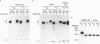Abstract
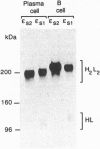
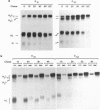
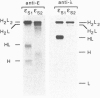
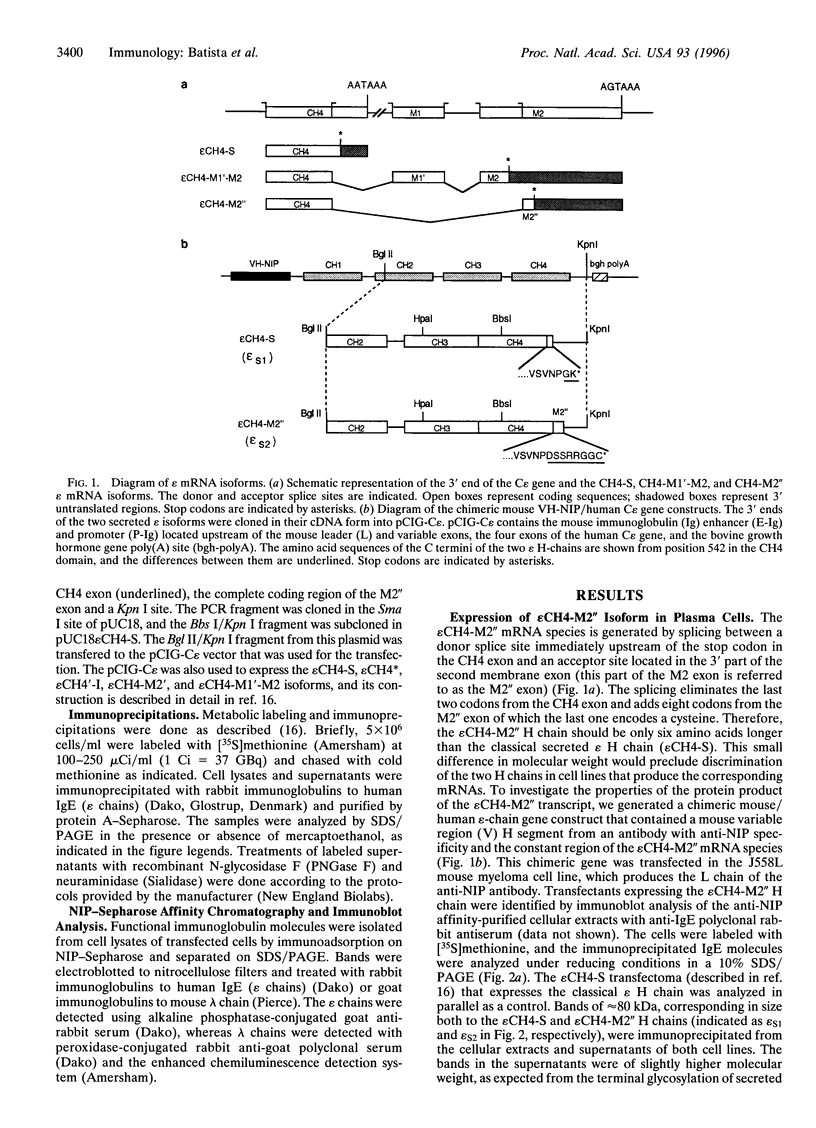
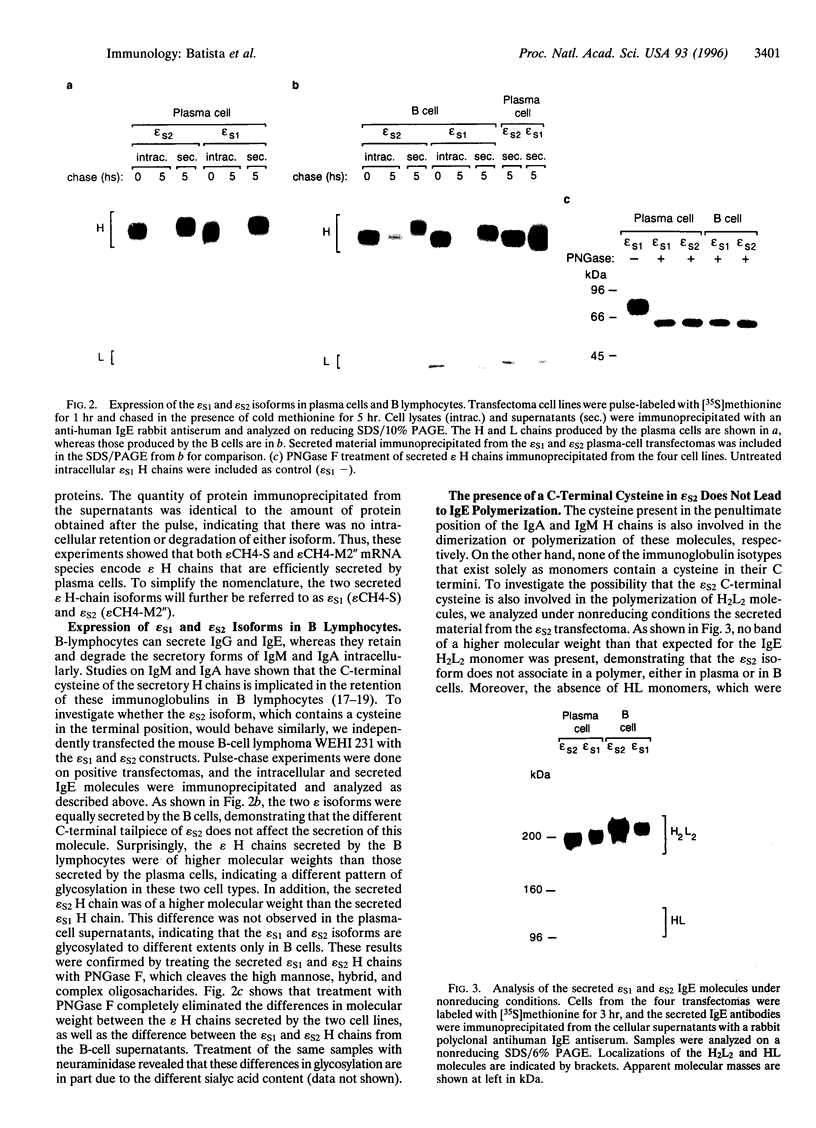
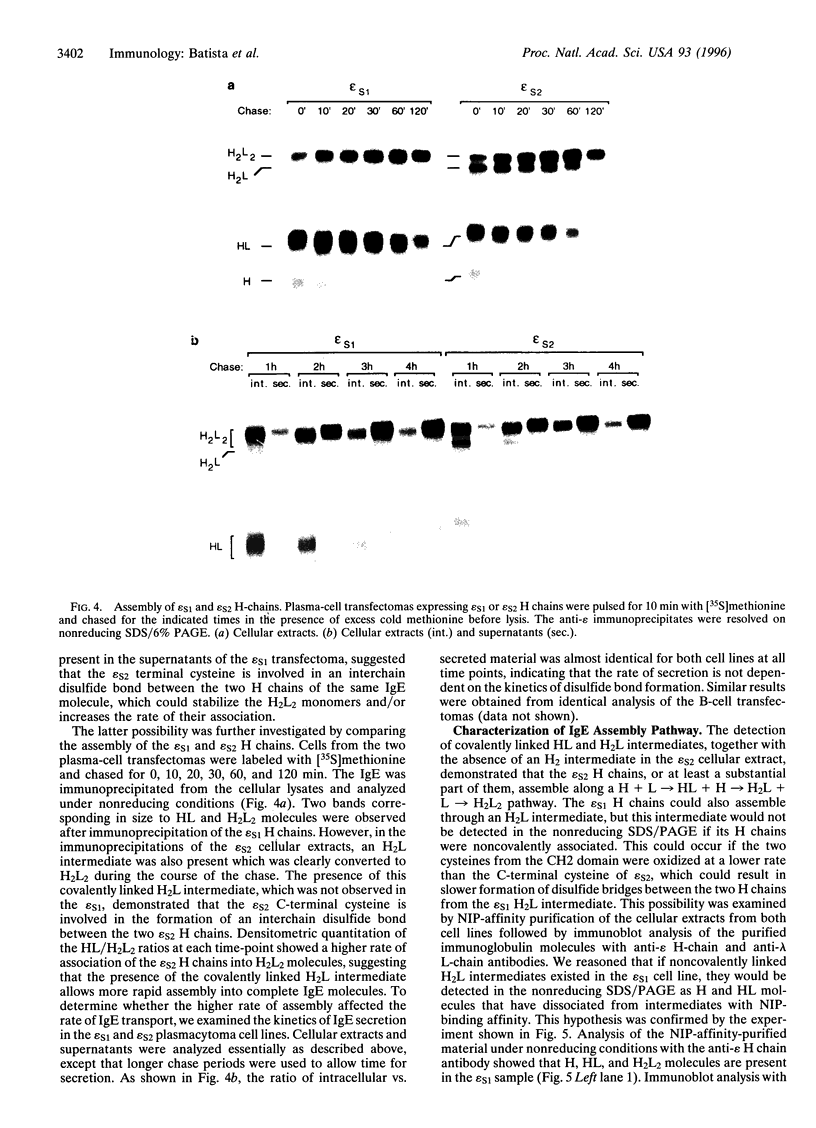
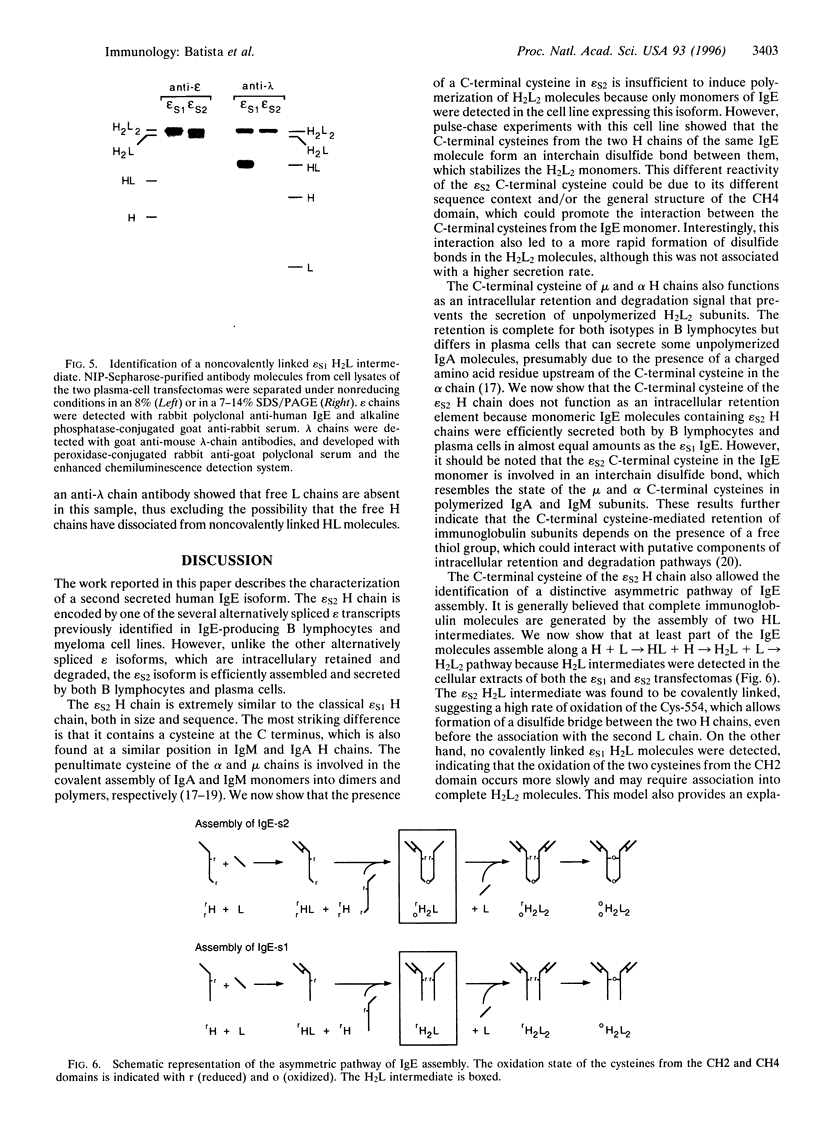
A number of alternatively spliced epsilon transcripts have been detected in IgE-producing B cells, in addition to the mRNAs encoding the classical membrane and secreted IgE heavy (H) chains. In a recent study, we examined the protein products of three of these alternatively spliced isoforms and found that they are intracellularly retained and degraded because of their inability to assemble into complete IgE molecules. We have now similarly examined a more recently described epsilon mRNA species that is generated by splicing between a donor splice site immediately upstream of the stop codon in the H-chain constant region exon 4 (CH4) and an acceptor site located in the 3' part of the second membrane exon. We show that this isoform is efficiently secreted by both plasma cells and B lymphocytes and therefore represents a second secreted IgE isoform (epsilon S2). The epsilon S2 H chain is only six amino acids longer than the classical secreted Ig H chain (epsilon S1) and contains a C-terminal cysteine, which is a characteristic sequence feature of mu and alpha H chains. However, unlike IgM and IgA, the epsilon S2 C-terminal cysteine (Cys-554) does not induce polymerization of H2L2 molecules (where L is light chain), but rather creates a disulfide bond between the two H chains that increases the rate of association into covalently bound H2L2 monomers. This C-terminal cysteine also does not function as an intracellular retention element because the epsilon S2 isoform was secreted in amounts equal to that of the epsilon S1, both in B lymphocytes and in plasma cells. The epsilon S2 H chains secreted by B lymphocytes differed from the epsilon S1 H chains in the extent of glycosylation. Interestingly, a difference in glycosylation between B-lymphocytes and plasma cells was also noted for both isoforms. The presence of the Cys-554 also allowed the identification of a distinctive asymmetric pathway of IgE assembly, common to both types of epsilon H chains.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batista F. D., Efremov D. G., Burrone O. R. Characterization and expression of alternatively spliced IgE heavy chain transcripts produced by peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 1;154(1):209–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batista F. D., Efremov D. G., Tkach T., Burrone O. R. Characterization of the human immunoglobulin epsilon mRNAs and their polyadenylation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Dec 11;23(23):4805–4811. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.23.4805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., Morrison S. L. Developmental regulation of membrane and secretory Ig gamma 2b mRNA. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):2072–2080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. L., Blattner F. R., Fitzmaurice L., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. Structure of genes for membrane and secreted murine IgD heavy chains. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):410–415. doi: 10.1038/296410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Sanchez D., Dotson A. R., Takenaka H., Saxon A. Diesel exhaust particles induce local IgE production in vivo and alter the pattern of IgE messenger RNA isoforms. J Clin Invest. 1994 Oct;94(4):1417–1425. doi: 10.1172/JCI117478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Sanchez D., Zhang K., Nutman T. B., Saxon A. Differential regulation of alternative 3' splicing of epsilon messenger RNA variants. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 15;155(4):1930–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fra A. M., Fagioli C., Finazzi D., Sitia R., Alberini C. M. Quality control of ER synthesized proteins: an exposed thiol group as a three-way switch mediating assembly, retention and degradation. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4755–4761. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenzi S., Fra A. M., Sparvoli A., Bet P., Rocco M., Sitia R. The efficiency of cysteine-mediated intracellular retention determines the differential fate of secretory IgA and IgM in B and plasma cells. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2477–2482. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman L. Characterization of four novel epsilon chain mRNA and a comparative analysis of genes for immunoglobulin E in rodents and man. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):159–167. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikutani H., Sitia R., Good R. A., Stavnezer J. Synthesis and processing of the alpha heavy chains of secreted and membrane-bound IgA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6436–6440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissim A., Jouvin M. H., Eshhar Z. Mapping of the high affinity Fc epsilon receptor binding site to the third constant region domain of IgE. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):101–107. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C., Davis F. M., Sun L. K., Liou R. S., Kim Y. W., Chang T. W. A new isoform of human membrane-bound IgE. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Gimmi E. R., Perry R. P. The developmentally regulated shift from membrane to secreted mu mRNA production is accompanied by an increase in cleavage-polyadenylation efficiency but no measurable change in splicing efficiency. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2324–2327. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. Regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA requires linkage of the poly(A) addition sites and is dependent on the length of the mu s-mu m intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8883–8887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. L., Perry R. P. The regulated production of mu m and mu s mRNA is dependent on the relative efficiencies of mu s poly(A) site usage and the c mu 4-to-M1 splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):726–738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Milstein C. P. Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes: evolutionary comparisons of C mu, C delta and C gamma genes and associated switch sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4509–4524. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. W., Liu F. T. Heterogeneous IgE glycoforms characterized by differential recognition of an endogenous lectin (IgE-binding protein). J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3024–3030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Choi E., Souza L., Carter C., Word C., Kuehl M., Eisenberg D., Wall R. Gene segments encoding transmembrane carboxyl termini of immunoglobulin gamma chains. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitia R., Neuberger M. S., Milstein C. Regulation of membrane IgM expression in secretory B cells: translational and post-translational events. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3969–3977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitia R., Neuberger M., Alberini C., Bet P., Fra A., Valetti C., Williams G., Milstein C. Developmental regulation of IgM secretion: the role of the carboxy-terminal cysteine. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):781–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90092-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truong M. J., Gruart V., Kusnierz J. P., Papin J. P., Loiseau S., Capron A., Capron M. Human neutrophils express immunoglobulin E (IgE)-binding proteins (Mac-2/epsilon BP) of the S-type lectin family: role in IgE-dependent activation. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):243–248. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercelli D., Helm B., Marsh P., Padlan E., Geha R. S., Gould H. The B-cell binding site on human immunoglobulin E. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):649–651. doi: 10.1038/338649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenberg A., de la Salle H., Hanau D., Liu F. T., Bieber T. Human keratinocytes release the endogenous beta-galactoside-binding soluble lectin immunoglobulin E (IgE-binding protein) which binds to Langerhans cells where it modulates their binding capacity for IgE glycoforms. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):777–785. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Word C. J., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. The murine immunoglobulin alpha gene expresses multiple transcripts from a unique membrane exon. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):887–898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. J., Owens R. J., Mackay G. A., Chan C. M., Shi J., Hide M., Francis D. M., Henry A. J., Sutton B. J., Gould H. J. Secretion of recombinant human IgE-Fc by mammalian cells and biological activity of glycosylation site mutants. Protein Eng. 1995 Feb;8(2):193–199. doi: 10.1093/protein/8.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Max E. E., Cheah H. K., Saxon A. Complex alternative RNA splicing of epsilon-immunoglobulin transcripts produces mRNAs encoding four potential secreted protein isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):456–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Saxon A., Max E. E. Two unusual forms of human immunoglobulin E encoded by alternative RNA splicing of epsilon heavy chain membrane exons. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):233–243. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]