Abstract
Tandem repeat loci such as minisatellites and trinucleotide repeats frequently show instability. We have investigated mutation at human minisatellite MS32 (locus D1S8) transferred to transgenic mice. Three lines of hemizygous transgenic mice were studied. A single-copy line (110D) was seen to be relatively stable, whilst two multicopy lines showed structural instability of the transgene in pedigrees (lines 109 and 110A). For both these lines, mutant structures were detected as a result of mutation events having occurred in the germline or early embryo. Structural changes seen included gain or loss of minisatellite repeat units (110A and 109), alteration of DNA flanking the minisatellite repeat array (109 only) or deletion of the entire transgene (109 only). This work demonstrates that tandem repeat transgenes can show instability and thus provide additional systems for the analysis of repetitive DNA structural change in mice.
Full text
PDF


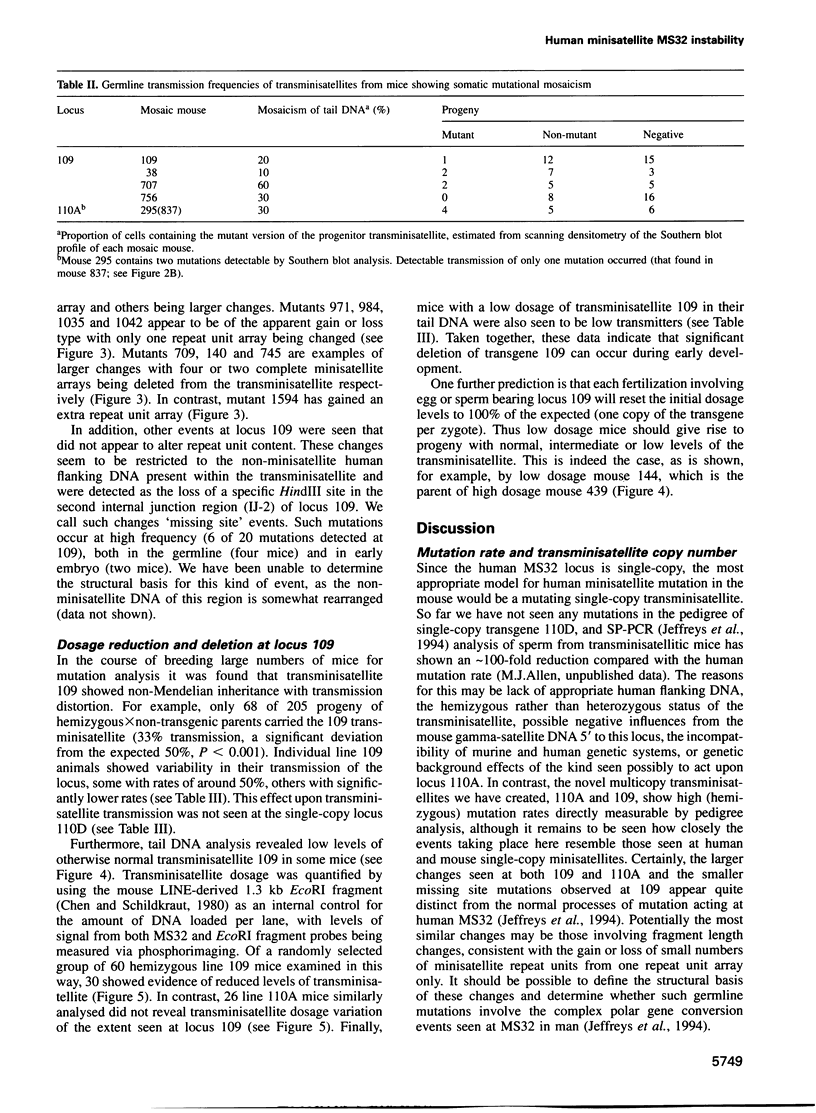

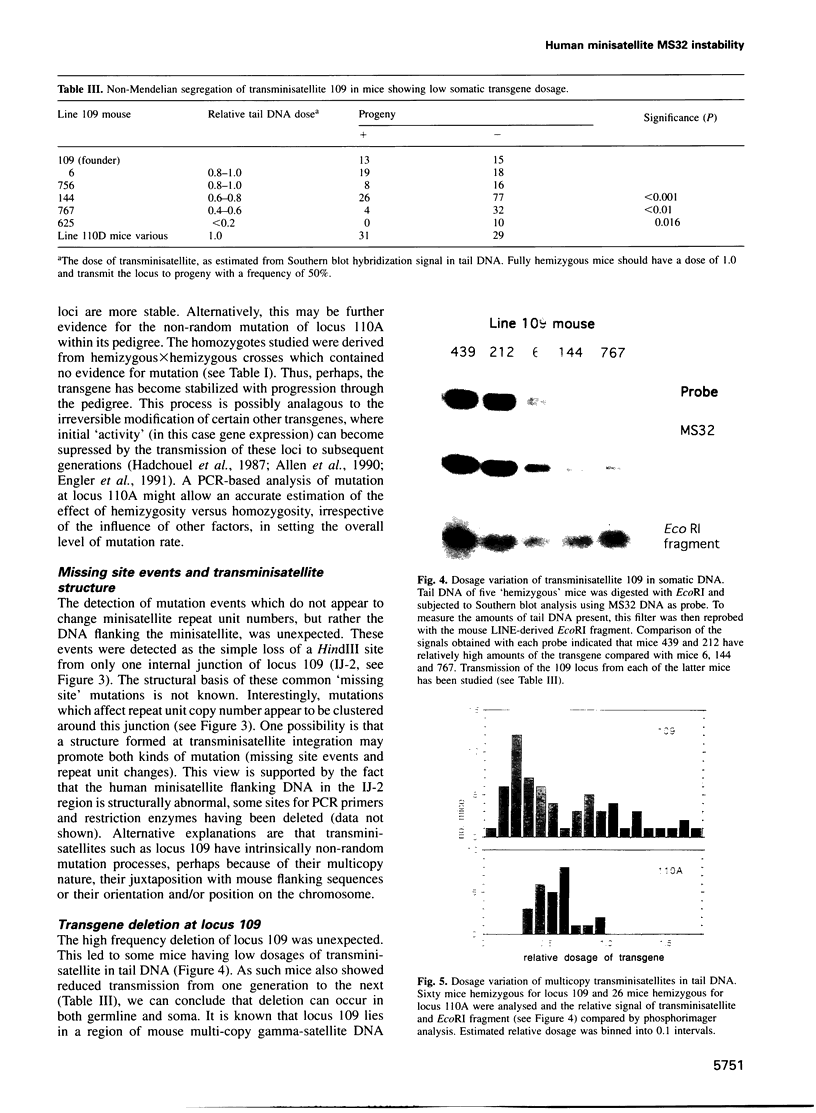


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. J., Jeffreys A. J., Surani M. A., Barton S., Norris M. L., Collick A. Tandemly repeated transgenes of the human minisatellite MS32 (D1S8), with novel mouse gamma satellite integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):2976–2981. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N. D., Norris M. L., Surani M. A. Epigenetic control of transgene expression and imprinting by genotype-specific modifiers. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):853–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90195-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour J. A., Harris P. C., Jeffreys A. J. Allelic diversity at minisatellite MS205 (D16S309): evidence for polarized variability. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1137–1145. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buard J., Vergnaud G. Complex recombination events at the hypermutable minisatellite CEB1 (D2S90). EMBO J. 1994 Jul 1;13(13):3203–3210. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butner K. A., Lo C. W. High frequency DNA rearrangements associated with mouse centromeric satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandley A. C., Mitchell A. R. Hypervariable minisatellite regions are sites for crossing-over at meiosis in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(3):152–155. doi: 10.1159/000132613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Schildkraut C. L. A family of moderately repetitive sequences in mouse DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4075–4090. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler P., Haasch D., Pinkert C. A., Doglio L., Glymour M., Brinster R., Storb U. A strain-specific modifier on mouse chromosome 4 controls the methylation of independent transgene loci. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90546-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstein R. M., Frankel W. N., Hsieh C. L., Durdik J. M., Rath S., Coffin J. M., Nisonoff A., Selsing E. Isotype switching of an immunoglobulin heavy chain transgene occurs by DNA recombination between different chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):537–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90450-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs M., Collick A., Kelly R. G., Jeffreys A. J. A tetranucleotide repeat mouse minisatellite displaying substantial somatic instability during early preimplantation development. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):121–128. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadchouel M., Farza H., Simon D., Tiollais P., Pourcel C. Maternal inhibition of hepatitis B surface antigen gene expression in transgenic mice correlates with de novo methylation. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):454–456. doi: 10.1038/329454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen G., Willems P., Coerwinkel M., Nillesen W., Smeets H., Vits L., Höweler C., Brunner H., Wieringa B. Gonosomal mosaicism in myotonic dystrophy patients: involvement of mitotic events in (CTG)n repeat variation and selection against extreme expansion in sperm. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):575–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., MacLeod A., Tamaki K., Neil D. L., Monckton D. G. Minisatellite repeat coding as a digital approach to DNA typing. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):204–209. doi: 10.1038/354204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Tamaki K., MacLeod A., Monckton D. G., Neil D. L., Armour J. A. Complex gene conversion events in germline mutation at human minisatellites. Nat Genet. 1994 Feb;6(2):136–145. doi: 10.1038/ng0294-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R., Bulfield G., Collick A., Gibbs M., Jeffreys A. J. Characterization of a highly unstable mouse minisatellite locus: evidence for somatic mutation during early development. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):844–856. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Nagawa F., Okazaki K., Kingsbury L., Yoshida K., Müller U., Larue D. T., Winer J. A., Sakano H. Detection of somatic DNA recombination in the transgenic mouse brain. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):81–86. doi: 10.1126/science.1925563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren A. Development of the mammalian gonad: the fate of the supporting cell lineage. Bioessays. 1991 Apr;13(4):151–156. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monckton D. G., Neumann R., Guram T., Fretwell N., Tamaki K., MacLeod A., Jeffreys A. J. Minisatellite mutation rate variation associated with a flanking DNA sequence polymorphism. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):162–170. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murti J. R., Bumbulis M., Schimenti J. C. High-frequency germ line gene conversion in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2545–2552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil D. L., Jeffreys A. J. Digital DNA typing at a second hypervariable locus by minisatellite variant repeat mapping. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1129–1135. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Warren S. T. Trinucleotide repeat instability: when and where? Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):107–108. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyniers E., Vits L., De Boulle K., Van Roy B., Van Velzen D., de Graaff E., Verkerk A. J., Jorens H. Z., Darby J. K., Oostra B. The full mutation in the FMR-1 gene of male fragile X patients is absent in their sperm. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):143–146. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie K. A., Brinster R. L., Storb U. Allelic exclusion and control of endogenous immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in kappa transgenic mice. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):517–520. doi: 10.1038/312517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle N. J., Clarkson R. E., Wong Z., Jeffreys A. J. Clustering of hypervariable minisatellites in the proterminal regions of human autosomes. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):352–360. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergnaud G., Mariat D., Apiou F., Aurias A., Lathrop M., Lauthier V. The use of synthetic tandem repeats to isolate new VNTR loci: cloning of a human hypermutable sequence. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90110-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Robert de Saint Vincent B., DeRose M. L. Effect of chromosomal position on amplification of transfected genes in animal cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):516–520. doi: 10.1038/307516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahls W. P., Wallace L. J., Moore P. D. Hypervariable minisatellite DNA is a hotspot for homologous recombination in human cells. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90719-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Z., Wilson V., Patel I., Povey S., Jeffreys A. J. Characterization of a panel of highly variable minisatellites cloned from human DNA. Ann Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;51(Pt 4):269–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1987.tb01062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrle D., Hennig I., Vogel W., Steinbach P. Mitotic stability of fragile X mutations in differentiated cells indicates early post-conceptional trinucleotide repeat expansion. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):140–142. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]