Abstract
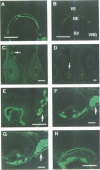
We report the molecular cloning and characterization of two secretory proteins specifically expressed in vomeronasal and posterior glands of the nasal septum, the ducts of which open into the lumen of the vomeronasal organ. These two proteins are members of the lipocalin superfamily, consisting of hydrophobic ligand carriers. We immunohistochemically localized one of the proteins in the mucus covering the vomeronasal sensory epithelium, where the primary reception of pheromone takes place. The immunoreactivity on the vomeronasal sensory epithelium was evident in the neonatal and post-pubertal periods, when the close contact between animals plays critical roles in suckling and sexual behaviors, respectively. These results suggest that small lipophilic molecules stimulate the accessory olfactory system to regulate the reproductive behavior of mice.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOJSEN-MOLLER F. TOPOGRAPHY OF THE NASAL GLANDS IN RATS AND SOME OTHER MAMMALS. Anat Rec. 1964 Sep;150:11–24. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091500103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchini A., Gaetani E., Cavaggioni A. Pheromone binding proteins of the mouse, Mus musculus. Experientia. 1992 Apr 15;48(4):419–421. doi: 10.1007/BF01923448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignetti E., Cattaneo P., Cavaggioni A., Damiani G., Tirindelli R. The pyrazine-binding protein and olfaction. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1988;90(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(88)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignetti E., Cavaggioni A., Pelosi P., Persaud K. C., Sorbi R. T., Tirindelli R. Purification and characterisation of an odorant-binding protein from cow nasal tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):227–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff R., Green M. H., Berg T., Norum K. R. Transport and storage of vitamin A. Science. 1990 Oct 19;250(4979):399–404. doi: 10.1126/science.2218545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breer H. Odor recognition and second messenger signaling in olfactory receptor neurons. Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;5(1):25–32. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr W. E., Gleeson R. A., Trapido-Rosenthal H. G. The role of perireceptor events in chemosensory processes. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):212–215. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaggioni A., Findlay J. B., Tirindelli R. Ligand binding characteristics of homologous rat and mouse urinary proteins and pyrazine-binding protein of calf. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1990;96(3):513–520. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(90)90049-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Clissold P. M., Al Shawi R., Beattie P., Bishop J. Structure of mouse major urinary protein genes: different splicing configurations in the 3'-non-coding region. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuschieri A., Bannister L. H. Some histochemical observations on the mucosubstances of the nasal glands of the mouse. Histochem J. 1974 Sep;6(5):543–558. doi: 10.1007/BF01003270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear T. N., Campbell K., Rabbitts T. H. Molecular cloning of putative odorant-binding and odorant-metabolizing proteins. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10376–10382. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Simon-Chazottes D., Fujino I., Yamada N., Hasegawa M., Miyawaki A., Yoshikawa S., Guénet J. L., Mikoshiba K. Widespread expression of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 1 gene (Insp3r1) in the mouse central nervous system. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(1):11–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getchell T. V., Margolis F. L., Getchell M. L. Perireceptor and receptor events in vertebrate olfaction. Prog Neurobiol. 1984;23(4):317–345. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(84)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann J. The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. The organization and function of the vomeronasal system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:325–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemiolo B., Harvey S., Novotny M. Promotion of the Whitten effect in female mice by synthetic analogs of male urinary constituents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen A. B., Kuijpers W., Denucé J. M. Morphological and histochemical aspects of the nasal glands in the rat. Anat Anz. 1981;149(1):51–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Wells R. G., Reed R. R. Isolation of an olfactory cDNA: similarity to retinol-binding protein suggests a role in olfaction. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1053–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.3493528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyawaki A., Furuichi T., Ryou Y., Yoshikawa S., Nakagawa T., Saitoh T., Mikoshiba K. Structure-function relationships of the mouse inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4911–4915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco H. L., Zanotti G. Three-dimensional structure and active site of three hydrophobic molecule-binding proteins with significant amino acid sequence similarity. Biopolymers. 1992 Apr;32(4):457–465. doi: 10.1002/bip.360320425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny M., Jemiolo B., Harvey S., Wiesler D., Marchlewska-Koj A. Adrenal-mediated endogenous metabolites inhibit puberty in female mice. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):722–725. doi: 10.1126/science.3945805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Hwang P. M., Sklar P. B., Venable J. C., Snyder S. H. Odorant-binding protein and its mRNA are localized to lateral nasal gland implying a carrier function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2383–2387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Reed R. R., Feinstein P. G., Snyder S. H. Molecular cloning of odorant-binding protein: member of a ligand carrier family. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):336–339. doi: 10.1126/science.3388043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Trifiletti R. R., Strittmatter S. M., Snyder S. H. Isolation and characterization of an olfactory receptor protein for odorant pyrazines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redl B., Holzfeind P., Lottspeich F. cDNA cloning and sequencing reveals human tear prealbumin to be a member of the lipophilic-ligand carrier protein superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20282–20287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Holtgreve-Grez H., Christiansen H. Possible role for salivary gland protein in taste reception indicated by homology to lipophilic-ligand carrier proteins. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):366–369. doi: 10.1038/343366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki C. J., Wellington J. L., Beauchamp G. K. Access of urinary nonvolatiles to the mammalian vomeronasal organ. Science. 1980 Feb 15;207(4432):781–783. doi: 10.1126/science.7352288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]