Abstract
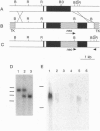
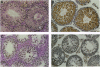
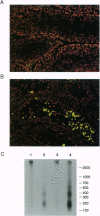
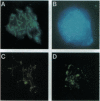
In addition to the five 70-kDa heat shock proteins (HSP70) common to germ cells and somatic tissues of mammals, spermatogenic cells synthesize HSP70-2 during meiosis. To determine if this unique stress protein has a critical role in meiosis, we used gene-targeting techniques to disrupt Hsp70-2 in mice. Male mice homozygous for the mutant allele (Hsp70-2 -/-) did not synthesize HSP70-2, lacked postmeiotic spermatids and mature sperm, and were infertile. However, neither meiosis nor fertility was affected in female Hsp70-2 -/- mice. We previously found that HSP70-2 is associated with synaptonemal complexes in the nucleus of meiotic spermatocytes from mice and hamsters. While synaptonemal complexes assembled in Hsp70-2 -/- spermatocytes, structural abnormalities became apparent in these cells by late prophase, and development rarely progressed to the meiotic divisions. Furthermore, analysis of nuclei and genomic DNA indicated that the failure of meiosis in Hsp70-2 -/- mice was coincident with a dramatic increase in spermatocyte apoptosis. These results suggest that HSP70-2 participates in synaptonemal complex function during meiosis in male germ cells and is linked to mechanisms that inhibit apoptosis.
Full text
PDF
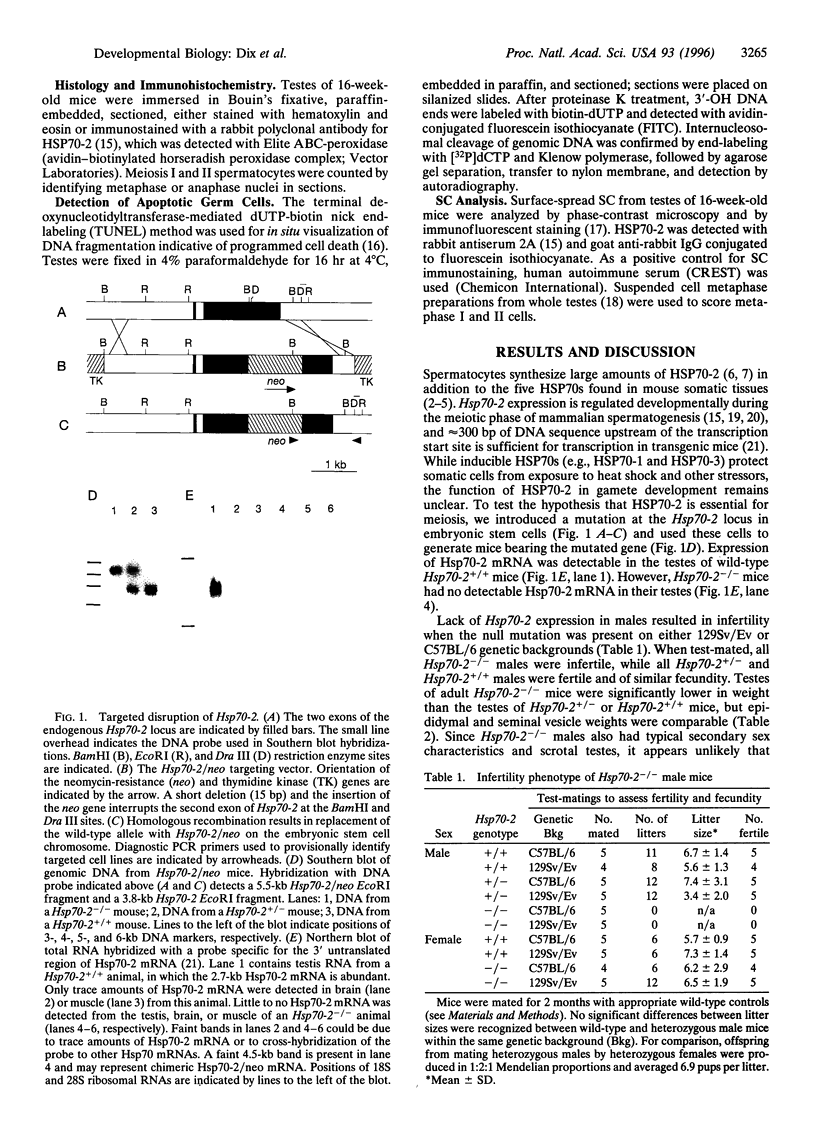
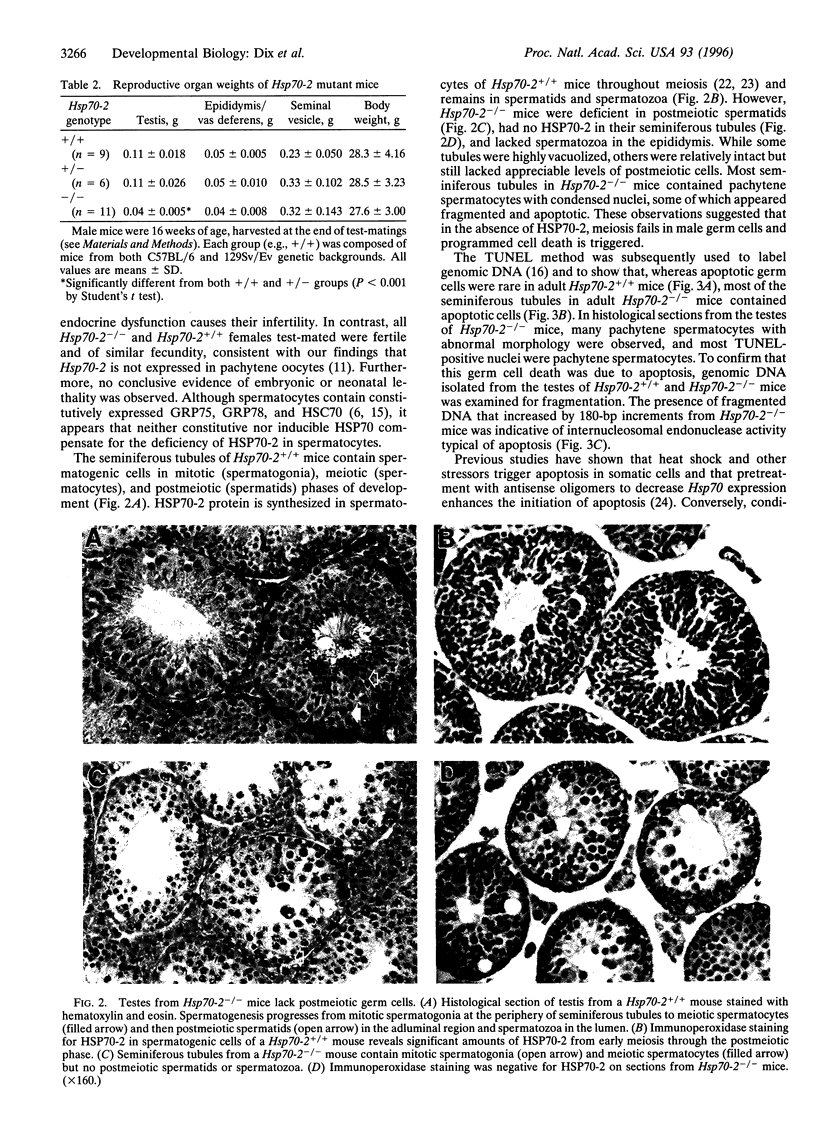
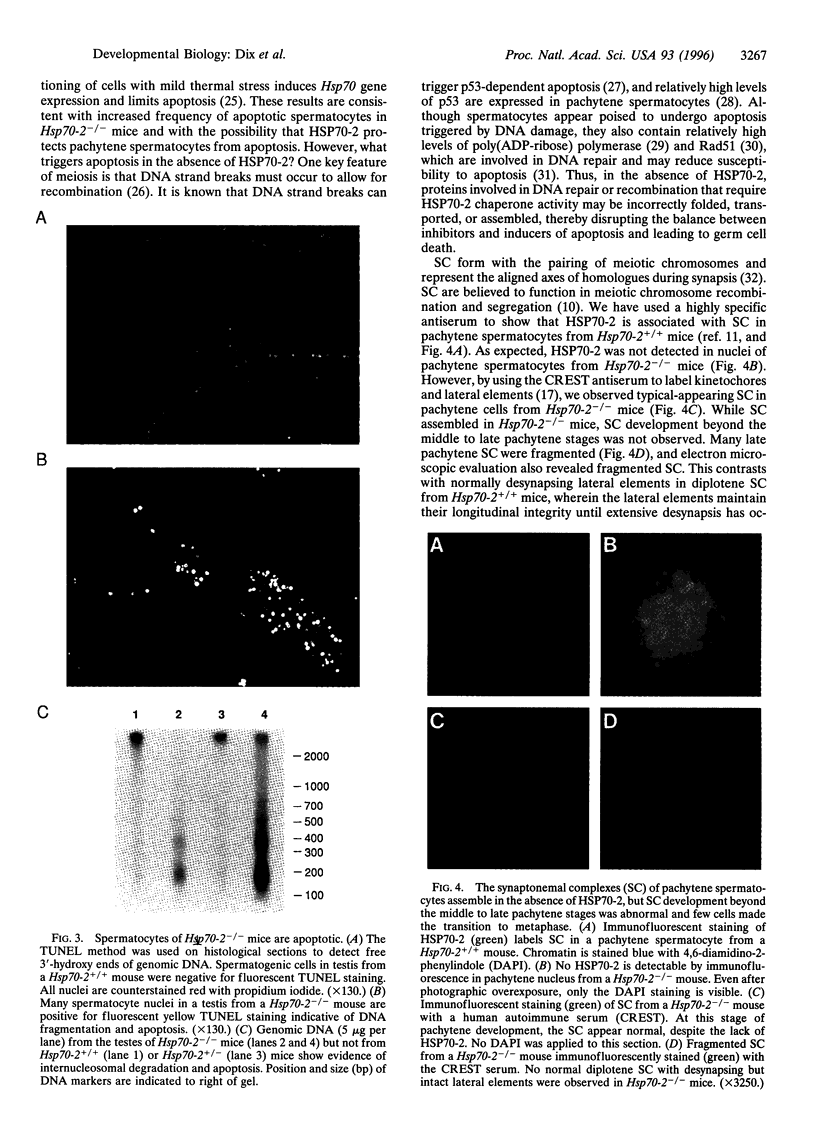

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adra C. N., Boer P. H., McBurney M. W. Cloning and expression of the mouse pgk-1 gene and the nucleotide sequence of its promoter. Gene. 1987;60(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. L., O'Brien D. A., Eddy E. M. A novel hsp70-like protein (P70) is present in mouse spermatogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):828–832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. L., O'Brien D. A., Jones C. C., Rockett D. L., Eddy E. M. Expression of heat shock proteins by isolated mouse spermatogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3260–3266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Bronner C. E., Zhang L., Plug A. W., Robatzek M., Warren G., Elliott E. A., Yu J., Ashley T., Arnheim N. Male mice defective in the DNA mismatch repair gene PMS2 exhibit abnormal chromosome synapsis in meiosis. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnycastle L. L., Yu C. E., Hunt C. R., Trask B. J., Clancy K. P., Weber J. L., Patterson D., Schellenberg G. D. Cloning, sequencing, and mapping of the human chromosome 14 heat shock protein gene (HSPA2). Genomics. 1994 Sep 1;23(1):85–93. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Gledhill S., Hooper M. L., Bird C. C., Wyllie A. H. p53 dependence of early apoptotic and proliferative responses within the mouse intestinal epithelium following gamma-irradiation. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1767–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domanico S. Z., DeNagel D. C., Dahlseid J. N., Green J. M., Pierce S. K. Cloning of the gene encoding peptide-binding protein 74 shows that it is a new member of the heat shock protein 70 family. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3598–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresser M., Pisetsky D., Warren R., McCarty G., Moses M. A new method for the cytological analysis of autoantibody specificities using whole-mount, surface-spread meiotic nuclei. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90494-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS E. P., BRECKON G., FORD C. E. AN AIR-DRYING METHOD FOR MEIOTIC PREPARATIONS FROM MAMMALIAN TESTES. Cytogenetics. 1964;3:289–294. doi: 10.1159/000129818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C., Welch W. J. Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:601–634. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebel L. B., Dworniczak B. P., Bautz E. K. Developmental regulation of a constitutively expressed mouse mRNA encoding a 72-kDa heat shock-like protein. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Golub E. I., Reddy G., Radding C. M., Ward D. C. Nuclear foci of mammalian Rad51 recombination protein in somatic cells after DNA damage and its localization in synaptonemal complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2298–2302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. S., Arbel T. Yeast genetics and the fall of the classical view of meiosis. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):301–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. R., Gasser D. L., Chaplin D. D., Pierce J. C., Kozak C. A. Chromosomal localization of five murine HSP70 gene family members: Hsp70-1, Hsp70-2, Hsp70-3, Hsc70t, and Grp78. Genomics. 1993 Apr;16(1):193–198. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozutsumi Y., Normington K., Press E., Slaughter C., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Identification of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein as glucose-regulated protein 78 on the basis of amino acid sequence, immunological cross-reactivity, and functional activity. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;11:115–137. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_11.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik Y. A., Kaufmann S. H., Desnoyers S., Poirier G. G., Earnshaw W. C. Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):346–347. doi: 10.1038/371346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa M., O'Brien D. A., Allen R. L., Eddy E. M. Heat-shock cognate protein (hsc71) and related proteins in mouse spermatogenic cells. Biol Reprod. 1989 Apr;40(4):843–852. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod40.4.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Fujimoto H. Cloning of a hsp70-related gene expressed in mouse spermatids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91909-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens P. B. Molecular perspectives of chromosome pairing at meiosis. Bioessays. 1994 Feb;16(2):101–106. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori C., Nakamura N., Kimura S., Irie H., Takigawa T., Shiota K. Programmed cell death in the interdigital tissue of the fetal mouse limb is apoptosis with DNA fragmentation. Anat Rec. 1995 May;242(1):103–110. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092420114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien D. A. Stage-specific protein synthesis by isolated spermatogenic cells throughout meiosis and early spermiogenesis in the mouse. Biol Reprod. 1987 Aug;37(1):147–157. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod37.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura T., Takenouchi N., Yamaguchi M., Matsukage A., Sugimura T., Esumi H. Striking similarity of the distribution patterns of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and DNA polymerase beta among various mouse organs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 30;172(2):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90683-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario M. O., Perkins S. L., O'Brien D. A., Allen R. L., Eddy E. M. Identification of the gene for the developmentally expressed 70 kDa heat-shock protein (P70) of mouse spermatogenic cells. Dev Biol. 1992 Mar;150(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D., Goldfinger N., Rotter V. Expression of p53 protein in spermatogenesis is confined to the tetraploid pachytene primary spermatocytes. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1487–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Kim H. S. Targeted gene duplication and disruption for analyzing quantitative genetic traits in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3612–3615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y. Q., Zhao X., Kariya Y., Fukata H., Teshigawara K., Uchida A. Induction of apoptosis by quercetin: involvement of heat shock protein. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 15;54(18):4952–4957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y. Q., Zhao X., Kariya Y., Teshigawara K., Uchida A. Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis by abrogation of heat-shock protein (HSP) 70 expression in tumor cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1995 Feb;40(2):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01520287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiltshire T., Park C., Caldwell K. A., Handel M. A. Induced premature G2/M-phase transition in pachytene spermatocytes includes events unique to meiosis. Dev Biol. 1995 Jun;169(2):557–567. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski J., Kordula T., Krawczyk Z. Isolation and nucleotide sequence analysis of the rat testis-specific major heat-shock protein (HSP70)-related gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 30;1048(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90027-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakeri Z. F., Wolgemuth D. J., Hunt C. R. Identification and sequence analysis of a new member of the mouse HSP70 gene family and characterization of its unique cellular and developmental pattern of expression in the male germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]