Abstract
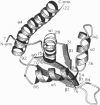
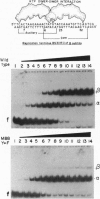
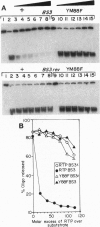
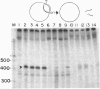
The replication terminator protein (RTP) of Bacillus subtilis causes polar fork arrest at replication termini by sequence-specific interaction of two dimeric proteins with the terminus sequence. The crystal structure of the RTP protein has been solved, and the structure has already provide valuable clues regarding the structural basis of its function. However, it provides little information as to the surface of the protein involved in dimer-dimer interaction. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we have identified three sites on the protein that appear to mediate the dimer-dimer interaction. Crystallographic analysis of one of the mutant proteins (Y88F) showed that its structure is unaltered when compared to the wild-type protein. The locations of the three sites suggested a model for the dimer-dimer interaction that involves an association between two beta-ribbon motifs. This model is supported by a fourth mutation that was predicted to disrupt the interaction and was shown to do so. Biochemical analyses of these mutants provide compelling evidence that cooperative protein-protein interaction between two dimers of RTP is essential to impose polar blocks to the elongation of both DNA and RNA chains.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastia D., Germino J., Crosa J. H., Ram J. The nucleotide sequence surrounding the replication terminus of R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2095–2099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussiere D. E., Bastia D., White S. W. Crystal structure of the replication terminator protein from B. subtilis at 2.6 A. Cell. 1995 Feb 24;80(4):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90519-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Luttropp L. K., Falkow S. Mode of replication of the conjugative R-plasmid RSF1040 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):454–466. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.454-466.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C., White S. W., Ramakrishnan V. The crystal structure of ribosomal protein L14 reveals an important organizational component of the translational apparatus. Structure. 1996 Jan 15;4(1):55–66. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Sugiono P., Guarente L., Davis R. W. Genetic selection for genes encoding sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3689–3693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Fischmann T. O., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of lac repressor core tetramer and its implications for DNA looping. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1721–1727. doi: 10.1126/science.7792597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiasa H., Marians K. J. Differential inhibition of the DNA translocation and DNA unwinding activities of DNA helicases by the Escherichia coli Tus protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11379–11385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Pelletier A. J., Tecklenburg M. L., Kuempel P. L. Identification of the DNA sequence from the E. coli terminus region that halts replication forks. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M., Tecklenburg M. L., Pelletier A. J., Kuempel P. L. tus, the trans-acting gene required for termination of DNA replication in Escherichia coli, encodes a DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1593–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Hidaka M. Core sequence of two separable terminus sites of the R6K plasmid that exhibit polar inhibition of replication is a 20 bp inverted repeat. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. F., Weaver A. J., Landry S. J., Gierasch L., Deisenhofer J. The crystal structure of the GroES co-chaperonin at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1996 Jan 4;379(6560):37–45. doi: 10.1038/379037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul S., Mohanty B. K., Sahoo T., Patel I., Khan S. A., Bastia D. The replication terminator protein of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis functions as a polar contrahelicase in gram-negative Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11143–11147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatri G. S., MacAllister T., Sista P. R., Bastia D. The replication terminator protein of E. coli is a DNA sequence-specific contra-helicase. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuempel P. L., Duerr S. A., Seeley N. R. Terminus region of the chromosome in Escherichia coli inhibits replication forks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3927–3931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley D. B., Smith M. T., Lewis P. J., Wake R. G. Protein-nucleoside contacts in the interaction between the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and the DNA terminator. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(4):771–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00947.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. H., Kornberg A., Hidaka M., Kobayashi T., Horiuchi T. Escherichia coli replication termination protein impedes the action of helicases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9104–9108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Harvey T. S., Yin Y., Yau P., Litchfield D., Arrowsmith C. H. Solution structure of the tetrameric minimum transforming domain of p53. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Dec;1(12):877–890. doi: 10.1038/nsb1294-877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Ralston G. B., Christopherson R. I., Wake R. G. Identification of the replication terminator protein binding sites in the terminus region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome and stoichiometry of the binding. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90147-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Smith M. T., Wake R. G. A protein involved in termination of chromosome replication in Bacillus subtilis binds specifically to the terC site. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3564–3567. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3564-3567.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louarn J., Patte J., Louarn J. M. Evidence for a fixed termination site of chromosome replication in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):295–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M. A., Sparks R. B., Helinski D. R. Bidirectional replication of plasmid R6K DNA in Escherichia coli; correspondence between origin of replication and position of single-strand break in relaxed complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2905–2909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P. P., Bussiere D. E., Hoffman D. W., Bastia D., White S. W. Crystallization and preliminary structural analysis of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18885–18889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miron A., Mukherjee S., Bastia D. Activation of distant replication origins in vivo by DNA looping as revealed by a novel mutant form of an initiator protein defective in cooperativity at a distance. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1205–1216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miron A., Patel I., Bastia D. Multiple pathways of copy control of gamma replicon of R6K: mechanisms both dependent on and independent of cooperativity of interaction of tau protein with DNA affect the copy number. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Echevarría M. J., Giménez-Gallego G., Sabariegos-Jareño R., Díaz-Orejas R. Kid, a small protein of the parD stability system of plasmid R1, is an inhibitor of DNA replication acting at the initiation of DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1995 Apr 7;247(4):568–577. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo T., Mohanty B. K., Lobert M., Manna A. C., Bastia D. The contrahelicase activities of the replication terminator proteins of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis are helicase-specific and impede both helicase translocation and authentic DNA unwinding. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 8;270(49):29138–29144. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo T., Mohanty B. K., Patel I., Bastia D. Termination of DNA replication in vitro: requirement for stereospecific interaction between two dimers of the replication terminator protein of Bacillus subtilis and with the terminator site to elicit polar contrahelicase and fork impedance. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 1;14(3):619–628. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sista P. R., Hutchinson C. A., 3rd, Bastia D. DNA-protein interaction at the replication termini of plasmid R6K. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):74–82. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sista P. R., Mukherjee S., Patel P., Khatri G. S., Bastia D. A host-encoded DNA-binding protein promotes termination of plasmid replication at a sequence-specific replication terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3026–3030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. T., Wake R. G. Definition and polarity of action of DNA replication terminators in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):648–657. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindells M. B. Identification of a common fold in the replication terminator protein suggests a possible mode for DNA binding. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Aug;20(8):300–302. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka I., Appelt K., Dijk J., White S. W., Wilson K. S. 3-A resolution structure of a protein with histone-like properties in prokaryotes. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):376–381. doi: 10.1038/310376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. S., Wake R. G. Restriction map of DNA spanning the replication terminus of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 5;171(2):119–137. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipple F. W., Kuldell N. H., Cheatham L. A., Hochschild A. Specificity determinants for the interaction of lambda repressor and P22 repressor dimers. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1212–1223. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickelgren I. Protein sculptors that help turn on genes. Science. 1995 Dec 8;270(5242):1587–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5242.1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]