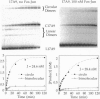
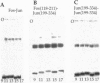
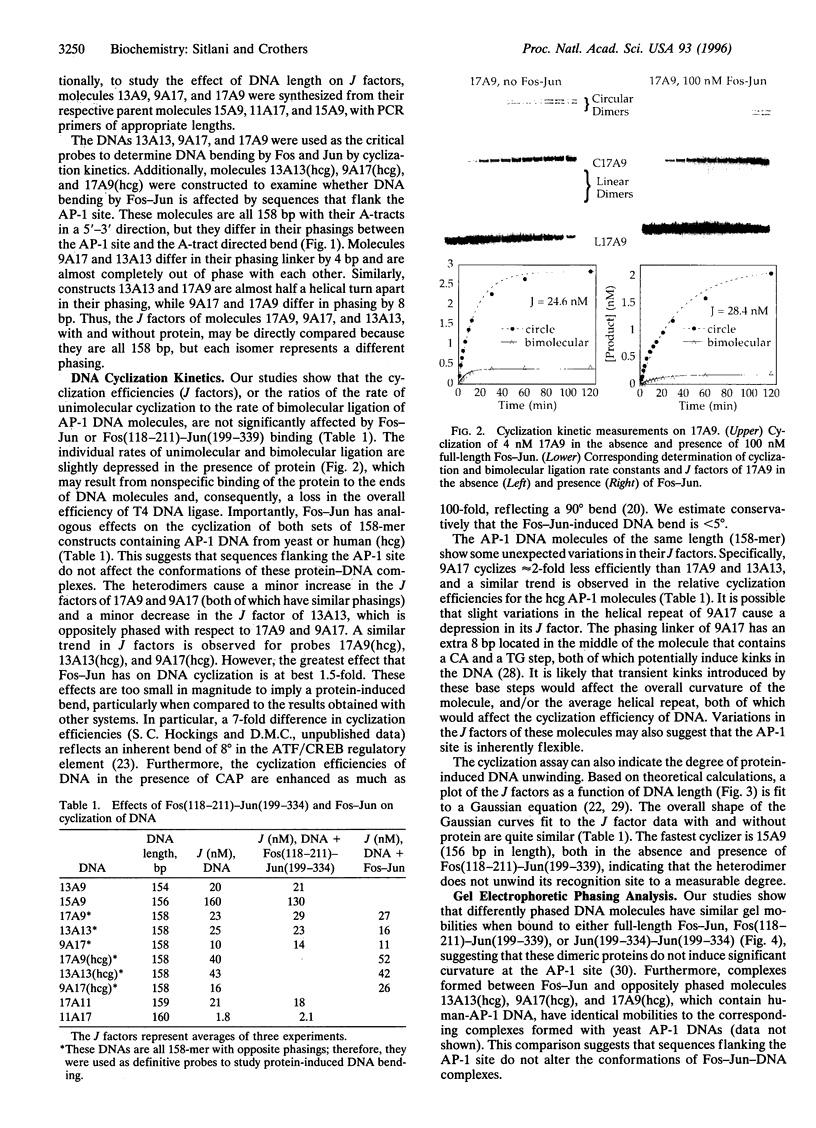
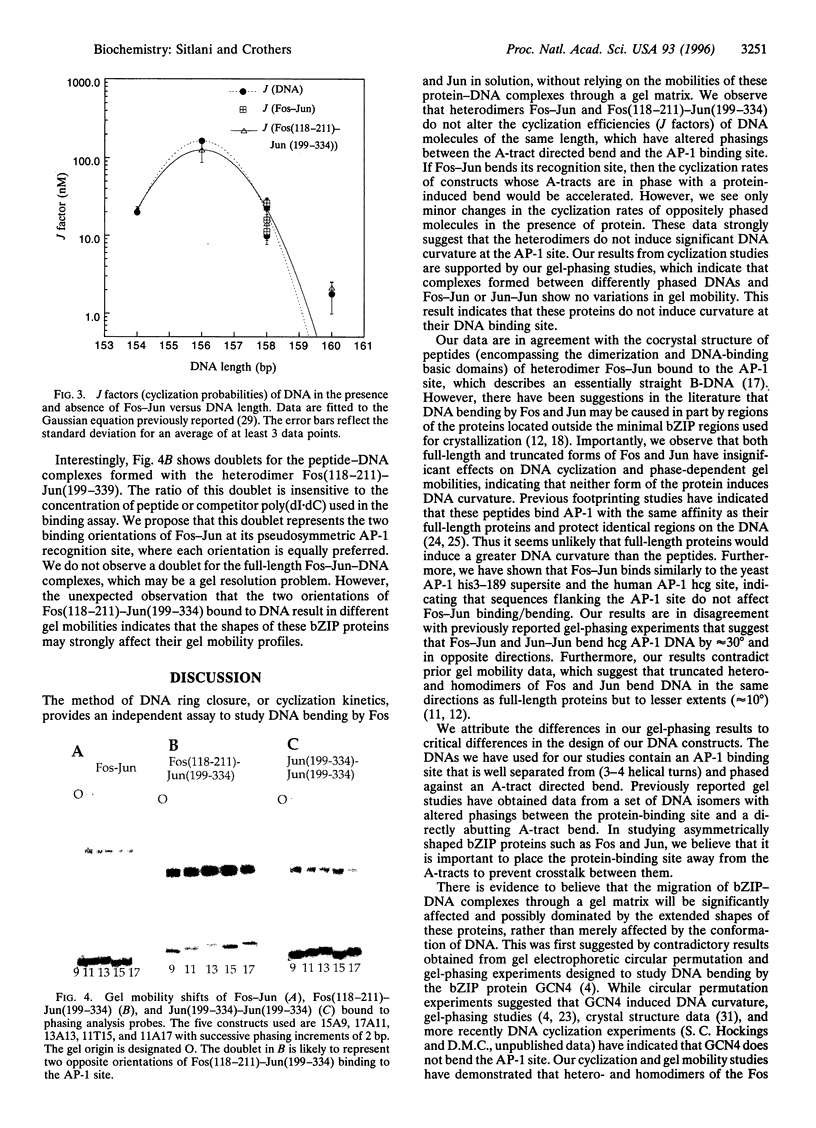
Abstract
We have used a solution-based DNA cyclization assay and a gel-phasing method to show that contrary to previous reports [Kerppola, T. K. & Curran, T. (1991) Cell 66, 317-326], basic region leucine zipper proteins Fos and Jun do not significantly bend their AP-1 recognition site. We have constructed two sets of DNA constructs that contain the 7-bp 5'-TGACTCA-3' AP-1 binding site, from either the yeast or the human collagenase gene, which is well separated from and phased by 3-4 helical turns against an A tract-directed bend. The cyclization probabilities of DNAs with altered phasings are not significantly affected by Fos-Jun binding. Similarly, Fos-Jun and Jun-Jun bound to differently phased DNA constructs show insignificant variations in gel mobilities. Both these methods independently indicate that Fos and Jun bend their AP-1 target site by <5 degrees, an observation that has important implications in understanding their mechanism of transcriptional regulation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Luk D., Curran T. Transcriptional regulation by Fos and Jun in vitro: interaction among multiple activator and regulatory domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abate C., Luk D., Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Expression and purification of the leucine zipper and DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun: both Fos and Jun contact DNA directly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J., Kahn J. D., Levene S. D. DNA bending, flexibility, and helical repeat by cyclization kinetics. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:3–29. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Gartenberg M. R., Shrader T. E. DNA bending in protein-DNA complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:118–146. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger T. E., Brandl C. J., Struhl K., Harrison S. C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted alpha helices: crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1223–1237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Ampe C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Molecular characterization of the GCN4-DNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6034–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover J. N., Harrison S. C. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA. Nature. 1995 Jan 19;373(6511):257–261. doi: 10.1038/373257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. D., Nash H. A. Functional replacement of a protein-induced bend in a DNA recombination site. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):251–254. doi: 10.1038/341251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T., Curran T. Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3720–3724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Crothers D. M. Protein-induced bending and DNA cyclization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. D., Yun E., Crothers D. M. Detection of localized DNA flexibility. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):163–166. doi: 10.1038/368163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. DNA bending by Fos and Jun: the flexible hinge model. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1210–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.1957173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Selective DNA bending by a variety of bZIP proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5479–5489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T., Curran T. Transcription. Zen and the art of Fos and Jun. Nature. 1995 Jan 19;373(6511):199–200. doi: 10.1038/373199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Burley S. K. 1.9 A resolution refined structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of TATAAAAG. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Sep;1(9):638–653. doi: 10.1038/nsb0994-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. L., Nikolov D. B., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):520–527. doi: 10.1038/365520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Crothers D. M. Ring closure probabilities for DNA fragments by Monte Carlo simulation. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90381-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara P. T., Bolshoy A., Trifonov E. N., Harrington R. E. Sequence-dependent kinks induced in curved DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Dec;8(3):529–538. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10507827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella D. N., Palmer C. R., Schepartz A. DNA targets for certain bZIP proteins distinguished by an intrinsic bend. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1130–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.8178171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Chow C. S., Lippard S. J. High-mobility-group 1 protein mediates DNA bending as determined by ring closures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9465–9469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Martín J., Espinosa M. Protein-induced bending as a transcriptional switch. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):805–807. doi: 10.1126/science.8387228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Voulalas P. J., Franza B. R., Jr, Curran T. Fos and Jun bind cooperatively to the AP-1 site: reconstitution in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1687–1699. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Baldwin R. L. Energetics of DNA twisting. I. Relation between twist and cyclization probability. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):957–981. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. H., Hagerman P. J. Application of the method of phage T4 DNA ligase-catalyzed ring-closure to the study of DNA structure. II. NaCl-dependence of DNA flexibility and helical repeat. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 20;212(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. H., Huth J. R., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Molecular basis of human 46X,Y sex reversal revealed from the three-dimensional solution structure of the human SRY-DNA complex. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):705–714. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]