Abstract
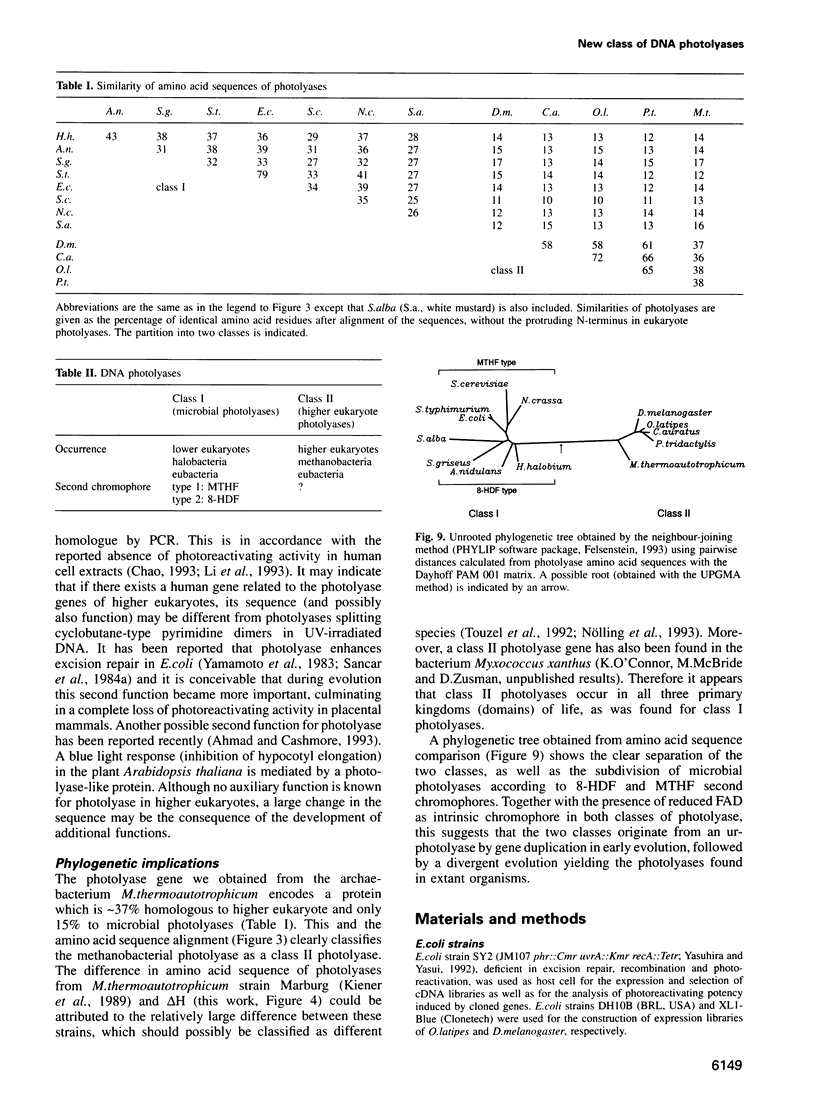
DNA photolyase specifically repairs UV light-induced cyclobutane-type pyrimidine dimers in DNA through a light-dependent reaction mechanism. We have obtained photolyase genes from Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly), Oryzias latipes (killifish) and the marsupial Potorous tridactylis (rat kangaroo), the first photolyase gene cloned from a mammalian species. The deduced amino acid sequences of these higher eukaryote genes show only limited homology with microbial photolyase genes. Together with the previously cloned Carassius auratus (goldfish) gene they form a separate group of photolyase genes. A new classification for photolyases comprising two distantly related groups is proposed. For functional analysis P.tridactylis photolyase was expressed and purified as glutathione S-transferase fusion protein from Escherichia coli cells. The biologically active protein contained FAD as light-absorbing cofactor, a property in common with the microbial class photolyases. Furthermore, we found in the archaebacterium Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum a gene similar to the higher eukaryote photolyase genes, but we could not obtain evidence for the presence of a homologous gene in the human genome. Our results suggest a divergence of photolyase genes in early evolution.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad M., Cashmore A. R. HY4 gene of A. thaliana encodes a protein with characteristics of a blue-light photoreceptor. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):162–166. doi: 10.1038/366162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batschauer A. A plant gene for photolyase: an enzyme catalyzing the repair of UV-light-induced DNA damage. Plant J. 1993 Oct;4(4):705–709. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04040705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl S. N., Setlow R. B., Regan J. D. DNA repair in Potorous tridactylus. Biophys J. 1974 Oct;14(10):791–803. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85949-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. S., Regan J. D. Photoreactivation and photoreactivating enzyme activity in an order of mammals (Marsupialia). Nature. 1969 Sep 6;223(5210):1066–1067. doi: 10.1038/2231066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eker A. P., Dekker R. H., Berends W. Photoreactivating enzyme from Streptomyces griseus-IV. On the nature of the chromophoric cofactor in Streptomyces griseus photoreactivating enzyme. Photochem Photobiol. 1981 Jan;33(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1981.tb04298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eker A. P., Hessels J. K., Meerwaldt R. Characterization of an 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin:NADPH oxidoreductase from Streptomyces griseus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 27;990(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(89)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eker A. P., Kooiman P., Hessels J. K., Yasui A. DNA photoreactivating enzyme from the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8009–8015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eker A. P., Yajima H., Yasui A. DNA photolyase from the fungus Neurospora crassa. Purification, characterization and comparison with other photolyases. Photochem Photobiol. 1994 Aug;60(2):125–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1994.tb05078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ina Y. ODEN: a program package for molecular evolutionary analysis and database search of DNA and amino acid sequences. Comput Appl Biosci. 1994 Feb;10(1):11–12. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki K., Takebe H. Comparative studies on photoreactivation of ultraviolet light-induced T4 endonuclease susceptible sites and sister-chromatid exchanges in Potorous cells. Mutat Res. 1985 Jun-Jul;150(1-2):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Hamm-Alvarez S., Payne G., Sancar G. B., Rajagopalan K. V., Sancar A. Identification of the second chromophore of Escherichia coli and yeast DNA photolyases as 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener A., Husain I., Sancar A., Walsh C. Purification and properties of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum DNA photolyase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13880–13887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Takao M., Oikawa A., Yasui A. Molecular characterization of a gene encoding a photolyase from Streptomyces griseus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4731–4744. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. F., Heelis P. F., Sancar A. Active site of DNA photolyase: tryptophan-306 is the intrinsic hydrogen atom donor essential for flavin radical photoreduction and DNA repair in vitro. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 25;30(25):6322–6329. doi: 10.1021/bi00239a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. F., Kim S. T., Sancar A. Evidence for lack of DNA photoreactivating enzyme in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. F., Sancar A. Active site of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase: mutations at Trp277 alter the selectivity of the enzyme without affecting the quantum yield of photorepair. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5698–5706. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. F., Sancar A. Cloning, sequencing, expression and characterization of DNA photolyase from Salmonella typhimurium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4885–4890. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki K., Tamada T., Nishida H., Inaka K., Yasui A., de Ruiter P. E., Eker A. P. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of photolyase (photoreactivating enzyme) from the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):167–169. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G., Wills M., Walsh C., Sancar A. Reconstitution of Escherichia coli photolyase with flavins and flavin analogues. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5706–5711. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabourin C. L., Ley R. D. Isolation and characterization of a marsupial DNA photolyase. Photochem Photobiol. 1988 May;47(5):719–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1988.tb02770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Franklin K. A., Sancar G. B. Escherichia coli DNA photolyase stimulates uvrABC excision nuclease in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7397–7401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B. DNA photolyases: physical properties, action mechanism, and roles in dark repair. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):147–160. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90002-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B. Sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae PHR1 gene and homology of the PHR1 photolyase to E. coli photolyase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8231–8246. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Heelis P. F. Purification of the yeast PHR1 photolyase from an Escherichia coli overproducing strain and characterization of the intrinsic chromophores of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15457–15465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W., Lorence M. C., Rupert C. S., Sancar A. Sequences of the Escherichia coli photolyase gene and protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):6033–6038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao M., Kobayashi T., Oikawa A., Yasui A. Tandem arrangement of photolyase and superoxide dismutase genes in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6323–6329. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6323-6329.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao M., Oikawa A., Eker A. P., Yasui A. Expression of an Anacystis nidulans photolyase gene in Escherichia coli; functional complementation and modified action spectrum of photoreactivation. Photochem Photobiol. 1989 Nov;50(5):633–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1989.tb04319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touzel J. P., Conway de Macario E., Nölling J., De Vos W. M., Zhilina T., Lysenko A. M. DNA relatedness among some thermophilic members of the genus Methanobacterium: emendation of the species Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum and rejection of Methanobacterium thermoformicicum as a synonym of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):408–411. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALEN K. H., BROWN S. W. Chromosomes in a marsupial (Potorous tridactylis) tissue culture. Nature. 1962 Apr 28;194:406–406. doi: 10.1038/194406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Jorns M. S. Reconstitution of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase with various folate derivatives. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1148–1152. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Satake M., Shinagawa H., Fujiwara Y. Amelioration of the ultraviolet sensitivity of an Escherichia coli recA mutant in the dark by photoreactivating enzyme. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(3):511–515. doi: 10.1007/BF00331084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuhira S., Yasui A. Visible light-inducible photolyase gene from the goldfish Carassius auratus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25644–25647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui A., Langeveld S. A. Homology between the photoreactivation genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;36(3):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui A., Takao M., Oikawa A., Kiener A., Walsh C. T., Eker A. P. Cloning and characterization of a photolyase gene from the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4447–4463. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui A., Yajima H., Kobayashi T., Eker A. P., Oikawa A. Mitochondrial DNA repair by photolyase. Mutat Res. 1992 Mar;273(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(92)90084-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gruijl F. R., Roza L. Photoreactivation in humans. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1991 Sep;10(4):367–371. doi: 10.1016/1011-1344(91)80022-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]