Abstract
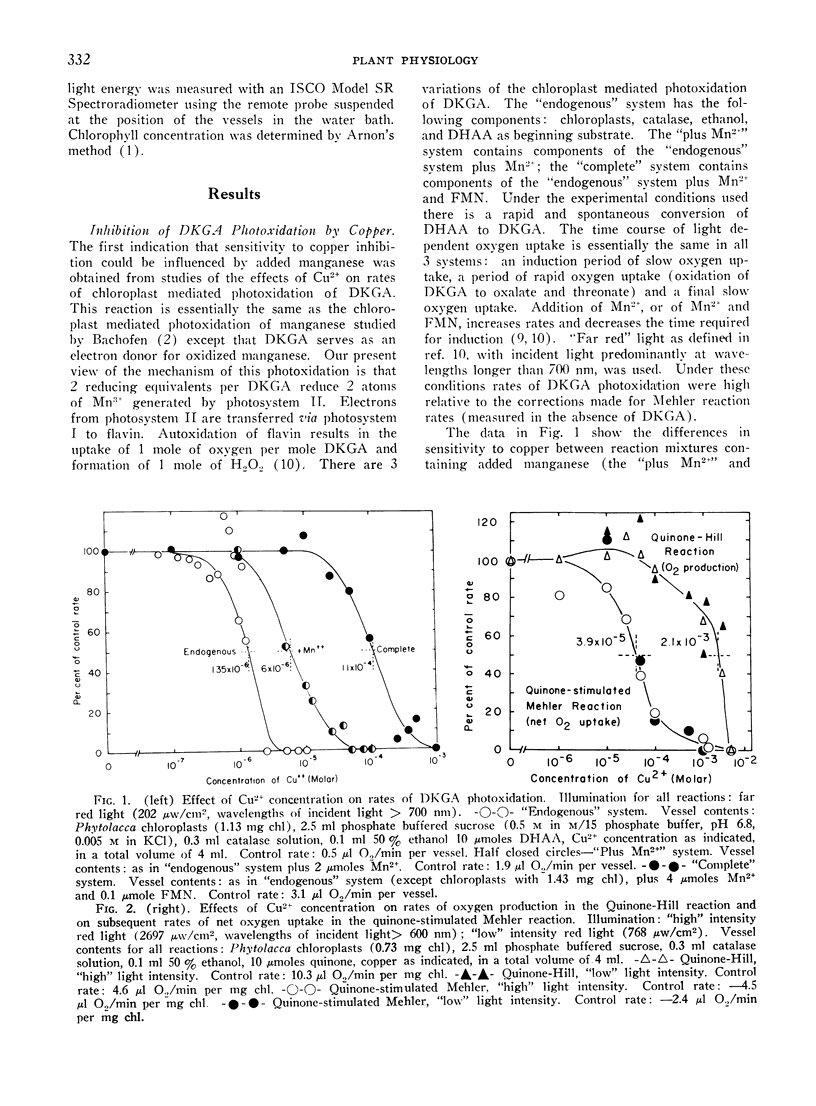
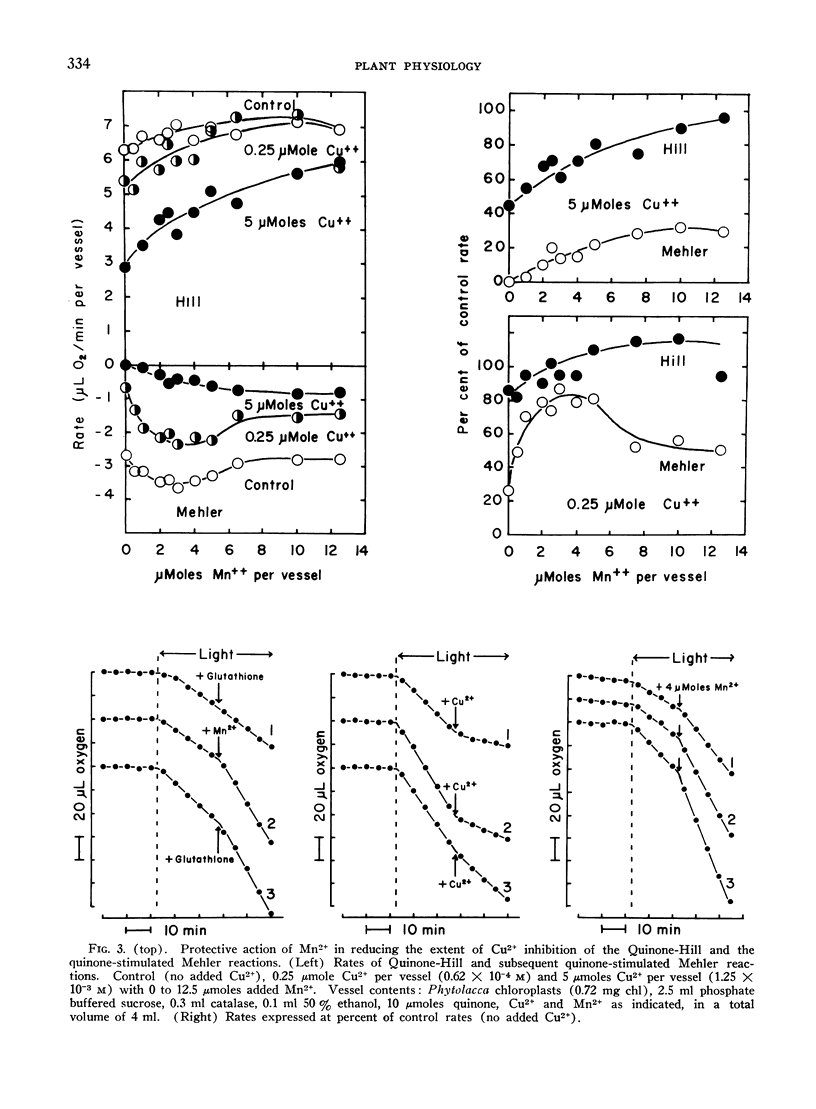
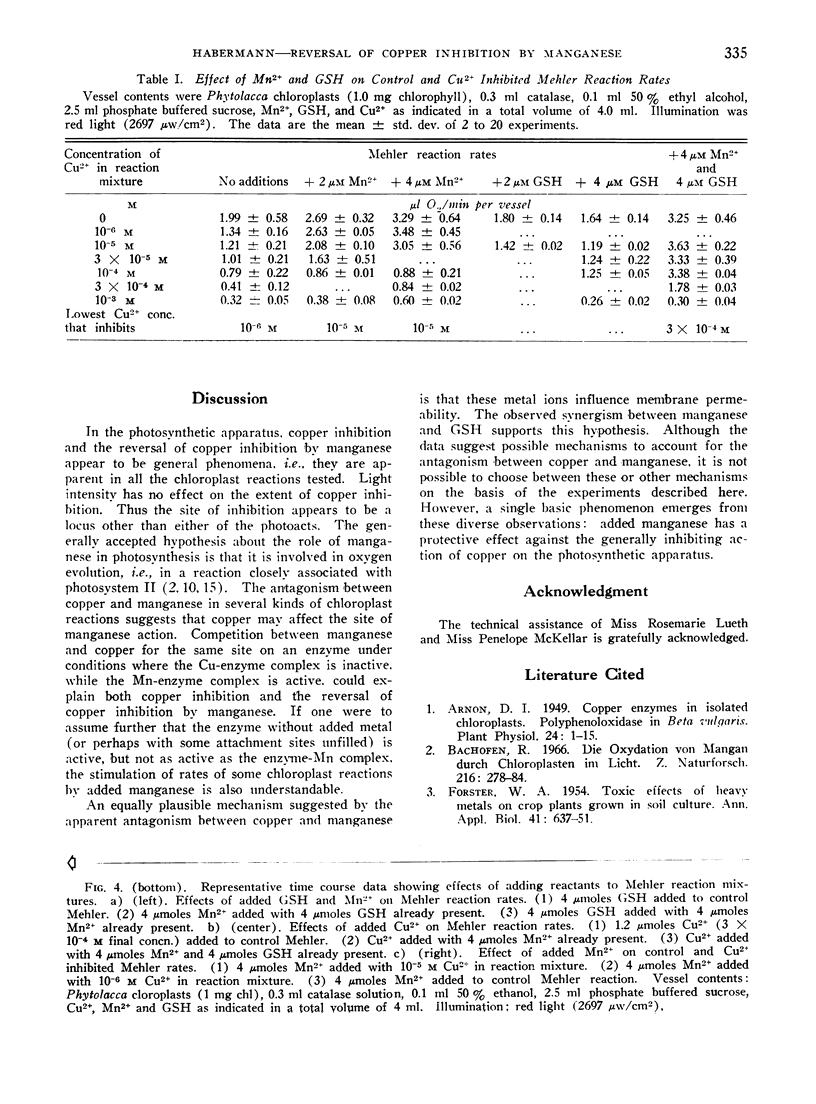
In the Mehler reaction, a Hill reaction utilizing molecular oxygen as the electron acceptor, rates of net oxygen uptake are stimulated by added manganous ions. Both whole cell photosynthesis and the Mehler reaction are inhibited by copper. Copper inhibition of the Mehler reaction can be reversed by manganese salts. Glutathione. which alone has no effect on Mehler reaction rates, enhances the effect of manganese in reversing copper inhibition. The effects of added Cu2+, Cu2+ and Mn2+, or Cu2+, Mn2+, and glutathione exhibit no induction phenomena when measured manometrically. Furthermore, the order of addition of these factors is unimportant: final rates are dependent only on the composition of reaction mixtures. Compared to the Mehler reaction, conventional Hill reactions are less sensitive to copper poisoning, while certain chloroplast mediated photoxidations (e.g. the photoxidation of diketogulonic acid) are far more sensitive. In all of the chloroplast mediated photoreactions tested, manganese is effective in reducing the sensitivity to copper poisoning.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRI K. V., KRISHNASWAMY P. R., RAO N. A. Studies on plant flavokinase. Biochem J. 1958 Sep;70(1):66–71. doi: 10.1042/bj0700066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann H. M. Light-dependent Oxygen Metabolism of Chloroplast Preparations. I. Stimulation Following Quinone Reduction. Plant Physiol. 1958 Jul;33(4):242–245. doi: 10.1104/pp.33.4.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATOH S., SHIRATORI I., TAKAMIYA A. Purification and some properties of spinach plastocyanin. J Biochem. 1962 Jan;51:32–40. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHLER A. H. Studies on reactions of illuminated chloroplasts. II. Stimulation and inhibition of the reaction with molecular oxygen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Dec;34(2):339–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdowall F. D. THE EFFECTS OF SOME INHIBITORS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS UPON THE PHOTOCHEMICAL REDUCTION OF A DYE BY ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jul;24(3):462–480. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.3.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


