Abstract
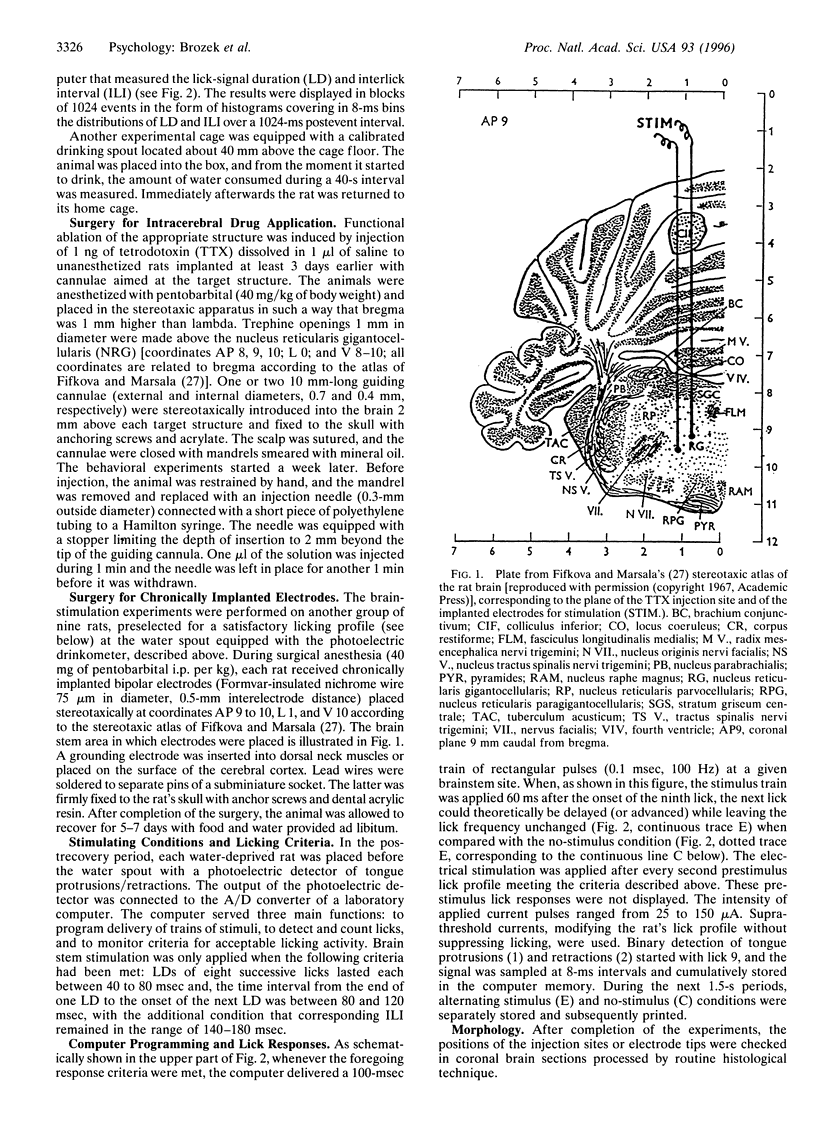
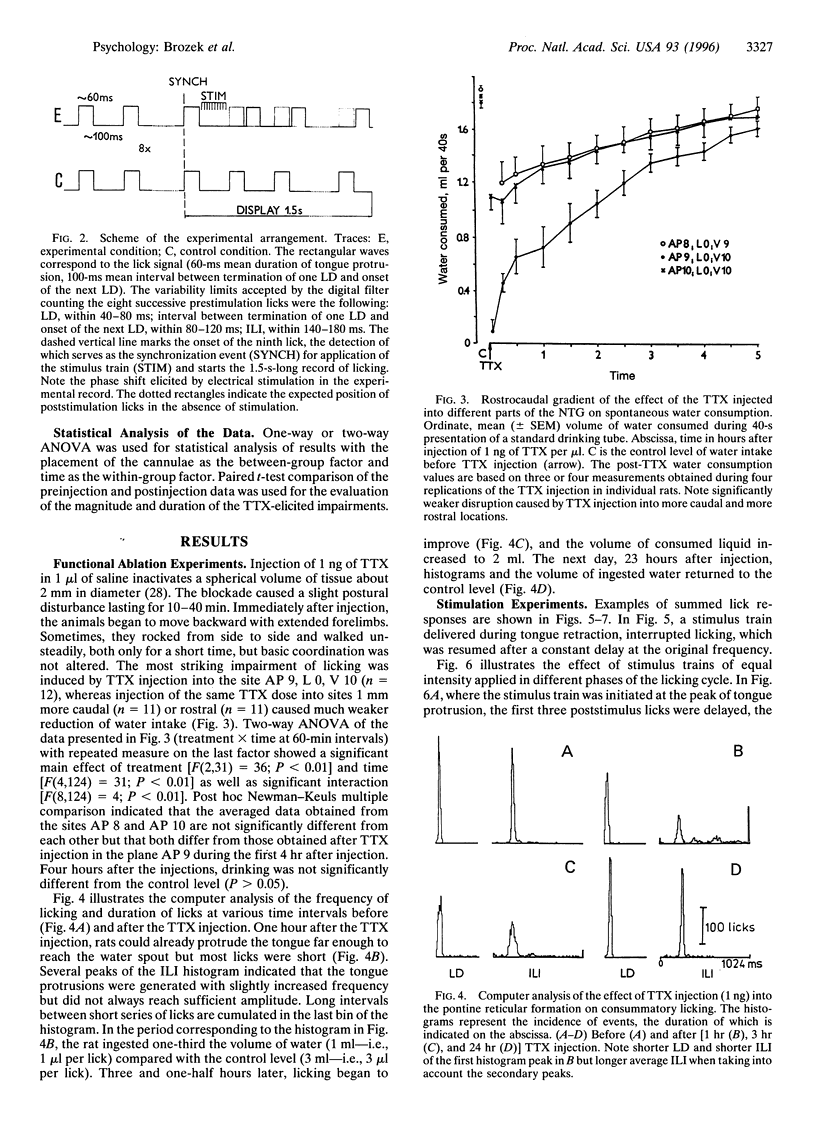
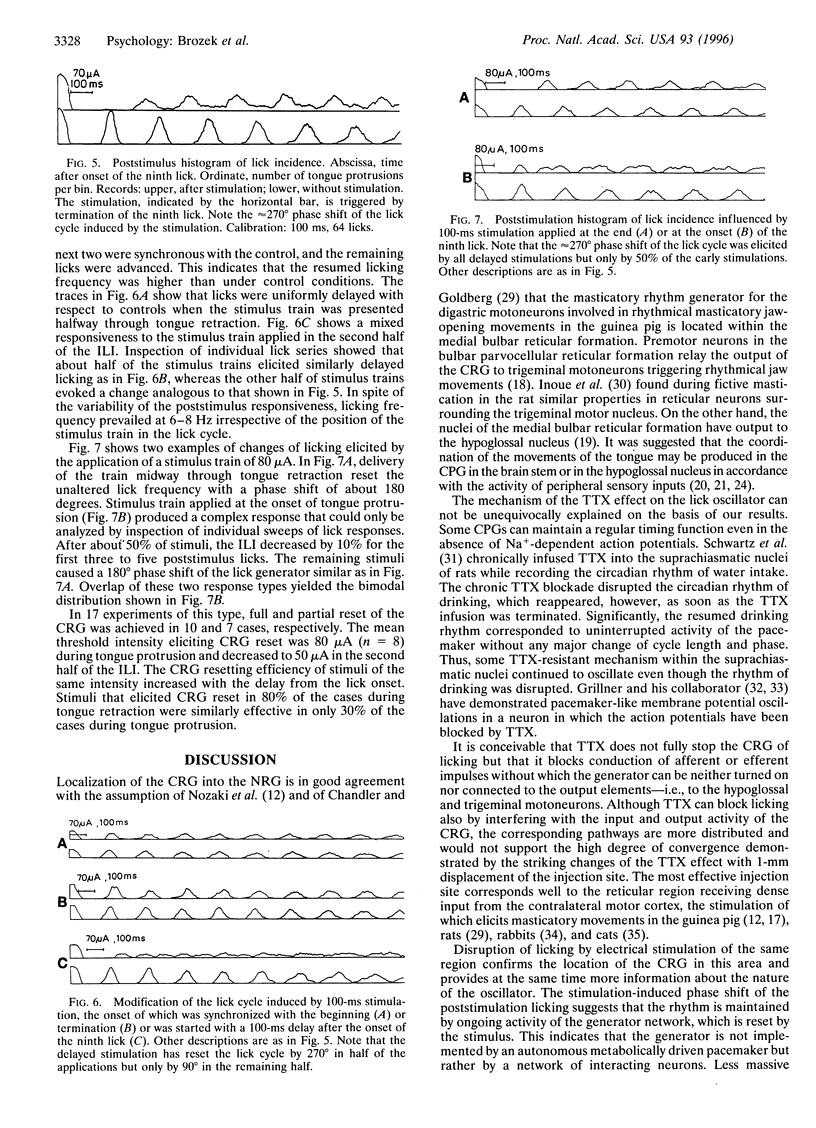
Localization of the central rhythm generator (CRG) of spontaneous consummatory licking was studied in freely moving rats by microinjection of tetrodotoxin (TTX) into the pontine reticular formation. Maximum suppression of spontaneous water consumption was elicited by TTX (1 ng) blockade of the oral part of the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis (NRG), whereas TTX injections into more caudal or rostral locations caused significantly weaker disruption of drinking. To verify the assumption that TTX blocked the proper CRG of licking rather than some relay in its output, spontaneously drinking thirsty rats were intracranially stimulated via electrodes chronically implanted into the oral part of the NRG. Lick-synchronized stimulation (a 100-ms train of 0.1-ms-wide rectangular pulses at 100 Hz and 25-150 microA) applied during continuous licking (after eight regular consecutive licks) caused a phase shift of licks emitted after stimulus delivery. The results suggest that the stimulation has reset the CRG of licking without changing its frequency. The reset-inducing threshold current was lowest during the tongue retraction and highest during the tongue protrusion period of the lick cycle. It is concluded that the CRG of licking is located in the oral part of NRG.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borke R. C., Nau M. E., Ringler R. L., Jr Brain stem afferents of hypoglossal neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1983 Jun 13;269(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90961-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler S. H., Goldberg L. J. Effects of pontomedullary reticular formation stimulation on the neuronal networks responsible for rhythmical jaw movements in the guinea pig. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Mar;59(3):819–832. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.3.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler S. H., Tal M. Brain-stem perturbations during cortically evoked rhythmical jaw movements: effects of activation of brain-stem loci on jaw muscle cycle characteristics. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):463–472. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00463.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler S. H., Turman J., Jr, Salem L., Goldberg L. J. The effects of nanoliter ejections of lidocaine into the pontomedullary reticular formation on cortically induced rhythmical jaw movements in the guinea pig. Brain Res. 1990 Aug 27;526(1):54–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90249-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway B. A., Hultborn H., Kiehn O. Proprioceptive input resets central locomotor rhythm in the spinal cat. Exp Brain Res. 1987;68(3):643–656. doi: 10.1007/BF00249807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbit J. D., Luschei E. S. Invariance of the rat's rate of drinking. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969 Sep;69(1):119–125. doi: 10.1037/h0027943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donga R., Lund J. P. Discharge patterns of trigeminal commissural last-order interneurons during fictive mastication in the rabbit. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Nov;66(5):1564–1578. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.5.1564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Wallén P., Brodin L., Lansner A. Neuronal network generating locomotor behavior in lamprey: circuitry, transmitters, membrane properties, and simulation. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:169–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner S., Wallén P. Central pattern generators for locomotion, with special reference to vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:233–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto N., Katayama T., Ishiwata Y., Nakamura Y. Induction of rhythmic jaw movements by stimulation of the mesencephalic reticular formation in the guinea pig. J Neurosci. 1989 Aug;9(8):2887–2901. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-08-02887.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Mesa N., Mamedov Z., Bures J. Motor learning in rats: modification of the pattern of reaching and licking by operant conditioning. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1985;34 (Suppl):49–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Masuda Y., Nagashima T., Yoshikawa K., Morimoto T. Properties of rhythmically active reticular neurons around the trigeminal motor nucleus during fictive mastication in the rat. Neurosci Res. 1992 Sep;14(4):275–294. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(92)90072-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jüch P. J., Van Willigen J. D., Broekhuijsen M. L., Ballintijn C. M. Peripheral influences on the central pattern-rhythm generator for tongue movements in the rat. Arch Oral Biol. 1985;30(5):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(85)90069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriellaars D. J., Brownstone R. M., Noga B. R., Jordan L. M. Mechanical entrainment of fictive locomotion in the decerebrate cat. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Jun;71(6):2074–2086. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.6.2074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. J., Masuda Y., Inoue T., Fuchihata H., Sumida A., Takada K., Morimoto T. Coordination of cortically induced rhythmic jaw and tongue movements in the rabbit. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Feb;69(2):569–584. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.2.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R. R. The intrinsic electrophysiological properties of mammalian neurons: insights into central nervous system function. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1654–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.3059497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydic R. Central pattern-generating neurons and the search for general principles. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2457–2468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2680703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mameli O., Melis F., De Riu P. L. Visual and vestibular projections to tongue motoneurons. Brain Res Bull. 1994;33(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mameli O., Melis F. Visual and somatosensory information to tongue motoneurons. Brain Res Bull. 1992 Feb;28(2):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(92)90185-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marowitz L. A., Halpern B. P. The effects of environmental constraints upon licking patterns. Physiol Behav. 1973 Aug;11(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(73)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y. Rhythmical jaw movements and lateral ponto-medullary reticular neurons in rats. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1987;86(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(87)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Enomoto S., Kato M. The role of medial bulbar reticular neurons in the orbital cortically induced masticatory rhythm in cats. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 24;202(1):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Katakura N. Generation of masticatory rhythm in the brainstem. Neurosci Res. 1995 Aug;23(1):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki S., Iriki A., Nakamura Y. Localization of central rhythm generator involved in cortically induced rhythmical masticatory jaw-opening movement in the guinea pig. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Apr;55(4):806–825. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.4.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki S., Iriki A., Nakamura Y. Trigeminal premotor neurons in the bulbar parvocellular reticular formation participating in induction of rhythmical activity of trigeminal motoneurons by repetitive stimulation of the cerebral cortex in the guinea pig. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Feb;69(2):595–608. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.2.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STELLAR E., HILL J. H. The rats rate of drinking as a function of water deprivation. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1952 Feb;45(1):96–102. doi: 10.1037/h0062150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz W. J., Gross R. A., Morton M. T. The suprachiasmatic nuclei contain a tetrodotoxin-resistant circadian pacemaker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1694–1698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallén P., Grillner S. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-induced, inherent oscillatory activity in neurons active during fictive locomotion in the lamprey. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2745–2755. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02745.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuravin I. A., Bures J. Extent of the tetrodotoxin induced blockade examined by pupillary paralysis elicited by intracerebral injection of the drug. Exp Brain Res. 1991;83(3):687–690. doi: 10.1007/BF00229849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



