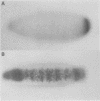
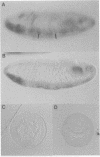
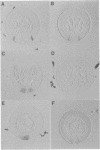
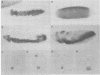
Abstract
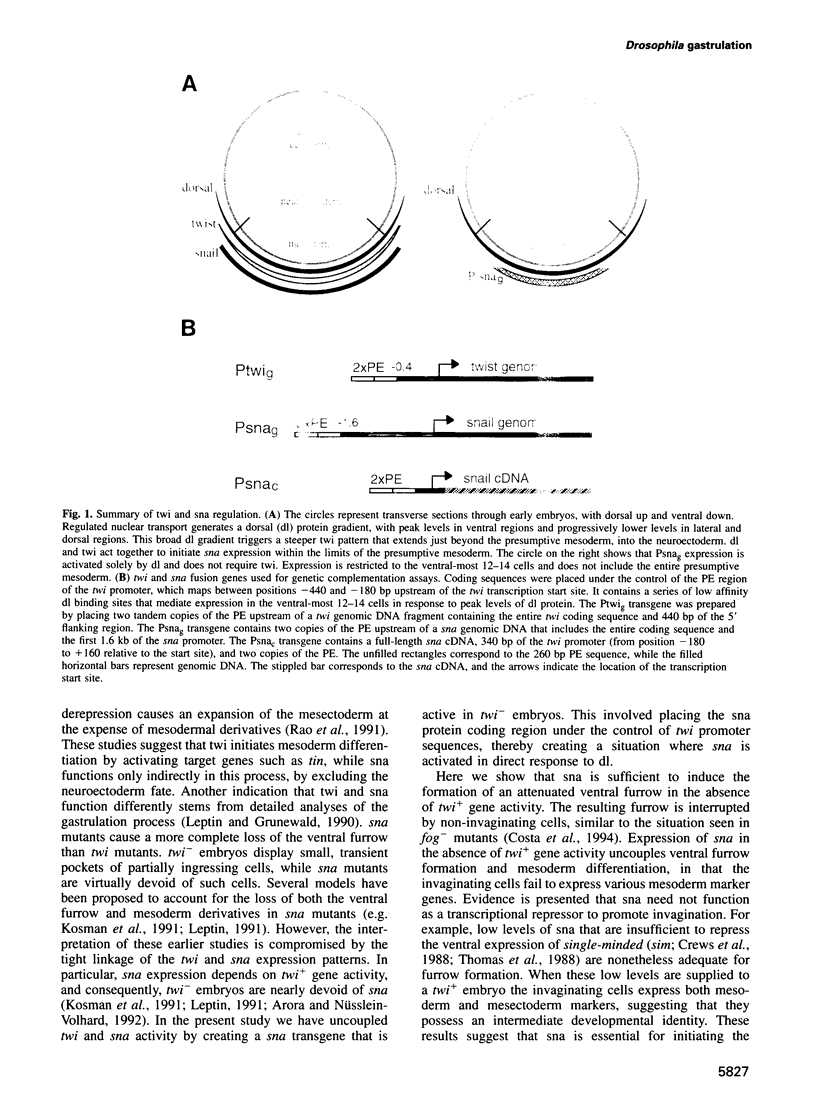
In Drosophila, ventral furrow formation and mesoderm differentiation are initiated by two regulatory genes, twist (twi) and snail (sna). Both genes are evolutionarily conserved and have also been implicated in vertebrate gastrulation. Evidence is presented that sna is sufficient to initiate the invagination of the ventral-most embryonic cells in the absence of twi+ gene activity. The invaginated cells fail to express mesoderm regulatory genes, suggesting that ventral furrow formation can be uncoupled from mesoderm differentiation. Despite the previous demonstration that sna functions as a sequence-specific transcriptional repressor, low levels of sna that fail to repress neuroectoderm determinants in the presumptive mesoderm are nonetheless able to promote invagination. Cells that possess an ambiguous developmental identity can initiate the invagination process, providing further evidence that ventral furrow formation need not be linked to mesoderm differentiation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberga A., Boulay J. L., Kempe E., Dennefeld C., Haenlin M. The snail gene required for mesoderm formation in Drosophila is expressed dynamically in derivatives of all three germ layers. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):983–992. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora K., Nüsslein-Volhard C. Altered mitotic domains reveal fate map changes in Drosophila embryos mutant for zygotic dorsoventral patterning genes. Development. 1992 Apr;114(4):1003–1024. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.4.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azpiazu N., Frasch M. tinman and bagpipe: two homeo box genes that determine cell fates in the dorsal mesoderm of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1325–1340. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier E., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. rhomboid, a gene required for dorsoventral axis establishment and peripheral nervous system development in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):190–203. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer R., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. A new homeobox-containing gene, msh-2, is transiently expressed early during mesoderm formation of Drosophila. Development. 1990 Nov;110(3):661–669. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.3.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer R. The gene tinman is required for specification of the heart and visceral muscles in Drosophila. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):719–729. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay J. L., Dennefeld C., Alberga A. The Drosophila developmental gene snail encodes a protein with nucleic acid binding fingers. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):395–398. doi: 10.1038/330395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Modolell J. Patterning of the Drosophila nervous system: the achaete-scute gene complex. Trends Genet. 1992 Jun;8(6):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90234-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Wilson E. T., Wieschaus E. A putative cell signal encoded by the folded gastrulation gene coordinates cell shape changes during Drosophila gastrulation. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S. T., Thomas J. B., Goodman C. S. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a nuclear protein with sequence similarity to the per gene product. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90538-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Lai Z. C., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila zfh-1 and zfh-2 genes encode novel proteins containing both zinc-finger and homeodomain motifs. Mech Dev. 1991 Jun;34(2-3):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90048-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler R., Bergmann A., Hiromi Y., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a gene involved in dorsoventral pattern formation of Drosophila, is related to the I kappa B gene family of vertebrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Steward R. Dorsoventral pattern formation in Drosophila: signal transduction and nuclear targeting. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S., Szymanski P., Levine M. Short-range repression permits multiple enhancers to function autonomously within a complex promoter. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1829–1838. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines J. W. A technique for embedding undecalcified bone samples for detecting alpha-emitters using vacuum impregnation with Spurr's resin. Biotech Histochem. 1992 Jan;67(1):45–49. doi: 10.3109/10520299209110005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt M., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The expression of a zebrafish gene homologous to Drosophila snail suggests a conserved function in invertebrate and vertebrate gastrulation. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1107–1118. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. D., Gurdon J. B. Gene activation in the amphibian mesoderm. Dev Suppl. 1991;1:95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Park R. E., Kosman D., Bier E., Levine M. The dorsal gradient morphogen regulates stripes of rhomboid expression in the presumptive neuroectoderm of the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1728–1739. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Park R. E., Kosman D., Yazdanbakhsh K., Levine M. dorsal-twist interactions establish snail expression in the presumptive mesoderm of the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1518–1530. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M. The dorsal morphogen gradient regulates the mesoderm determinant twist in early Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1881–1891. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Levine M. Binding affinities and cooperative interactions with bHLH activators delimit threshold responses to the dorsal gradient morphogen. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90402-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam Z., Minden J. S., Agard D. A., Sedat J. W., Leptin M. Drosophila gastrulation: analysis of cell shape changes in living embryos by three-dimensional fluorescence microscopy. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):365–370. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. Characterization of the Drosophila cactus locus and analysis of interactions between cactus and dorsal proteins. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M., Arora K. Establishment of the mesoderm-neuroectoderm boundary in the Drosophila embryo. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):118–122. doi: 10.1126/science.1925551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Fortini M. E., Rubin G. M. The embryonic expression patterns of zfh-1 and zfh-2, two Drosophila genes encoding novel zinc-finger homeodomain proteins. Mech Dev. 1991 Jun;34(2-3):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90049-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
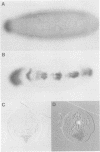
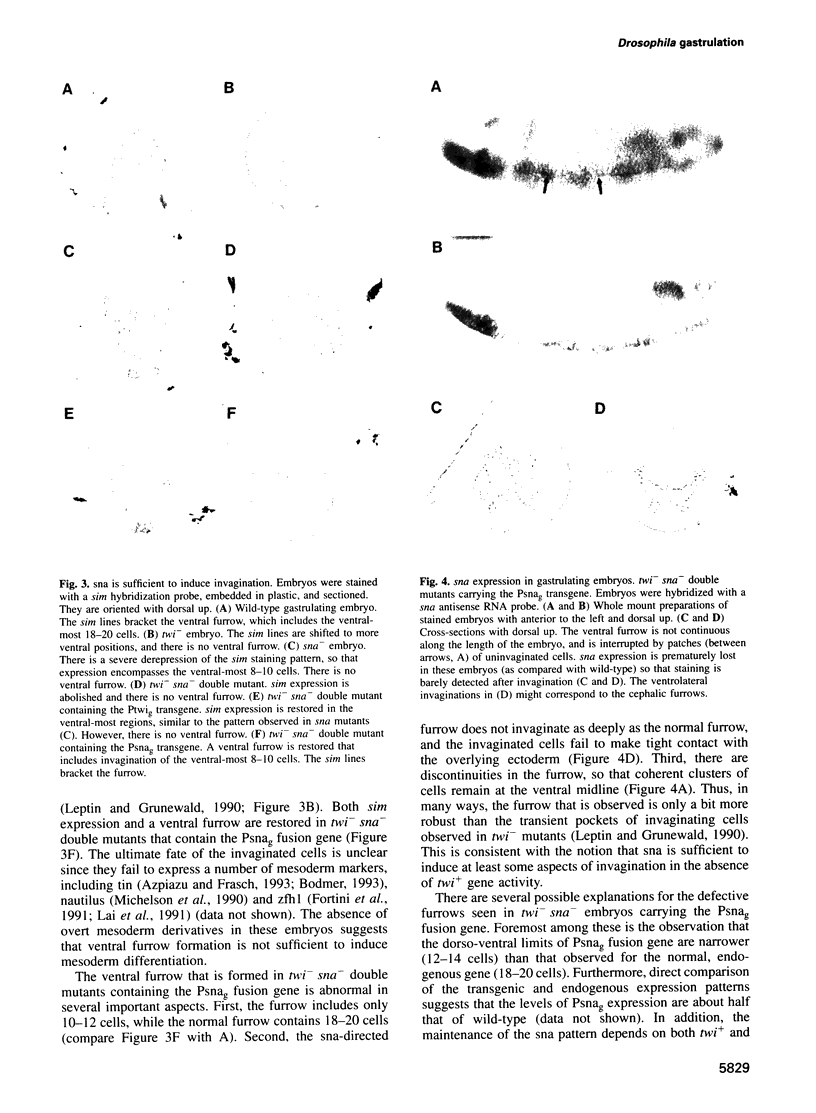
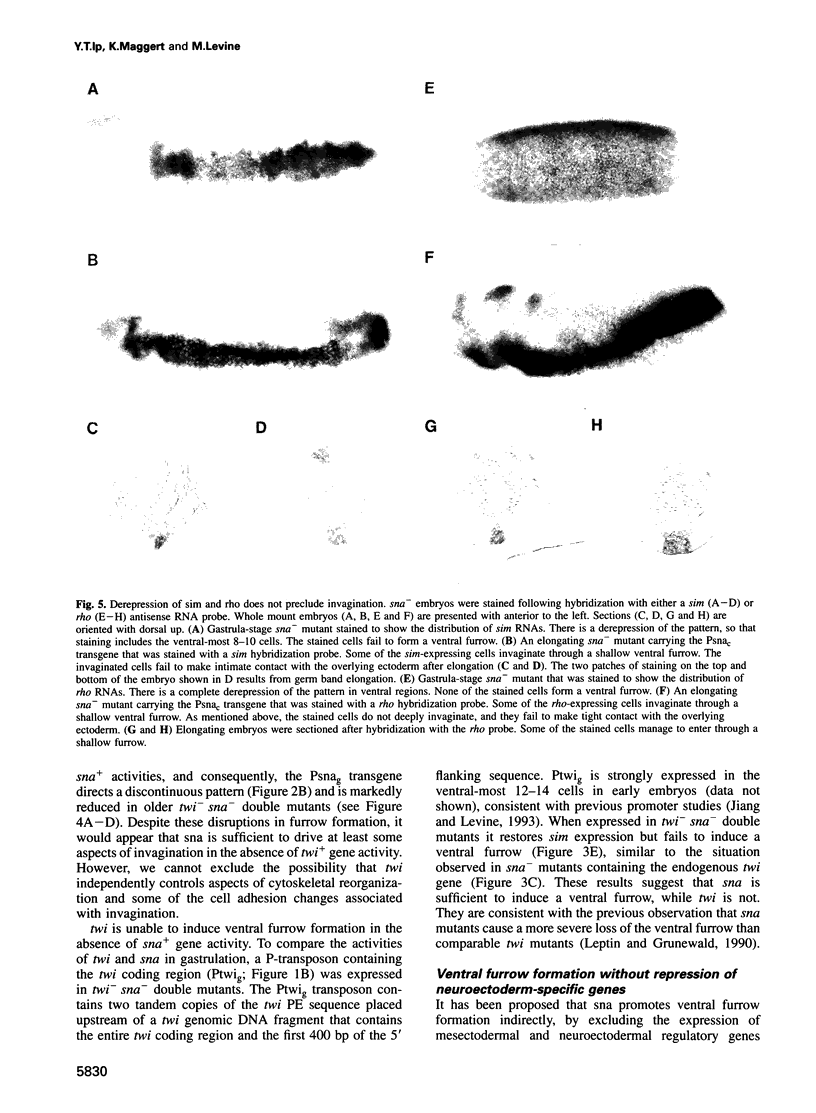
- Leptin M., Grunewald B. Cell shape changes during gastrulation in Drosophila. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):73–84. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M. twist and snail as positive and negative regulators during Drosophila mesoderm development. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1568–1576. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Baltimore D. Regulation of the NF-kappa B/rel transcription factor and I kappa B inhibitor system. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90014-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Abmayr S. M., Bate M., Arias A. M., Maniatis T. Expression of a MyoD family member prefigures muscle pattern in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2086–2097. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambu J. R., Franks R. G., Hu S., Crews S. T. The single-minded gene of Drosophila is required for the expression of genes important for the development of CNS midline cells. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90288-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto M. A., Bennett M. F., Sargent M. G., Wilkinson D. G. Cloning and developmental expression of Sna, a murine homologue of the Drosophila snail gene. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):227–237. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.1.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto M. A., Sargent M. G., Wilkinson D. G., Cooke J. Control of cell behavior during vertebrate development by Slug, a zinc finger gene. Science. 1994 May 6;264(5160):835–839. doi: 10.1126/science.7513443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. J., Huang J. D., Courey A. J. Functional analysis of the Drosophila twist promoter reveals a dorsal-binding ventral activator region. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1892–1901. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks S., Wieschaus E. The Drosophila gastrulation gene concertina encodes a G alpha-like protein. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90652-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransick A., Davidson E. H. A complete second gut induced by transplanted micromeres in the sea urchin embryo. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1134–1138. doi: 10.1126/science.8438164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransick A., Ernst S., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Whole mount in situ hybridization shows Endo 16 to be a marker for the vegetal plate territory in sea urchin embryos. Mech Dev. 1993 Aug;42(3):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90001-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao Y., Vaessin H., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Neuroectoderm in Drosophila embryos is dependent on the mesoderm for positioning but not for formation. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1577–1588. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Bennett M. F. Identification in Xenopus of a structural homologue of the Drosophila gene snail. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):967–973. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrons H., Knust E., Campos-Ortega J. A. The Enhancer of split complex and adjacent genes in the 96F region of Drosophila melanogaster are required for segregation of neural and epidermal progenitor cells. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):481–503. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Maternal-Zygotic Gene Interactions during Formation of the Dorsoventral Pattern in Drosophila Embryos. Genetics. 1983 Nov;105(3):615–632. doi: 10.1093/genetics/105.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Franco del Amo F., Gridley T. Isolation of Sna, a mouse gene homologous to the Drosophila genes snail and escargot: its expression pattern suggests multiple roles during postimplantation development. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):1033–1039. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeton D., Parks S., Costa M., Wieschaus E. Gastrulation in Drosophila: the formation of the ventral furrow and posterior midgut invaginations. Development. 1991 Jul;112(3):775–789. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.3.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F., Stoetzel C., Thisse B. Sequence-specific transactivation of the Drosophila twist gene by the dorsal gene product. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1191–1201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90014-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. B., Crews S. T., Goodman C. S. Molecular genetics of the single-minded locus: a gene involved in the development of the Drosophila nervous system. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venuti J. M., Gan L., Kozlowski M. T., Klein W. H. Developmental potential of muscle cell progenitors and the myogenic factor SUM-1 in the sea urchin embryo. Mech Dev. 1993 Apr;41(1):3–14. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A. A conserved signal transduction pathway regulating the activity of the rel-like proteins dorsal and NF-kappa B. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Aug;4(8):767–771. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.8.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley M., Noguchi P. D., Sensabaugh S. M., Odenwald W. F., Kassis J. A. The Drosophila gene escargot encodes a zinc finger motif found in snail-related genes. Mech Dev. 1992 Feb;36(3):117–127. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90063-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf C., Thisse C., Stoetzel C., Thisse B., Gerlinger P., Perrin-Schmitt F. The M-twist gene of Mus is expressed in subsets of mesodermal cells and is closely related to the Xenopus X-twi and the Drosophila twist genes. Dev Biol. 1991 Feb;143(2):363–373. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90086-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]