Figure 2.
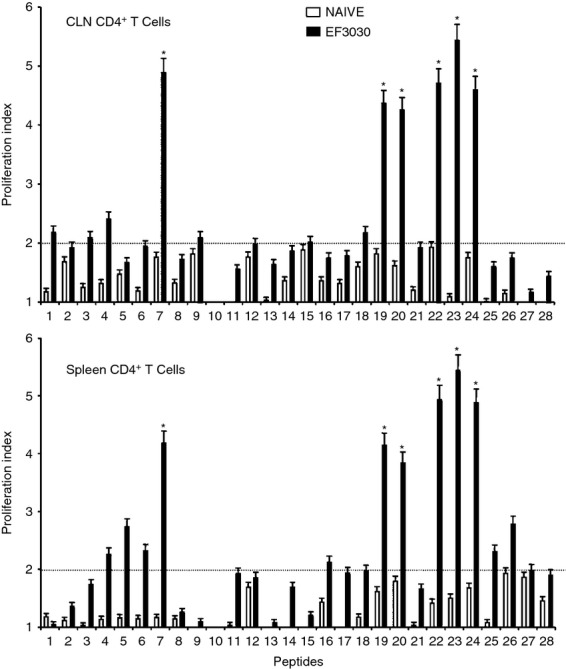
Proliferation responses of pneumococcal surface adhesin A (PsaA) peptide-specific systemic and mucosal CD4+ T cells during pneumococcal carriage. Cervical lymph node (CLN) and splenic lymphocytes were isolated, 28 days after intranasal challenge, from both Streptococcus pneumoniae strain EF3030 challenged (▮), and naive (□) F1 (B6 × BALB/c) group mice. CD4+ T cells were incubated with 1 μm of PsaA peptide (15-amino acid peptides that overlapped every 11 residues) plus mitomycin C-treated naive syngeneic feeder cells, for 3 days, at a ratio of 5 : 1 × 106 cells. Proliferation was measured by 5-bromo-2′-deoxy uridine incorporation, which was measured by ELISA. The data presented are the mean optical density at 450 nm (OD450). Experimental groups consisted of 10 mice. The results were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) of the response from three replicates. (*) represents the peptides showing significantly higher proliferation response. Dotted line (–) represents the cut-off value above which the values were considered significant.
