Abstract
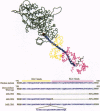
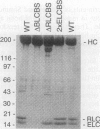
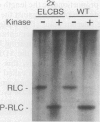
The myosin head consists of a globular catalytic domain that binds actin and hydrolyzes ATP and a neck domain that consists of essential and regulatory light chains bound to a long alpha-helical portion of the heavy chain. The swinging neck-level model assumes that a swinging motion of the neck relative to the catalytic domain is the origin of movement. This model predicts that the step size, and consequently the sliding velocity, are linearly related to the length of the neck. We have tested this point by characterizing a series of mutant Dictyostelium myosins that have different neck lengths. The 2xELCBS mutant has an extra binding site for essential light chain. The delta RLCBS mutant myosin has an internal deletion that removes the regulatory light chain binding site. The delta BLCBS mutant lacks both light chain binding sites. Wild-type myosin and these mutant myosins were subjected to the sliding filament in vitro motility assay. As expected, mutants with shorter necks move slower than wild-type myosin in vitro. Most significantly, a mutant with a longer neck moves faster than the wild type, and the sliding velocities of these myosins are linearly related to the neck length, as predicted by the swinging neck-lever model. A simple extrapolation to zero speed predicts that the fulcrum point is in the vicinity of the SH1-SH2 region in the catalytic domain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M., Reisler E. Effect of nucleotide binding on the proximity of the essential sulfhydryl groups of myosin. Chemical probing of movement of residues during conformational transitions. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5559–5563. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Crowder M. S., Wendt C. H., Barnett V. A., Thomas D. D. Muscle cross-bridges: do they rotate? Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;170:413–427. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4703-3_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Manstein D. J., Spudich J. A. Complementation of myosin null mutants in Dictyostelium discoideum by direct functional selection. Dev Biol. 1990 Feb;137(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90260-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Titus M. A., Manstein D. J., Ruppel K. M., Spudich J. A. Molecular genetic tools for study of the cytoskeleton in Dictyostelium. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:319–334. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96029-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer J. T., Mehta A. D., Spudich J. A. Characterization of single actin-myosin interactions. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):291S–297S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer J. T., Simmons R. M., Spudich J. A. Single myosin molecule mechanics: piconewton forces and nanometre steps. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):113–119. doi: 10.1038/368113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittes F., Mickey B., Nettleton J., Howard J. Flexural rigidity of microtubules and actin filaments measured from thermal fluctuations in shape. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(4):923–934. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Yang Y. Z., Korn E. D. Polymerization of Acanthamoeba actin. Kinetics, thermodynamics, and co-polymerization with muscle actin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7474–7479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Flexibility of DNA. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:265–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada Y., Sakurada K., Aoki T., Thomas D. D., Yanagida T. Mechanochemical coupling in actomyosin energy transduction studied by in vitro movement assay. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 5;216(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith S., Eden D. Myosin-ATP chemomechanics. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 16;32(10):2455–2458. doi: 10.1021/bi00061a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Yanagida T., Goldman Y. E. Compliance of thin filaments in skinned fibers of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):1000–1010. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79975-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdusse A., Cohen C. Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2 A resolution: implications for regulation. Structure. 1996 Jan 15;4(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J., Ashmore J. F. Stiffness of sensory hair bundles in the sacculus of the frog. Hear Res. 1986;23(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(86)90178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., St Claire Allen T., Sabido-David C., Craik J. S., Brandmeier B., Kendrick-Jones J., Corrie J. E., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Tilting of the light-chain region of myosin during step length changes and active force generation in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):688–691. doi: 10.1038/375688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishijima A., Harada Y., Kojima H., Funatsu T., Higuchi H., Yanagida T. Single-molecule analysis of the actomyosin motor using nano-manipulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):1057–1063. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itakura S., Yamakawa H., Toyoshima Y. Y., Ishijima A., Kojima T., Harada Y., Yanagida T., Wakabayashi T., Sutoh K. Force-generating domain of myosin motor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 15;196(3):1504–1510. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jontes J. D., Wilson-Kubalek E. M., Milligan R. A. A 32 degree tail swing in brush border myosin I on ADP release. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):751–753. doi: 10.1038/378751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishino A., Yanagida T. Force measurements by micromanipulation of a single actin filament by glass needles. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):74–76. doi: 10.1038/334074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Fluorescent actin filaments move on myosin fixed to a glass surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6272–6276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Toyoshima Y. Y., Uyeda T. Q., Spudich J. A. Assays for actin sliding movement over myosin-coated surfaces. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:399–416. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96035-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Waller G. S., Trybus K. M. Skeletal muscle myosin light chains are essential for physiological speeds of shortening. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):454–456. doi: 10.1038/365454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maita T., Yajima E., Nagata S., Miyanishi T., Nakayama S., Matsuda G. The primary structure of skeletal muscle myosin heavy chain: IV. Sequence of the rod, and the complete 1,938-residue sequence of the heavy chain. J Biochem. 1991 Jul;110(1):75–87. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Lowey S. Preparation of myosin and its subfragments from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata H., Hakozaki H., Yoshikawa H., Suzuki N., Kinosita K., Jr, Nishizaka T., Ishiwata S. Stepwise motion of an actin filament over a small number of heavy meromyosin molecules is revealed in an in vitro motility assay. J Biochem. 1994 Apr;115(4):644–647. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy J. E., Burns J. E., Kendrick-Jones J., Tregear R. T., White D. C. Movement and force produced by a single myosin head. Nature. 1995 Nov 9;378(6553):209–212. doi: 10.1038/378209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Perry S. V. An electrophoretic study of the low-molecular-weight components of myosin. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):31–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1190031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. S., Taylor E. W. Reactions of 1-N6-ethenoadenosine nucleotides with myosin subfragment 1 and acto-subfragment 1 of skeletal and smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11920–11929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppel K. M., Uyeda T. Q., Spudich J. A. Role of highly conserved lysine 130 of myosin motor domain. In vivo and in vitro characterization of site specifically mutated myosin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):18773–18780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. How molecular motors work. Nature. 1994 Dec 8;372(6506):515–518. doi: 10.1038/372515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L. A., Schwarz R. P., Jr, Chock P. B., Eisenberg E. Mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Evidence that adenosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis can occur without dissociation of the actomyosin complex. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3895–3909. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. Cultivation and synchronous morphogenesis of Dictyostelium under controlled experimental conditions. Methods Cell Biol. 1987;28:9–29. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. L., Ravid S., Spudich J. A. Control of nonmuscle myosins by phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:721–759. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga M., Sutoh K., Wakabayashi T. Structure and structural change of the myosin head. Adv Biophys. 1991;27:157–167. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(91)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima Y. Y., Kron S. J., McNally E. M., Niebling K. R., Toyoshima C., Spudich J. A. Myosin subfragment-1 is sufficient to move actin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):536–539. doi: 10.1038/328536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Myosin step size. Estimation from slow sliding movement of actin over low densities of heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):699–710. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90287-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Spudich J. A. A functional recombinant myosin II lacking a regulatory light chain-binding site. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1867–1870. doi: 10.1126/science.8266074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibert P., Cohen C. Domains, motions and regulation in the myosin head. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Aug;9(4):296–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01773873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi K., Tokunaga M., Kohno I., Sugimoto Y., Hamanaka T., Takezawa Y., Wakabayashi T., Amemiya Y. Small-angle synchrotron x-ray scattering reveals distinct shape changes of the myosin head during hydrolysis of ATP. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):443–447. doi: 10.1126/science.1411537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller G. S., Ouyang G., Swafford J., Vibert P., Lowey S. A minimal motor domain from chicken skeletal muscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 23;270(25):15348–15352. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.25.15348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., De Lozanne A., Leinwand L. A., Spudich J. A. Conserved protein domains in a myosin heavy chain gene from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9433–9437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Active site trapping of nucleotides by crosslinking two sulfhydryls in myosin subfragment 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4966–4970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker M., Wilson-Kubalek E. M., Smith J. E., Faust L., Milligan R. A., Sweeney H. L. A 35-A movement of smooth muscle myosin on ADP release. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):748–751. doi: 10.1038/378748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X., Harrison D. H., Schlichting I., Sweet R. M., Kalabokis V. N., Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C. Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):306–312. doi: 10.1038/368306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]