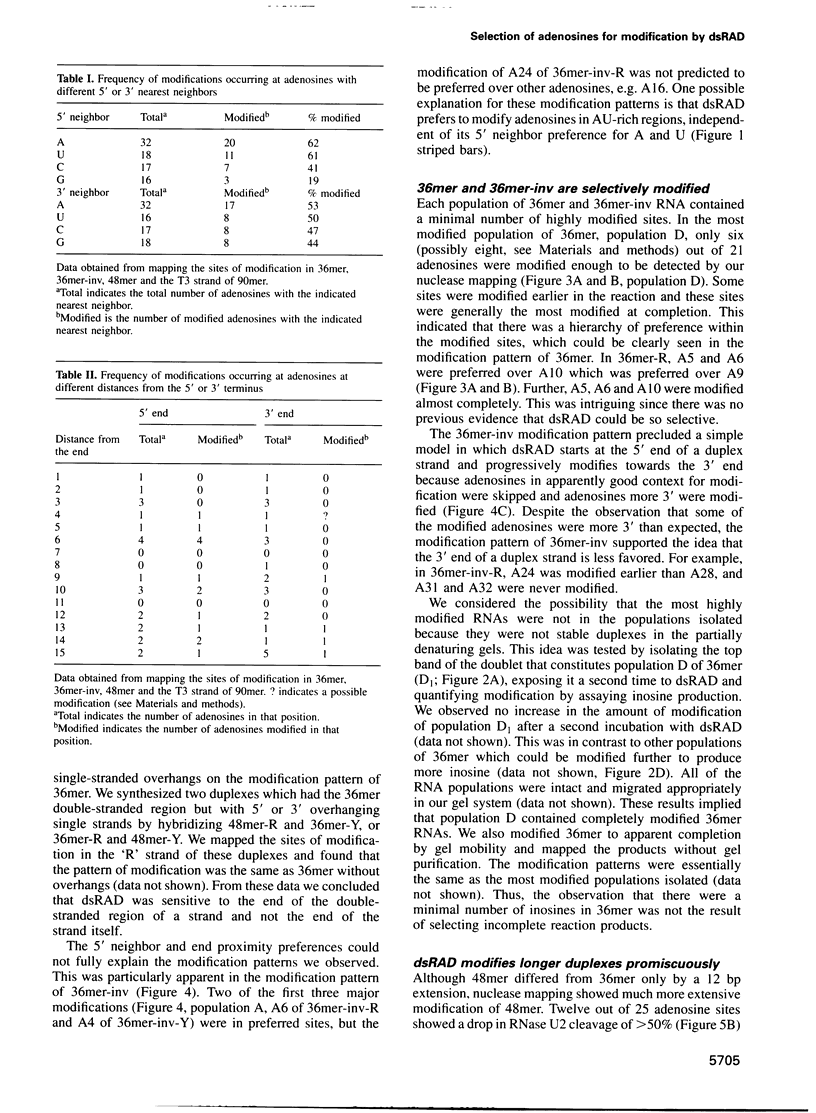
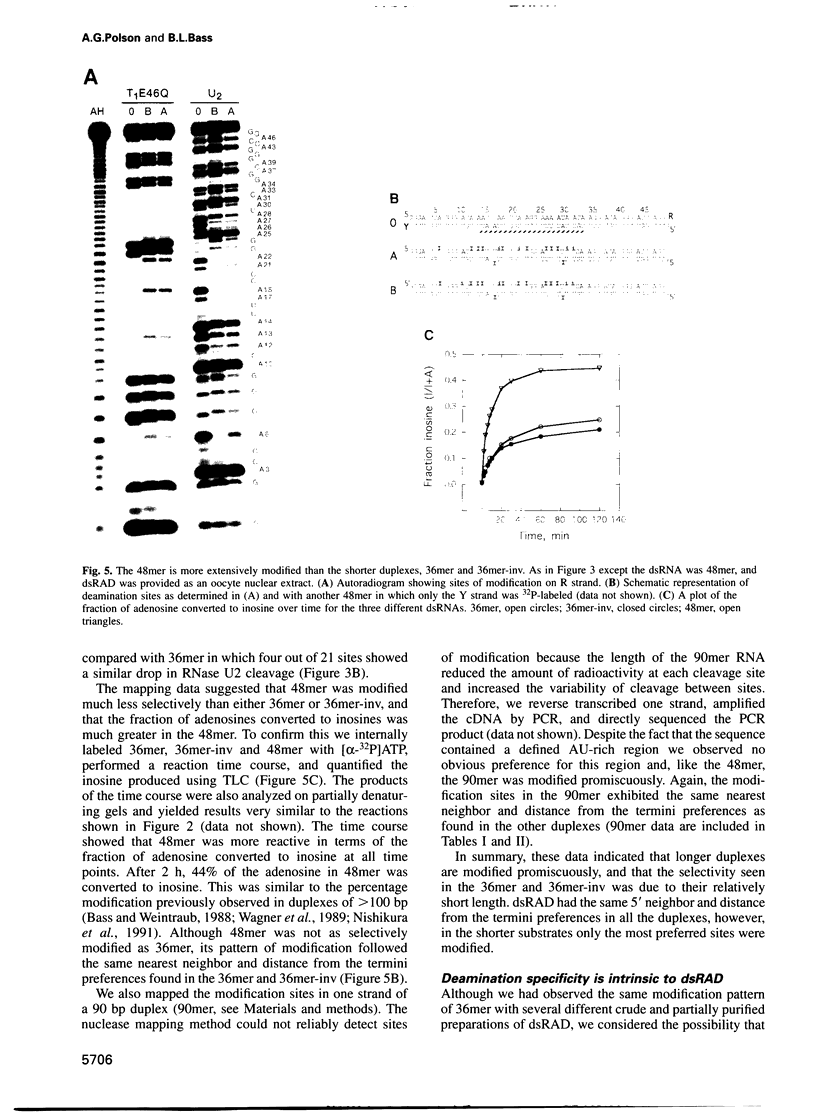
Double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminase (dsRAD), previously called the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) unwinding/modifying activity, modifies adenosines to inosines within dsRNA. We used ribonuclease U2 and a mutant of ribonuclease T1 to map the sites of modification in several RNA duplexes. We found that dsRAD had a 5' neighbor preference (A = U > C > G) but no apparent 3' neighbor preference. Further, the proximity of the strand termini affected whether an adenosine was modified. Most importantly, dsRAD exhibited selectivity, modifying a minimal number of adenosines in short dsRNAs. Our results suggest that the specific editing of glutamate receptor subunit B mRNA could be performed in vivo by dsRAD without the aid of specificity factors, and support the hypothesis that dsRAD is responsible for hypermutations in certain RNA viruses.
Full text
PDF



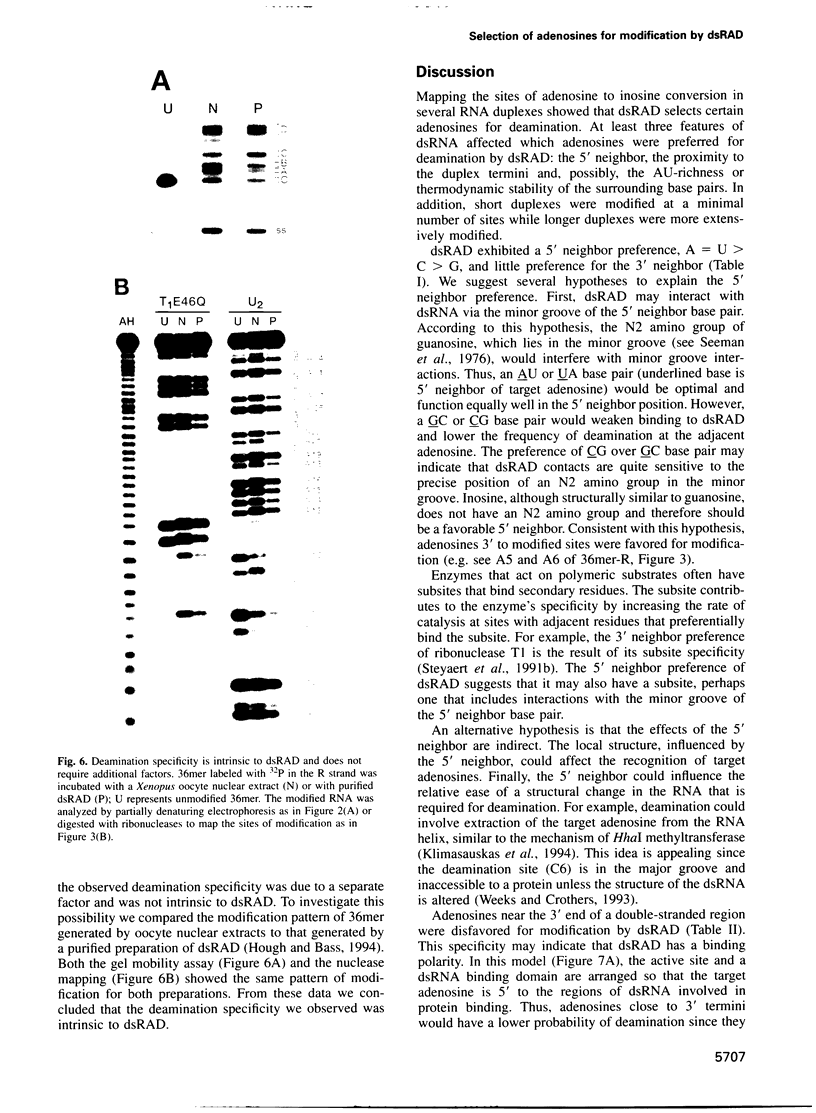




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BASILIO C., WAHBA A. J., LENGYEL P., SPEYER J. F., OCHOA S. Synthetic polynucleotides and the amino acid code. V. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:613–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Hurst S. R., Singer J. D. Binding properties of newly identified Xenopus proteins containing dsRNA-binding motifs. Curr Biol. 1994 Apr 1;4(4):301–314. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H. A developmentally regulated activity that unwinds RNA duplexes. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90239-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H. An unwinding activity that covalently modifies its double-stranded RNA substrate. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1089–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass B. L., Weintraub H., Cattaneo R., Billeter M. A. Biased hypermutation of viral RNA genomes could be due to unwinding/modification of double-stranded RNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):331–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Billeter M. A. Mutations and A/I hypermutations in measles virus persistent infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;176:63–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77011-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R. RNA editing. RNA duplexes guide base conversions. Curr Biol. 1994 Feb 1;4(2):134–136. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(94)00030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Dideoxy sequencing of RNA using reverse transcriptase. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:121–130. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Single F. N., Köhler M., Sommer B., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. RNA editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR-B: a base-paired intron-exon structure determines position and efficiency. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1361–1370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90622-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough R. F., Bass B. L. Purification of the Xenopus laevis double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9933–9939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Predicting optimal and suboptimal secondary structure for RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:281–306. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U., Garner T. L., Sanford T., Speicher D., Murray J. M., Nishikura K. Purification and characterization of double-stranded RNA adenosine deaminase from bovine nuclear extracts. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13480–13489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. W. An antisense mRNA directs the covalent modification of the transcript encoding fibroblast growth factor in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimasauskas S., Kumar S., Roberts R. J., Cheng X. HhaI methyltransferase flips its target base out of the DNA helix. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler M., Burnashev N., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Determinants of Ca2+ permeability in both TM1 and TM2 of high affinity kainate receptor channels: diversity by RNA editing. Neuron. 1993 Mar;10(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90336-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. G., Dimock K., Kang C. Y. Numerous transitions in human parainfluenza virus 3 RNA recovered from persistently infected cells. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):760–763. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90913-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Yoo C., Kim U., Murray J. M., Estes P. A., Cash F. E., Liebhaber S. A. Substrate specificity of the dsRNA unwinding/modifying activity. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3523–3532. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04916.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara P. J., Nichol S. T., Horodyski F. M., Holland J. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus defective interfering particles can contain extensive genomic sequence rearrangements and base substitutions. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polson A. G., Crain P. F., Pomerantz S. C., McCloskey J. A., Bass B. L. The mechanism of adenosine to inosine conversion by the double-stranded RNA unwinding/modifying activity: a high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 10;30(49):11507–11514. doi: 10.1021/bi00113a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Melton D. A. Antisense RNA injections in fertilized frog eggs reveal an RNA duplex unwinding activity. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):599–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccomanno L., Bass B. L. The cytoplasm of Xenopus oocytes contains a factor that protects double-stranded RNA from adenosine-to-inosine modification. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5425–5432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharmeen L., Bass B., Sonenberg N., Weintraub H., Groudine M. Tat-dependent adenosine-to-inosine modification of wild-type transactivation response RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8096–8100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeiky Y. A., Iatrou K. Developmental regulation of covalent modification of double-stranded RNA during silkmoth oogenesis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 5;218(3):517–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90698-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Köhler M., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H. RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90568-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Brown N. H., Gall J. G., Jantsch M. A conserved double-stranded RNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10979–10983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steyaert J., Opsomer C., Wyns L., Stanssens P. Quantitative analysis of the contribution of Glu46 and Asn98 to the guanosine specificity of ribonuclease T1. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 15;30(2):494–499. doi: 10.1021/bi00216a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steyaert J., Wyns L., Stanssens P. Subsite interactions of ribonuclease T1: viscosity effects indicate that the rate-limiting step of GpN transesterification depends on the nature of N. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8661–8665. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartanian J. P., Meyerhans A., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Selection, recombination, and G----A hypermutation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1779–1788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1779-1788.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. W., Nishikura K. Cell cycle expression of RNA duplex unwindase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):770–777. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. W., Smith J. E., Cooperman B. S., Nishikura K. A double-stranded RNA unwinding activity introduces structural alterations by means of adenosine to inosine conversions in mammalian cells and Xenopus eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Crothers D. M. Major groove accessibility of RNA. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1574–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.7690496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda T., Inoue Y. Studies of catalysis by ribonuclease U2. Steady-state kinetics for transphosphorylation of oligonucleotide and synthetic substrates. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):364–369. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]