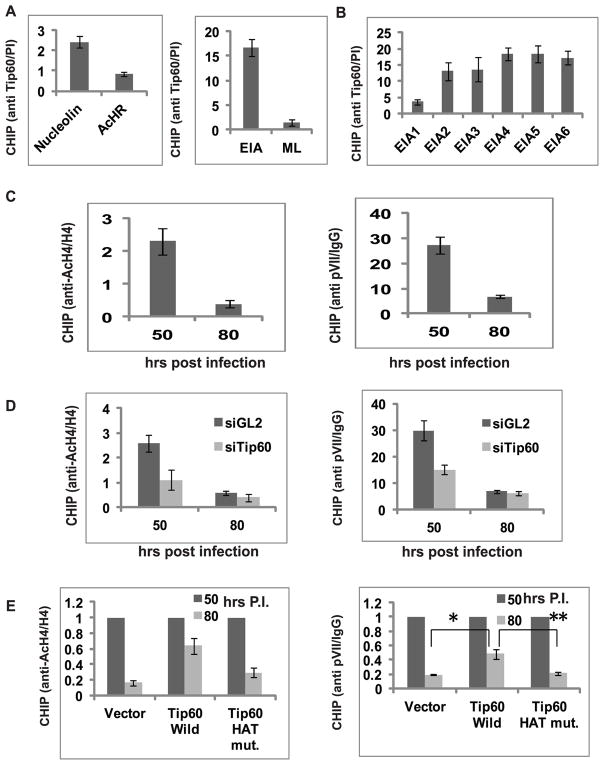
Figure 4. Tip60 binds to EIA promoter, acetylates histone H4.
(A) Tip60 binds to EIA promoter. ChIP assay was performed in MCF10A cells 72 hours after infection with dl309 strain. Ratio of qPCR signal in Tip60 immunoprecipitate relative to that in pre-immune serum immunoprecipitate shows occupancy of Tip60 on EIA promoter. ML- major late promoter. Nucleolin and AcHR were taken as positive and negative control cellular promoters for Tip60 binding. Mean ± SD (n=3).
(B) Primers covering 6 regions of the (Supp Fig. S3) EIA promoter were used in the ChIP assay for Tip60 as in (A). Tip60 binds more near the start site of the EIA transcript. Mean ± SD, n=3.
(C) Acetylated histone H4 and pVII at the EIA promoter decreases after Tip60 degradation at 62 hr post infection. ChIP analysis at EIA promoter at 50 hr and 80 hrs after infection. The rest is as in (A). Mean ± SD, n=3.
(D) Tip60 knockdown accelerates the decrease of H4 acetylation and pVII occupancy at the EIA promoter. ChIP assay was performed in dl309-infected MCF10A cells transfected with control siGL2 or siTip60. Level of acetylated H4 and pVII determined by ChIP assay 50 and 80 hrs after infection. mean ± SD, n=3.
(E) Tip60 HAT activity stimulates H4 acetylation and pVII occupancy at EIA promoter. Relative Q-PCR signal ratio at 80 hrs post infection (50 hrs ratio=1) in cells stably transfected with empty vector or plasmids expressing Tip60 wild type or HAT mutant. ChIP for acetylated H4 and pVII. Mean ± SD, n=3. (*P<0.005and **P<0.005 by Student’s t test).