Abstract
Background
Many behavioral and physiological variables exhibit daily rhythmicity. Few investigations of the daily rhythmicity in nociception have been conducted, and conflicting results have been obtained. The present study evaluated the daily rhythmicity in nociception in Wistar rats.
Methods
Nociception was investigated by Eddy's hot plate method, tail immersion method, and tail clip method. The latency between the noxious stimulus and the animal's response was recorded as reaction time. Separate groups of rats were tested in 4-hour intervals for 24 hours.
Results
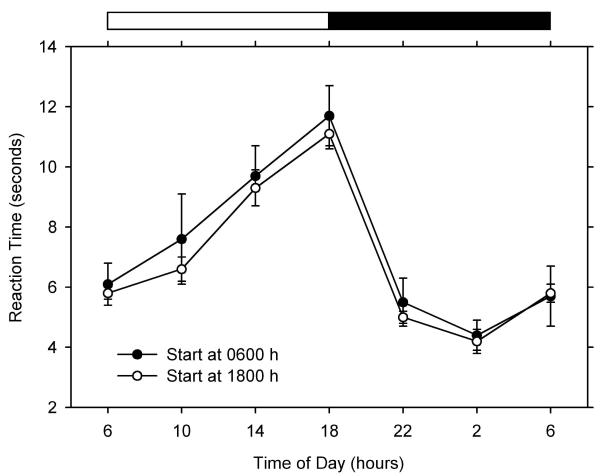
There was clear daily variation in response latency. Reaction time was shortest a few hours before lights-on and longest at the light-dark transition.
Conclusion
Nociception exhibits robust daily rhythmicity in rats. Sensitivity to pain is highest late in the dark phase of the light-dark cycle and lowest at the light-dark transition.
Background
Daily rhythmicity is an ubiquitous property of the physiology and behavior of animals [1]. Understanding of the daily rhythmicity in nociception is important for the standardization of studies of analgesic drugs. Yet, few studies have investigated the daily rhythmicity in nociception. Although studies on rats [2] and golden hamsters [3] have indicated the occurrence of greater pain sensitivity during the dark phase of the light-dark cycle, another study on rats indicated the occurrence of greater sensitivity during the light phase [4], and a study on mice indicated the occurrence of two daily peaks in sensitivity, one during the light phase and one during the dark phase [5]. Therefore, a re-evaluation of the daily rhythmicity in nociception seemed warranted.
Methods
Male albino Wistar rats were purchased from the Chellamuthu Trust, Madurai. They were housed in microlon cages maintained at 25 ± 1°C under an L12:D12 light-dark cycle.
Nociception was evaluated by Eddy's hot plate method, tail immersion method, and tail clip method. The latency between the noxious stimulus and the animal's response was recorded as reaction time. Rats previously adapted to an L12:D12 light-dark cycle were divided into 7 groups of 6 animals and tested at one of 7 times of day 4 hours apart. The same groups of animals were retested a week later with the same protocol, except that the animals initially tested first during the light phase of the light-dark cycle were tested first during the dark phase, and vice versa.
Results and discussion
The results are shown in Fig. 1. Reaction time (average of the three methods) was longest at the transition from light to darkness and shortest a few hours before the transition from darkness to light. This suggests greater pain sensitivity late in the dark phase, which is in agreement with previous studies in rats and golden hamsters [2,3]. Another study in rats suggested the occurrence of greater sensitivity during the light phase [4], but this was probably an artifact of the experimental procedure, as only two time points during the day were reported. A study on mice suggested the occurrence of two daily peaks in sensitivity, one during the light phase and one during the dark phase [5]. The amplitude of the daily variation in latencies was much smaller in that study than in ours, and it is possible that random oscillations were interpreted as a daily rhythm. Alternatively, species differences may account for the difference in the results.
Figure 1.
Daily rhythmicity of nociception in rats The figure shows the daily variation in reaction time to nociceptive stimulation. Each data point corresponds to the mean (±SE) of 6 rats. The horizontal bar at the top indicates the timing of the light-dark cycle.
Conclusion
It is concluded that nociception exhibits robust daily rhythmicity in rats. Sensitivity to pain is highest late in the dark phase of the light-dark cycle and lowest at the light-dark transition.
Competing interests
We, the authors declare that we have not received funds from any agency or organization for carrying out this work.
Authors' contributions
AJMC – Designed the study
NJM – Carried out the study
CV – Carried out the replicate study
NM and SJP – Evaluated the data statistically
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Prof. M. Nagarajan for the encouragement throughout the study.
Contributor Information
AJM Christina, Email: tinatina38@rediffmail.com.
NJ Merlin, Email: njmerlin@rediffmail.com.
C Vijaya, Email: vijak2@rediffmail.com.
S Jayaprakash, Email: jpkmcp@hotmail.com.
N Murugesh, Email: murugesh56@rediffmail.com.
References
- Takahashi JS, Turek FW, Moore RY. Circadian Clocks. New York, Kluwer/Plenum; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Gomez M, Cruz Y, Salas M, Hudson R, Pacheco P. Assessing pain threshold in the rat: changes with estrus and time of day. Physiol Behav. 1994;55:651–657. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(94)90040-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickard GE. Circadian rhythm of nociception in the golden hamster. Brain Res. 1987;425:395–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90529-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld JP, Rice PE. Diurnal rhythms in nociceptive thresholds of rats. Physiol Behav. 1979;23:419–420. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(79)90391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecka AM, Sroczynska I. Circadian rhythm of pain in male mice. Gen Pharmacol. 1998;31:809–810. doi: 10.1016/S0306-3623(98)00076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]