Abstract
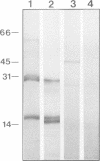
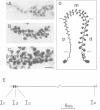
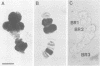
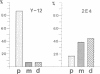
Transcriptionally active Balbiani ring (BR) genes in the salivary glands of the dipteran Chironomus tentans were studied by immunoelectron microscopy to establish the distribution of spliceosome components along a specific pre-messenger ribonucleoprotein (pre-mRNP) fiber. The BR genes are 35-40 kb in size with three introns close to the 5' end and one close to the 3' end; a very large middle portion lacks introns. As a rule the 5' introns are spliced concomitant with transcription in the promoter proximal third of the gene, while the 3' intron is spliced post-transcriptionally. The BR genes with growing pre-mRNPs were visualized in situ, while completed and released pre-mRNPs were isolated from the nucleoplasm and studied unfolded on a grid surface. An anti-snRNP antibody (Y12) bound mainly to the promoter proximal third of the BR gene (86%) and only to a minor extent to the middle and distal thirds (7 and 7% respectively). An antibody to an hnRNP protein reacted with the proximal, middle and distal regions to an increasing extent (17, 38 and 45% respectively), reflecting the increase in size of the growing transcription product. In the nucleoplasmic pre-mRNP particle only one end of the RNP fiber was labeled by Y 12, presumably the 3' end; the anti-hnRNP antibody decorated the entire RNP fiber. Thus, the snRNPs do not associate along the whole pre-mRNP fiber but rather bind to the 5' and 3' ends, i.e. the regions containing the introns. The results also imply that the spliceosomes both assemble and disassemble rapidly on the pre-mRNP fiber.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amero S. A., Raychaudhuri G., Cass C. L., van Venrooij W. J., Habets W. J., Krainer A. R., Beyer A. L. Independent deposition of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins and small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles at sites of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8409–8413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baurén G., Wieslander L. Splicing of Balbiani ring 1 gene pre-mRNA occurs simultaneously with transcription. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Michaud S., Kingston J., Reed R. Protein components specifically associated with prespliceosome and spliceosome complexes. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1986–2000. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):754–765. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneholt B. The transcribed template and the transcription loop in Balbiani rings. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1992 Aug;16(8):709–715. doi: 10.1016/s0309-1651(05)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deimel B., Louis C. H., Sekeris C. E. The presence of small molecular weight RNAs in nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles carrying HnRNA. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):80–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egyházi E. Inhibition of Balbiani ring RNA synthesis at the initiation level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):947–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Immunoelectron microscope visualization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigens within spread transcription complexes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Ultrastructural distribution of nuclear ribonucleoproteins as visualized by immunocytochemistry on thin sections. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):358–363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Puvion E. The ultrastructural visualization of nucleolar and extranucleolar RNA synthesis and distribution. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;65:255–299. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61962-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Callan H. G. The sphere organelle contains small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6635–6639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G. Spliceosomes and snurposomes. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1499–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1828621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. F. Small nuclear RNA molecules in nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes from mouse erythroleukemia cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3228–3236. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Spector D. L. Will the real splicing sites please light up? Curr Biol. 1992 Apr;2(4):188–190. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90516-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb M. M., Daneholt B. Characterization of active transcription units in Balbiani rings of Chironomus tentans. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):835–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I. A glimpse into the spliceosome. Curr Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):62–64. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90154-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lezzi M., Meyer B., Mähr R. Heat shock phenomena in Chironomus tentans I. In vivo effects of heat, overheat, and quenching on salivary chromosome puffing. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):327–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00327356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth A., Alexciev K., Mehlin H., Wurtz T., Skoglund U., Daneholt B. Demonstration of a 7-nm RNP fiber as the basic structural element in a premessenger RNP particle. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Apr;199(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90437-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lührmann R., Kastner B., Bach M. Structure of spliceosomal snRNPs and their role in pre-mRNA splicing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 30;1087(3):265–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90001-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Tollervey D., Séraphin B. Small nuclear RNAs in messenger RNA and ribosomal RNA processing. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):47–53. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matunis E. L., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Association of individual hnRNP proteins and snRNPs with nascent transcripts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(2):219–228. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Krainer A. R. Regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing by hnRNP A1 and splicing factor SF2. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90477-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mähr R., Meyer B., Daneholt B., Eppenberger H. M. Activation of Balbiani ring genes in Chironomus tentans after a pilocarpine-induced depletion of the secretory products from the salivary gland lumen. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheim Y. N., Miller O. L., Jr, Beyer A. L. RNP particles at splice junction sequences on Drosophila chorion transcripts. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Beggs J. D., Finnegan D. J., Lührmann R. Polypeptide components of Drosophila small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5877–5882. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Mimori T., Gottlieb E., Steitz J. A. The structure of mammalian small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Identification of multiple protein components reactive with anti-(U1)ribonucleoprotein and anti-Sm autoantibodies. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5907–5914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvion-Dutilleul F. Morphology of transcription at cellular and molecular levels. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;84:57–101. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvion E., Viron A., Assens C., Leduc E. H., Jeanteur P. Immunocytochemical identification of nuclear structures containing snRNPs in isolated rat liver cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 May;87(2):180–189. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. Protein composition of mammalian spliceosomes assembled in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8031–8035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass H., Pederson T. Transcription-dependent localization of U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins at major sites of gene activity in polytene chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):911–926. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund U., Andersson K., Björkroth B., Lamb M. M., Daneholt B. Visualization of the formation and transport of a specific hnRNP particle. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90542-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund U., Andersson K., Strandberg B., Daneholt B. Three-dimensional structure of a specific pre-messenger RNP particle established by electron microscope tomography. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):560–564. doi: 10.1038/319560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Associations between distinct pre-mRNA splicing components and the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3467–3481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Splicing takes a holliday. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):888–889. doi: 10.1126/science.1386941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Immunochemistry on ultrathin frozen sections. Histochem J. 1980 Jul;12(4):381–403. doi: 10.1007/BF01011956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. Interactions of small nuclear RNA's with precursor messenger RNA during in vitro splicing. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1918–1925. doi: 10.1126/science.1411506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. The Balbiani ring multigene family: coding repetitive sequences and evolution of a tissue-specific cell function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1994;48:275–313. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60858-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtz T., Lönnroth A., Ovchinnikov L., Skoglund U., Daneholt B. Isolation and initial characterization of a specific premessenger ribonucleoprotein particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):831–835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Sauterer R. A. Cell biology of the snRNP particles. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]