Figure 4.
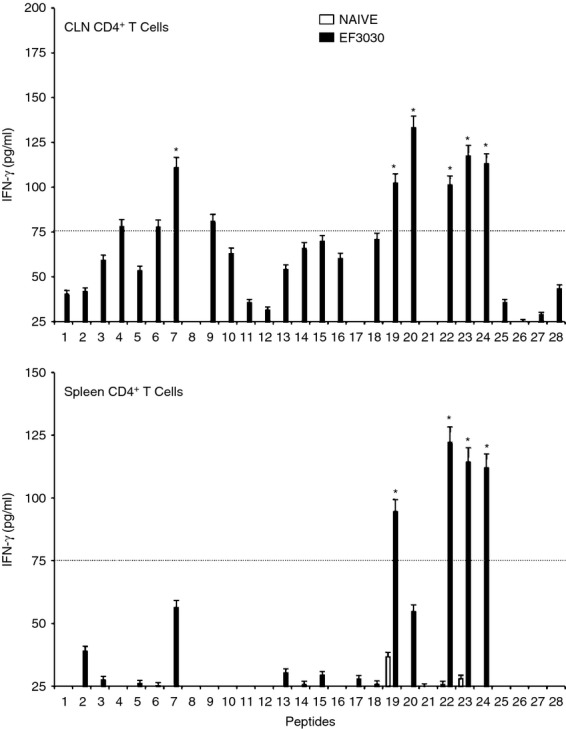
Pneumococcal surface adhesin A (PsaA) peptide-specific interferon-γ (IFN-γ) secretion by CD4+ T cells following pneumococcal challenge. Groups of 10 F1 (B6 × BALB/c) mice were intranasally challenged with 107 colony-forming units of Streptococcus pneumoniae strain EF3030 in a 15 μl volume of Ringer's solution. Cervical lymph node (CLN) and splenic lymphocytes were isolated, 28 days after intranasal challenge, from both S. pneumoniae strain EF3030 challenged (▮), and naive (□) group mice. CD4+ T cells were incubated with 1 μm of PsaA peptide (15 amino acid peptides that overlapped every 11 residues) plus mitomycin C-treated naive syngeneic feeder cells, for 3 days, at a ratio of 5 : 1 × 106 cells. The results were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) of the response from three replicates. IFN-γ production of cultured supernatants was determined by Luminex capable of detecting > 2 pg/ml of IFN-γ. (*) represents the peptides showing significantly higher cytokine response. Dotted line represents the cut-off value above which the values were considered significant.
