M. Kadomatsu, S. Nakajima, H. Kato, L. Gu, Y. Chi, J. Yao and M. Kitamura.
The authors inform the readers of this article [1] that Figure 4a in this article was reproduced from a different experiment published in a previous report (Cell Death Differ 18: 1876–1888, 2011; Fig. 5b) [2]. The authors apologise for this mistake and the corrected version of Figure 4a showing the activation of eIF2a by cordycepin/3′-deoxyadenosine is below.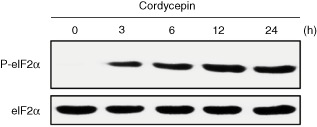
References
- 1.Kadomatsu M, Nakajima S, Kato H, Gu L, Chi Y, Yao J, Kitamura M. Cordycepin as a sensitizer to tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced apoptosis through eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α)-and mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)-mediated inhibition of nuclear factor (NF)-κB. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012;168:325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kitamura M, Kato H, Saito Y, Nakajima S, Takahashi S, Johno H, Gu L, Katoh R. Aberrant, differential and bidirectional regulation of the unfolded protein response towards cell survival by 3′-deoxyadenosine. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18:1876–1888. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


