Abstract
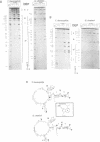
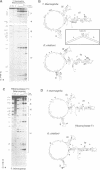
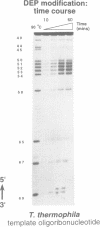
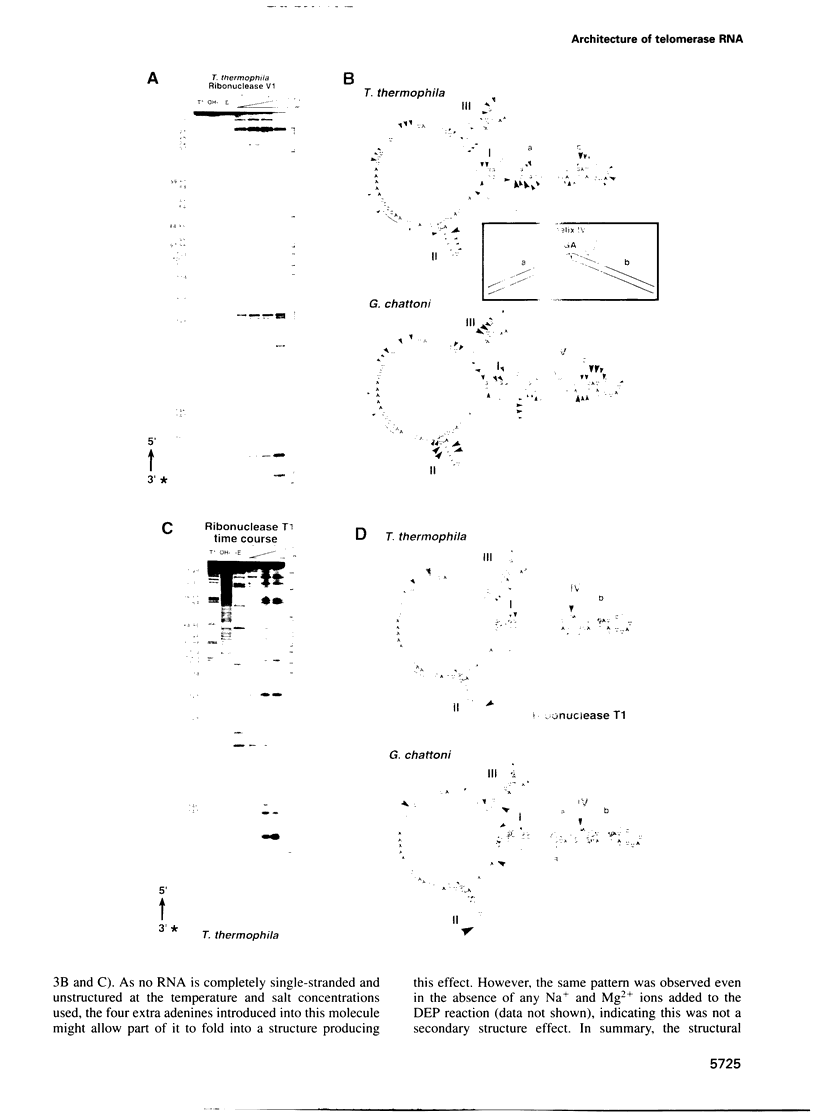
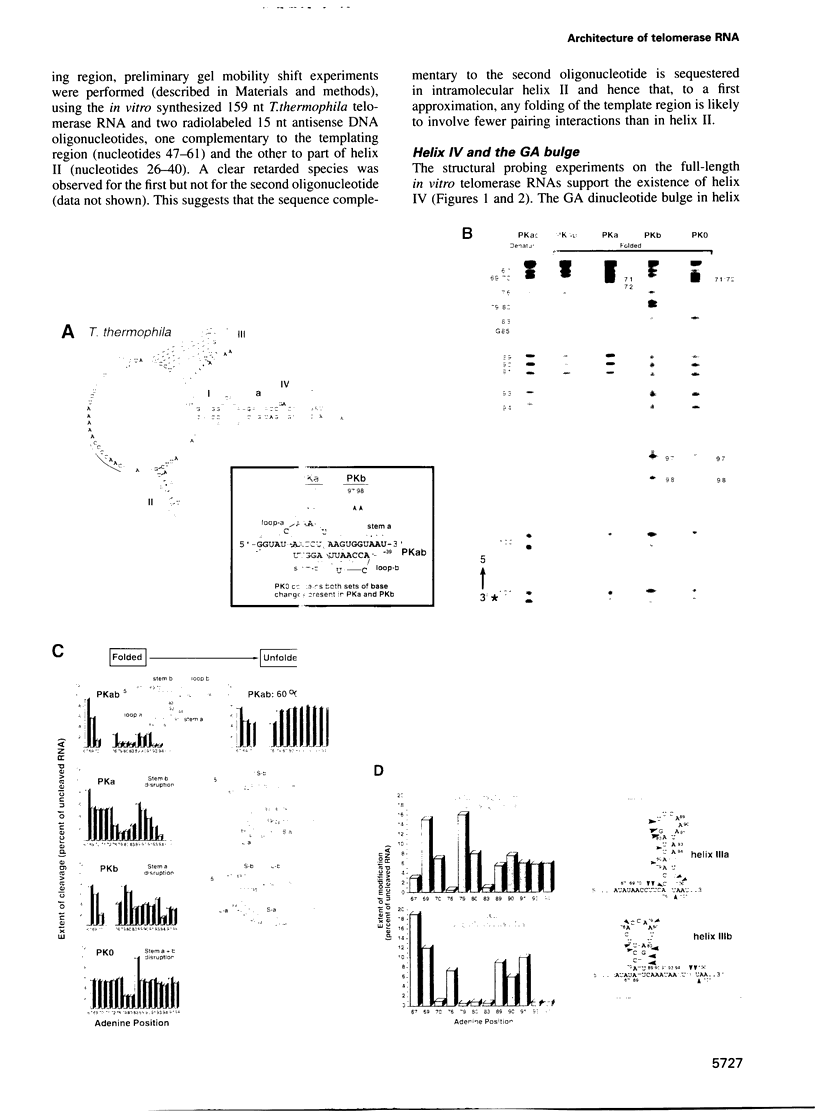
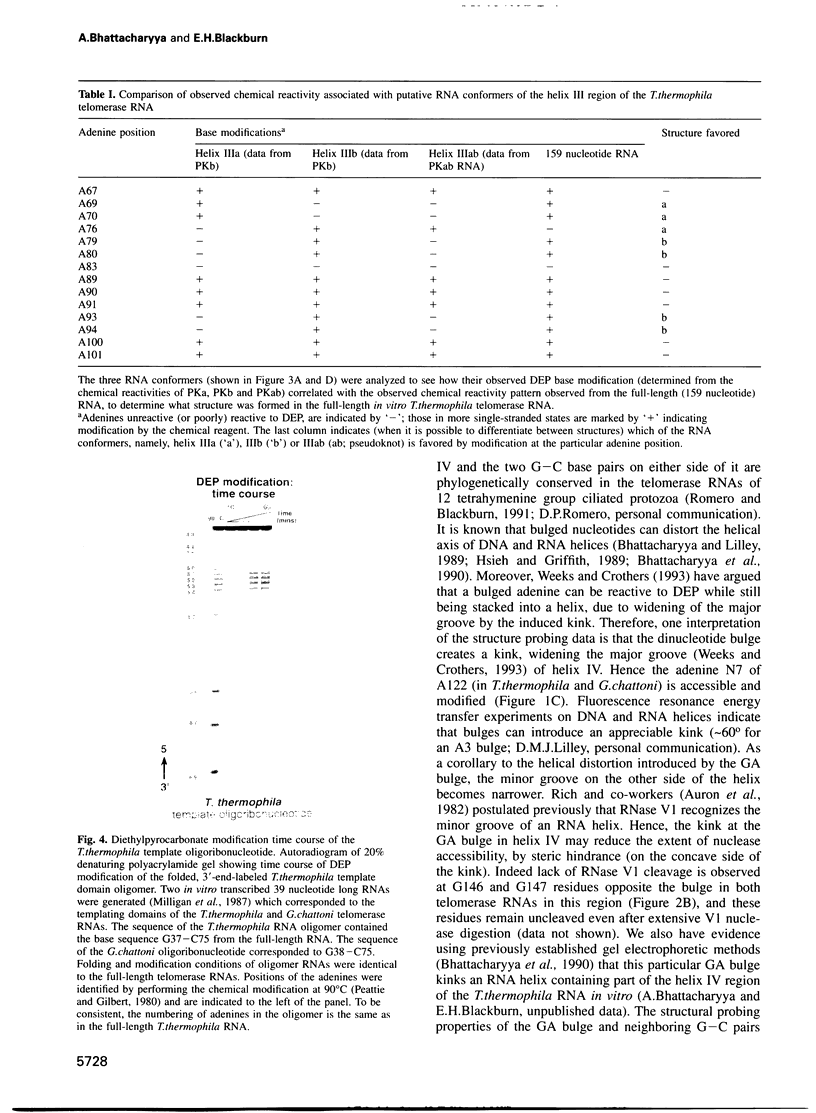
Telomerase, an essential ribonucleoprotein reverse transcriptase, adds telomeric DNA to the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. We examined the conformational properties of the naked RNA moiety of telomerase from two related ciliates, Tetrahymena thermophila and Glaucoma chattoni. As well as finding evidence for features proposed previously on the basis of phylogenetic comparisons, novel conserved structural properties were revealed. Specifically, although the region around helix III was previously proposed to form a pseudoknot, our results indicate that in the naked RNA this region maintains a level of 'plasticity', probably in an equilibrium favoring one of two helices. In addition, these studies reveal that the templating domain is not entirely single-stranded as previously proposed, but is ordered due to constraints imposed by other parts of the RNA. Finally, our results suggest that the GA bulge in helix IV may introduce a structurally conserved kink. We now propose a 'two-domain' structure for the telomerase RNA based on function: one conformationally flexible domain, which includes the template and the region around helix III, involved with enzymatic function, and a second largely helical domain, including helices I and IV and the proposed kink, which may serve as a scaffold for protein binding.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auron P. E., Weber L. D., Rich A. Comparison of transfer ribonucleic acid structures using cobra venom and S1 endonucleases. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4700–4706. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya A., Lilley D. M. The contrasting structures of mismatched DNA sequences containing looped-out bases (bulges) and multiple mismatches (bubbles). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):6821–6840. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.6821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya A., Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M. RNA bulges and the helical periodicity of double-stranded RNA. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):484–487. doi: 10.1038/343484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya A., Murchie A. I., von Kitzing E., Diekmann S., Kemper B., Lilley D. M. Model for the interaction of DNA junctions and resolving enzymes. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1191–1207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90928-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K., Greider C. W. Tetrahymena telomerase catalyzes nucleolytic cleavage and nonprocessive elongation. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1364–1376. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Avilion A. A., LeFeuvre C. E., Stewart N. G., Greider C. W., Harley C. B., Bacchetti S. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1921–1929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Hirte H. W., Bacchetti S., Harley C. B. Telomerase activity in human ovarian carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):2900–2904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.2900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A. Control of transcription termination by RNA-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:893–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.004333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann C., Baudin F., Mougel M., Romby P., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B. Probing the structure of RNAs in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9109–9128. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederick C. A., Grable J., Melia M., Samudzi C., Jen-Jacobson L., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J. M. Kinked DNA in crystalline complex with EcoRI endonuclease. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):327–331. doi: 10.1038/309327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. The telomere terminal transferase of Tetrahymena is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme with two kinds of primer specificity. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90576-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haasnoot C. A., Hilbers C. W., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Singh U. C., Pattabiraman N., Kollman P. A. On loop folding in nucleic acid hairpin-type structures. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Apr;3(5):843–857. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10508468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Dempster M., Dunlop M. G., Thompson A. M., Green D. K., Allshire R. C. Telomere reduction in human colorectal carcinoma and with ageing. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):866–868. doi: 10.1038/346866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh C. H., Griffith J. D. Deletions of bases in one strand of duplex DNA, in contrast to single-base mismatches, produce highly kinked molecules: possible relevance to the folding of single-stranded nucleic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeCuyer K. A., Crothers D. M. Kinetics of an RNA conformational switch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3373–3377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeCuyer K. A., Crothers D. M. The Leptomonas collosoma spliced leader RNA can switch between two alternate structural forms. Biochemistry. 1993 May 25;32(20):5301–5311. doi: 10.1021/bi00071a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Blackburn E. H. Sequence-specific DNA primer effects on telomerase polymerization activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6586–6599. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leviev I. G., Rodriguez-Fonseca C., Phan H., Garrett R. A., Heilek G., Noller H. F., Mankin A. S. A conserved secondary structural motif in 23S rRNA defines the site of interaction of amicetin, a universal inhibitor of peptide bond formation. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1682–1686. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowman H. B., Draper D. E. On the recognition of helical RNA by cobra venom V1 nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5396–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheeters D. S., Stormo G. D., Gold L. Autogenous regulatory site on the bacteriophage T4 gene 32 messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):517–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90634-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. Recognition of a chromosome truncation site associated with alpha-thalassaemia by human telomerase. Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):454–456. doi: 10.1038/353454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Ribosomes. Drugs and the RNA world. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):302–303. doi: 10.1038/353302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Noller H. F. A functional pseudoknot in 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2203–2214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Chen L., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Role of RNA structure in arginine recognition of TAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3680–3684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tan R., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Conformation of the TAR RNA-arginine complex by NMR spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1621097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Wyatt J. R., Tinoco I., Jr A pseudoknotted RNA oligonucleotide. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):283–286. doi: 10.1038/331283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Wyatt J. R., Tinoco I., Jr Conformation of an RNA pseudoknot. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):437–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90192-O. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan F. A., Bhattacharyya A., McAteer S., Lilley D. M. Kinking of RNA helices by bulged bases, and the structure of the human immunodeficiency virus transactivator response element. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 20;226(2):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90947-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero D. P., Blackburn E. H. A conserved secondary structure for telomerase RNA. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shippen-Lentz D., Blackburn E. H. Functional evidence for an RNA template in telomerase. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):546–552. doi: 10.1126/science.1689074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Moazed D., Noller H. F. Structural analysis of RNA using chemical and enzymatic probing monitored by primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:481–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gauss P., Thermes C., Groebe D. R., Gayle M., Guild N., Stormo G., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Uhlenbeck O. C., Tinoco I., Jr CUUCGG hairpins: extraordinarily stable RNA secondary structures associated with various biochemical processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani G., Cheong C., Tinoco I., Jr Structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3280–3289. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Crothers D. M. Major groove accessibility of RNA. Science. 1993 Sep 17;261(5128):1574–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.7690496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock J., Moazed D., Cannon M., Davies J., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with A- and P-site-specific bases in 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3099–3103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Walker G. T. Deoxynucleotide-containing oligoribonucleotide duplexes: stability and susceptibility to RNase V1 and RNase H. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7833–7842. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Blackburn E. H. Developmentally programmed healing of chromosomes by telomerase in Tetrahymena. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90077-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Bradley J. D., Attardi L. D., Blackburn E. H. In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):126–132. doi: 10.1038/344126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dam E., van Belkum A., Pleij K. A conserved pseudoknot in telomerase RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6951–6951. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]