Abstract
The human microbiome is influenced by a number of factors, including environmental exposure to microbes. Because many humans spend a large amount of time in built environments, it can be expected that the microbial ecology of these environments will influence the human microbiome. In an attempt to further understand the microbial ecology of built environments, the microbiota of car interiors was analyzed using culture dependent and culture independent methods. While it was found that the number and type of bacteria varied widely among the cars and sites tested, Staphylococcus and Propionibacterium were nearly always the dominant genera found at the locations sampled. Because Staphylococcus is of particular concern to human health, the characteristics of this genus found in car interiors were investigated. Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. aureus, and S. warnerii were the most prevalent staphylococcal species found, and 22.6% of S. aureus strains isolated from shared community vehicles were resistant to methicillin. The reduction in the prevalence of pathogenic bacteria in cars by using silver-based antimicrobial surface coatings was also evaluated. Coatings containing 5% silver ion additives were applied to steering wheels, placed in cars for five months and were found to eliminate the presence of culturable pathogenic bacteria recovered from these sites relative to controls. Together, these results provide new insight into the microbiota found in an important built environment, the automobile, and potential strategies for controlling the presence of human pathogens.
Keywords: Staphylococcus, microbial ecology of built environments, fomite, antimicrobial coatings
Introduction
The environments that humans encounter daily are sources of exposure to microbial communities and some are of potential concern to human health. Humans spend a significant amount of time indoors and thus the microbial ecology of indoor environments likely impacts the human microbiome (Klepeis et al. 2001; Kembel et al. 2012). In the past few years studies have emerged that examine the microbial communities of built environments. Current evidence suggests that indoor microbiomes originate mainly from outside air or the human skin (Pakarinen et al. 2008; Rintala et al. 2008; Grice & Segre 2011).
The microbial species present in a built environment are predominantly determined by exposure to microbes and selection of certain microbial types by the environment (Martiny et al. 2006). Previously, most studies examining the microbiome of built environments have concentrated on buildings, with a particular focus on health care settings (Rintala et al. 2008; Tringe et al. 2008; Amend et al. 2010; Kembel et al. 2012). In this study, both culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches were utilized to study the microbial ecology of the automobile built environment. Automobiles are potentially important fomites for exposure to microbes as many individuals spend a significant amount of time in this setting.
The Staphylococcus genus is of particular importance concerning fomite colonization and transmission to humans. Staphylococci frequently colonize human skin and mucosal surfaces, and thus are likely to be transmitted to inanimate surfaces that humans come into contact with (Safdar & Bradley 2008; Foster 2009; Pynnonen et al. 2011; Payne et al. 2013). Of particular concern is Staphylococcus aureus, which has the capacity to cause a variety of devastating infectious diseases (Lowy 1998; Klevens et al. 2007; Otto 2012). S. aureus infections and outbreaks have previously been associated with exposures to a multitude of contaminated fomites including whirlpools, razors, towels, handrails and toys (Miller & Diep 2008; Kassem 2011). Because staphylococci can colonize commonly touched inanimate objects, it is feasible that interior surfaces of automobiles could serve as reservoirs for pathogenic staphylococci and may play an important role in human colonization and infection.
This study addresses three general questions. First, what is the relative abundance of microbes at different frequently touched automobile surface interiors? Second, what is the composition of the microbial communities found in automobile interiors? Third, can automobile interior surfaces be designed to resist colonization by potential pathogens?
Materials and methods
Sample collection and bacterial culturing
Samples were collected from indicated automobile interior sites using Whatman neutralizing buffer swabs (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Piscataway, NJ, USA). These swabs were wetted in the provided storage/transport buffer and ∼ 6.5 cm2 of the indicated surface was sampled. The swabs were suspended in 2 ml of sterile phosphate buffer saline (PBS) and vortexed for 30 s to re-suspend the bacteria. For culturing, suspended samples were serially diluted in sterile PBS to extinction. Dilutions were plated on nutrient agar (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and TSA blood agar (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and incubated for 3 days at 30°C.
Bacterial isolate identification via partial 16S rRNA PCR amplification and sequencing
For 16S rRNA sequencing, single colonies were suspended in 100 μl of sterile water and heated to 100°C for 15 min. The suspension was centrifuged for 10 s at 6,400 rpm and 5 μl of each suspension were used as the template for PCR amplification of the 16S rRNA gene. PCR was performed using a mix of 25 μl of GoTaq® Green Master Mix (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), 18 μl of PCR certified water (Promega), and 1 μl each of forward primer (8FPL, AGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG) and reverse primer (806R, GGACTACCAGGGTATCTAAT) as previously described (Vornhagen et al. 2013). PCR products were cleaned using the QIAquick PCR Purification System (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The purified DNA was checked for quantity and purity using a NanoQuant Tecan M200 (Tecan, Durham, NC, USA). Sequencing was performed by the DNA Sequencing Core at the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor, MI, USA) using Applied Biosystems 3730xl DNA Analyzers (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA), BigDyev3.1 chemistry (MCLAB, San Francisco, CA, USA), and the protocols recommended by the manufacturer. Resulting partial 16s rRNA gene sequences were analyzed using CHROMAS (Brisbane, Australia) and compared to known sequences in the National Center for Biotechnology (NCBI) database using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST).
Culture-independent analysis
For culture-independent analysis, car interiors were sampled as described above and swab tips were removed and placed in sterile 2.0 ml vials. Samples were stored at −80°C prior to analysis by pyrosequencing. DNA was extracted using a modified Qiagen DNA preparation kit, which included incubating the swab in lysis buffer for 1 h, bead-beating utilizing a Qiagen Tissue Lyser, and column capture, purification and elution of DNA. PCR was conducted to generate barcoded amplicons with linkers. To prepare for FLX sequencing, the size and concentration of DNA fragments were determined by using DNA chips within a Bio-Rad Experion Automated Electrophoresis Station (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) and a TBS-380 Fluorometer (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). A sample containing 9.6 × 106 molecules μl−1 of double-stranded DNA with an average size of 625 bp was mixed with 9.6 million DNA capture beads and subsequently amplified by emulsion PCR. After bead recovery and enrichment, the bead-attached DNAs were denatured with NaOH, and sequencing primers were annealed. A two-region 454 sequencing run was performed on a 70 × 75 GS PicoTiterPlate using a Genome Sequencer FLX System (Roche, Nutley, NJ, USA). Following sequencing, all failed sequence reads, low quality sequence ends (Avg Q25), short reads < 150 bp (final mean length 412 bp) and tags and primers were removed. Sequence collections were then depleted of any non-bacterial sequences, sequences with ambiguous base calls, sequences with homopolymers > 5 bp in length, and chimeras as previously described (Bailey et al. 2010; Callaway et al. 2010; Capone et al. 2011; Handl et al. 2011). To determine the predicted identity of microorganisms in the remaining sequences, they were de-noised, de-replicated, and OTU clustering was performed using uClust (www.drive5.com). Sequences were then queried using BLASTn against a highly curated custom database of high quality 16s bacterial sequences derived and manually curated from NCBI. Using a NET analysis pipeline, the resulting BLASTn outputs were compiled and data reduction analysis was performed as described previously (Bailey et al. 2010; Callaway et al. 2010; Handl et al. 2011; Capone et al. 2011). Bacteria were classified at the closest well-characterized genus. Rarefaction analysis was conducted using QIIME (Caporaso et al. 2010). Sequences were de-noised and chimeras removed using UCHIME (Edgar et al. 2011). Sequences < 250 bp were removed and sequences > 250 bp were trimmed to 250 bp. Sequences were then normalized to 1,200 bp and 10 iterations of rarefaction were performed to evaluate the number of species present.
Measurements of antibacterial activity on surfaces
To determine the ability of S. aureus (strain ATCC6538P) to colonize different engineered car surfaces, the procedure outlined in the Japanese International Standard for Measurement of antibacterial activity on plastic surfaces, JIS Z 2801, was utilized. Briefly, two surfaces were examined: a polycarbonate/ABS (Sabic Cycoloy MC8002, Ford Motor Company, Dearborn, MI, USA) hard plastic surface with the same formulation used to mold many interior car parts and a soft polyurethane foam surface used to cover steering wheels. The PC/ABS substrata were coated with a black, two-component, solvent borne urethane coating (Product 318LE/303LE, Red Spot Paint, Evansville, IN, USA) designed for interior automotive trim. The polyurethane foam substrates were coated with a 1-component waterborne coating (Red Spot Paint, product 458 W) using an in-mold process typically used for automotive steering wheels. In addition to a control formulation of each of the above coatings, which contained no antimicrobial additives, four formulations of each coating were prepared with the addition of antimicrobial additives to the liquid coatings described above (458 W and 318LE/303LE). These coatings contained: 3% Agion silver ion (Sciessent, Wakefield, MA, USA), 5% Agion silver ion, 1% micronized polyolefin wax coated with nanosilver (Deurex MXAg 9,520, Deurex AG, Germany), and 4% silane quaternary ammonium salt (Biosafe HM4100, Biosafe, Pittsburgh, PA, USA). Each formulation was sprayed on the respective substratum at a thickness of ∼25 μm. After coating, the panels were cut into 50 × 50 mm squares and sterilized by submerging in 70% EtOH. S. aureus test inoculum of 6 × 105 was generated by suspending bacteria in dilute nutrient broth (1:500) and 400 μl of the suspension were placed on the plastic surfaces that were placed in the Petri dish. The surfaces were covered with a sterile piece of stomacher bag (40 × 40 mm) that spread the inoculum evenly over the surface. Samples were incubated at 35°C at a relative humidity > 90% for 24 h. Bacteria were recovered from the plastic surfaces by adding 10 ml of SCDLP broth (17 g l−1 casein peptone, 3 g l−1 soybean peptone, 5 g l−1 NaCl, 2.5 g l−1 Na2HPO4, 2.5 g l−1 glucose, 1 g l−1 lecithin, 7 g l−1 poly-oxyethylene sorbitan monooleate) to the plastic surface and vigorously pipetting up and down to remove attached bacteria. The number of viable colony-forming units (CFUs) remaining on the surfaces was determined by plating serial dilutions in nutrient agar, incubating for 48 h at 35°C and counting colonies.
To assess the long-term efficacy of the coatings formulated to resist microbial colonization, some coated materials were aged via an artificial accelerated weathering protocol, SAE J2412. During the test, surface specimen exposures were monitored based on measured light at 1.06 W m−2 (@ 420 nm) using a lamp and filter combination that closely mimics the wavelength distribution of light transmitted through automotive glass. Specimens were cycled between a 1 h dark cycle at 38°C and 95% humidity and a 3 h light cycle at 70°C and 50% humidity. Surface specimens were removed after exposures of 2,500 kJ m−2 and 5,000 kJ m−2 for evaluation.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
All S. aureus isolates were tested for susceptibility to the antimicrobials listed in Table 3 using the Clinical and Lab Standards Institute broth microdilution method (Bou 2007). Mueller–Hinton broth was purchased from BDD and MIC plates were incubated at 35°C for 24 h. S. aureus strains ATCC 25,923 and ATCC 29,213 were utilized as control strains for each antimicrobial susceptibility assay.
Table 3.
Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles for methicillin sensitive (MSSA) and methicillin resistant (MRSA) S. aureus isolates collected from shared cars.
| Number of susceptible isolates (%) among |
||
|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | MSSA (n = 120) | MRSA (n = 35) |
| Penicillin | 11 (9.1) | 0 (0) |
| Oxacillin | 120 (100) | 0 (0) |
| Erythromycin | 94 (78.3) | 8 (22.8) |
| Gentamicin | 120 (100) | 35 (100) |
| Levofloxacin | 120 (100) | 12 (34.3) |
| Rifampin | 120 (100) | 35 (100) |
| Tetracycline | 118 (98.3) | 33 (94.3) |
| Vancomycin | 120 (100) | 35 (100) |
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using a 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Results are expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) of the mean, unless otherwise indicated.
Results
Relative abundance of colony-forming units at interior car locations
To gain insight into relative abundance of bacterial colonization in different areas of car interiors which might serve as fomites, locations that were reasoned to come into frequent contact with the driver were swabbed (indicated in Figure 1A). A total of 18 cars from the Ford Motor Company employee fleet were swabbed. Analysis of colony-forming units (CFUs) from each site revealed that each swabbed location had culturable bacteria present and that there was significant variation in total CFUs in each location from car to car (Figure 1B). However, by this analysis, the most highly colonized locations with over 100 culturable CFUs per 6.5 cm2 surface area were areas of frequent touching by the occupants, including locations on the steering wheel (A, K), the gear shifter (C), door handles and window switches (E, G), and the center console near the beverage holder (D).
Figure 1.

Analysis of CFUs present at different car interior locations. (A) Image of a typical car interior with swab sampling sites labels. Swabs of 6.5 × 6.5 cm area were collected from (A) steering wheel, (B) radio volume knob, (C) gear shifter, (D) center console, (E) door latch, (F) door lock, (G) door lock control, (H) door handle, (I) window control, (J) cruise control button, and (K) interior steering wheel. (B) Number of CFUs isolated from swab locations A–K from 18 different cars. ns = not sampled.
Culture independent analysis of bacteria in car interiors
To gain insight into the types of bacteria present on highly colonized areas culture independent analysis was conducted. Steering wheels (A), gear shifters (C), and the center console (D) were swabbed in five cars (car numbers: 19, 21, 22, 23, 24) and extracted DNA was subjected to bTEFAP FLX massively parallel pyrosequencing. Each sampled site possessed a unique bacterial community at the genus level (Table 1). The most dominant bacterial genera that were present at all sampled sites were Staphylococcus and Propionibacterium.
Table 1.
Estimated relative abundance of bacterial genera (%) from swabs of the indicated car locations as determined by bTEFAP.
| Genus | 19A | 19C | 19D | 21C | 21D | 22C | 22D | 23A | 23C | 23D | 24A | 24C | 24D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus | 77.1 | 74.1 | 10.2 | 19.1 | 3.32 | 14.0 | 63.7 | 12.5 | 10.5 | 1.05 | 19.7 | 29.2 | 28.2 |
| Propionibacterium | 9.72 | 17.5 | 3.5 | 7.44 | 0.50 | 6.04 | 2.75 | 22.6 | 8.53 | .06 | 21.3 | 17.4 | 0.08 |
| Pantoea | 1.21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 5.01 | 0 | 98.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Exiguobacterium | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 91.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | .03 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Acidovorax | 1.23 | 0.17 | 6.55 | 3.41 | 0 | 9.22 | 0.02 | 7.55 | 3.75 | 0 | 11.5 | 2.96 | 23.5 |
| Streptococcus | 1.02 | 0.07 | 4.17 | 7.30 | 0 | 12.5 | 5.49 | 5.80 | 0 | 0.06 | 9.93 | 13.2 | 5.15 |
| Clostridium | 0.15 | 1.16 | 0 | 14.3 | 0 | 3.00 | 0.11 | 0.23 | 13.1 | 0.03 | 1.79 | 5.67 | 1.93 |
| Mycobacterium | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0 | 38.0 | .05 | 0 | 0 | 0.13 |
| Massilia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.3 | 0.04 | 1.83 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 0 | 8.45 |
| Acinetobacter | 0.64 | 1.32 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0 | 2.61 | 0 | 1.66 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 9.06 | 1.48 | 3.22 |
| Micromonospora | 0.05 | 0 | 19.0 | 0 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sphingomonas | 0 | 0 | 5.89 | 0 | 0.05 | 4.99 | 0 | 0 | 1.72 | 0.02 | 3.02 | 0 | 2.92 |
| Corynebacterium | 0.61 | 0 | 0 | 2.49 | 0 | 0.19 | 0 | 4.03 | 0 | 0 | 7.06 | 6.89 | 1.42 |
| Dehalococcoides | 0.07 | 0 | 10.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.71 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Brevundimonas | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gemella | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.10 | 0.24 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 5.21 | 0 |
| Trichococcus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pseudomonas | 0 | 1.02 | 0.03 | 3.20 | 0.08 | 2.18 | 0.68 | 1.79 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 5.66 |
| Knoellia | 0.01 | 0 | 11.3 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Maricaulis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Geitlerinema | 1.78 | 0.11 | 0 | 5.76 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 2.34 | 0.34 |
| Microbacterium | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.10 | 0 | 7.54 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 1.80 |
| Micrococcus | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 17.3 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 7.87 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.77 | 0.82 | 0 |
| Ewingella | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.03 | 9.29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bacillus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.32 | 0.07 | 5.23 | 3.07 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 | 7.13 | 7.35 | 0 |
| Roseomonas | 0.43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.93 |
| Xylanimicrobium | 0.58 | 0.02 | 7.47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Kineococcus | 1.65 | 0.02 | 7.18 | 0 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Thermomonas | 0 | 0 | 7.58 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Veillonella | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 1.22 | 5.75 |
| Ralstonia | 0 | 0 | 0.86 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.26 | 5.53 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.60 |
| Solimonas | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6.90 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Comamonas | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0 | 1.37 | 0.02 | 2.03 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.98 | 0.15 | 1.72 |
| Streptomyces | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.93 | 1.11 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 4.99 | 0 | 0 |
| Stenotrophomons | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.25 | 0 | 0 | 1.88 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.15 |
| Janibacter | 0 | 1.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.09 | 2.77 | 3.42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Other genera | 3.51 | 3.43 | 4.84 | 1.85 | 2.05 | 3.01 | 3.92 | 3.33 | 6.84 | 0.36 | 2.09 | 5.86 | 1.05 |
Note: 19, 21, 22, 23, 24 are car identifiers and locations are A – steering wheel, C – gear shift knob, D – area near cup holder (see Figure 1A). The relative percentage of sequences assigned to a given taxonomic classification (genera) for each individual sample is arranged from highest to lowest across samples. The 36 most abundant genera are shown and the remaining that were at low levels are grouped as together as ‘other genera’.
Genus-level differences extended to the level of bacterial class and upon averaging across samples from the five cars, 38.3% of the sequences derived from bTEFAP were members of the class Bacilli (car 19: 52.1%, car 21: 56.0%, car 22: 55.9%, car 23: 7.4%, car 24: 20.3%); 21.4% were members of the class Actinobacteria (car 19: 28.5%, car 21: 10%, car 22: 15.9%, car 23: 25.1%, car 24: 27.2%), 10.9% were Gammaproteobacteria (car 19: 3.2%, car 21: 4.1%, car 22: 8.5%, car 23: 38.7%, car 24: 7.5%); 9.47% were Betaproteobacteria (car 19: 3.3%, car 21: 12.7%, car 22: 5.6%, car 23: 8.2%, car 24: 17.8%); 6.8% were Alphaproteobacteria (car 19: 4.1%, car 21: 2.5%, car 22: 7.2%, car 23: 12.1%, car 24: 8.2%), and 5.6% were Clostridia (car 19: 1.9%, car 21: 8.9%, car 22: 3.1%, car 23: 5.3%, car 24: 9.1%). The remaining 7.5% comprised 10 other bacterial classes.
Staphylococcus species present in car interiors
Because the genus Staphylococcus was determined to be a dominant member of the car interior microbiome and many staphylococcal species have the potential to be dangerous opportunistic pathogens, the identity of the staphylococcal species present was determined. Isolates that grew on nutrient agar and blood agar plates for the culture-dependent CFU analysis (Figure 1B) were patched onto mannitol salt agar, which is a selective medium for members of the Staphylococcus genus. DNA was isolated from 87 patched colonies that grew on mannitol salt agar, 16s rRNA DNA was amplified and sequenced, and the resulting sequences were analyzed to determine Staphylococcus species (Table 2). Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. aureus, and S. warneii were found to be the most frequently isolated staphylococci, making up 87% of the staphylococcal isolates (representing 43, 31, and 13% respectively).
Table 2.
Staphylococcal species present at different swab locations. Ratio indicates number of positive samples per Staphylococcus organism isolated at the site.
| Swab location | S. aureus | S. epidermidis | S. caprae | S. sciuri | S. capitis | S. cohnii | S. saprophyticus | S. xylosus | S. warneii | S. hominis | S. haemolyticus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8/18 | 9/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 1/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 |
| B | 2/9 | 5/9 | 1/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 1/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 |
| C | 6/15 | 6/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 1/15 | 1/15 | 1/15 |
| D | 5/18 | 10/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 | 3/18 | 0/18 | 0/18 |
| E | 2/9 | 4/9 | 1/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 0/9 | 1/9 | 0/9 | 1/9 |
| J | 2/10 | 3/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 1/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 4/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| K | 2/8 | 1/8 | 0/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 0/8 | 0/8 | 0/8 |
| A–K | 27/87 | 38/87 | 2/87 | 1/87 | 2/87 | 1/87 | 1/87 | 1/87 | 11/87 | 1/87 | 2/87 |
Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of S. aureus isolates
The ability to withstand antibiotic treatment is one of the reasons S. aureus is a prominent and dangerous pathogen. Of particular concern is methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), which has become a major nosocomial and community pathogen. S. aureus strains that are methicillin resistant have a mecA gene that encodes for a unique penicillin-binding protein that has decreased affinity for β-lactam antibiotics (Lambert 2005). To determine the prevalence of MRSA isolates from car interiors, the steering wheels of 30 community-shared cars (Zipcars) were swabbed and streaked onto mannitol salt agar. Colonies that grew and were able to ferment mannitol were confirmed to be S. aureus by 16s rRNA amplification and sequencing. On average, at least five S. aureus isolates (155 total) from each of the 30 cars was tested for methicillin resistance by plating culture dilutions onto tryptic soy agar containing 10 μg ml−1 methicillin. Of the 155 isolates tested, 35 (22.6%) were found to be methicillin resistant and these isolates were confirmed as mecA positive by PCR. Isolates (35 MRSA and 120 MSSA) were also tested for susceptibility to other clinically relevant antibiotics (Table 3). All MSSA isolates were sensitive to oxacillin, gentamicin, levofloxacin, rifampin, and vancomycin. In addition most were sensitive to tetracycline (98%) and erythromycin (78%), but only 9% were sensitive to penicillin. The 35 MRSA isolates were all sensitive to gentamicin, rifampin, and vancomycin, and 94% were sensitive to tetracycline. Susceptibility to levofloxacin and erythromycin was 34% and 22% respectively, and as expected all were resistant to the β-lactams penicillin and oxacillin.
Analysis of antimicrobial surfaces for S. aureus colonization
Considering that antibiotic resistant S. aureus was frequently found in car interiors and this environment might serve as a fomite that could lead to increased colonization of occupants, strategies to reduce or eliminate S. aureus colonization were investigated. Since most interior touch surfaces are painted to enhance the component's appearance or feel, antimicrobial additives were added to the typical coating formulations to assess the efficacy in inhibiting microbial colonization (Figure 2). Both steering wheel grip (soft) and center trim (hard) coating formulations were assessed for the ability to resist S. aureus colonization. Four automotive paint formulations containing commercially available antimicrobial additives (3% silver ion, 5% silver ion, 1% nanosilver coated micronized wax, and 4% silane quaternary ammonium salt) were used to coat both hard and soft surfaces and all of these significantly reduced the ability of S. aureus to colonize the surface over a 24 h time period (Figure 2A and 2B). To test the durability of these antimicrobial coated surfaces, they were exposed to an artificial weathering process that mimics exposures likely to occur inside an automobile (UV light, heat, and humidity conditions common to car interiors). The 1% nanosilver (Deurex) and 4% silane quaternary ammonium salt (Biosafe) treated surfaces lost anti-S. aureus colonization properties after artificial weathering, whereas the silver ion treated surfaces retained the ability to resist colonization (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
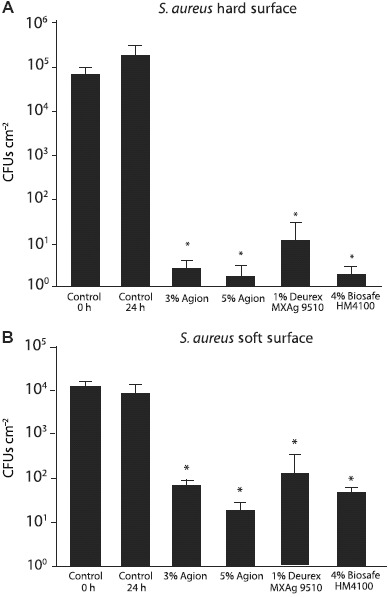
Analysis of car interior plastics treated with antimicrobial formulations for the ability to resist S. aureus surface colonization. Hard plastic surfaces (A) or soft plastic surfaces (B) that were either untreated (control) or sprayed with the indicated antimicrobial formulations were exposed to 6 × 105 CFUs of S. aureus and the number of CFUs present after 24 h was determined. Error bars show the SE of the mean; *p < 0.005 vs 24 h control.
Figure 3.
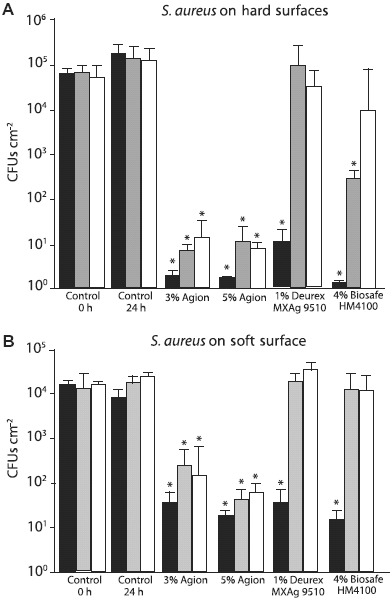
Analysis of artificially weathered car interior plastics treated with antimicrobial formulations for the ability to resist S. aureus surface colonization. Hard plastic surfaces (A) or soft plastic surfaces (B) that were either untreated (control) or sprayed with indicated antimicrobial formulations were artificially weathered then incubated with upto 6 × 105 CFUs S. aureus. The number of CFUs present after 24 h was determined. Black bars are unweathered surfaces, gray bars were exposed to 2,500 kJ m−2, and white bars were exposed to 5,000 kJ m−2. Error bars the SE of the mean; *p < 0.005 vs the comparable 24 h control.
Analysis of antimicrobial surfaces in cars
Next 5% Agion silver ion treated surfaces were examined to determine whether they would reduce pathogen colonization when placed in automobiles. The steering wheels of five cars from the Ford Motor Company motor fleet which are driven daily were swabbed at hard trim piece locations (T1–3) or soft exterior locations (S1–5) on standard production steering wheels (Figure 4A). Swabs of the non-silver treated production steering wheel locations were plated on nutrient agar and TSA blood agar to determine total CFUs per location (Figure 4B, TPro & SPro). Swabs were also plated onto mannitol agar and S. aureus and S. epidermidis were confirmed to be found on every production steering wheel by 16s rRNA analysis. After swabbing, the production steering wheel was removed and replaced with a 5% silver ion treated steering wheel. Five months later the steering wheel was swabbed at the same locations and CFUs were determined (Figure 4B, TAg & SAg). All swabs from the silver treated steering wheels had significantly fewer CFUs. 16s rRNA analysis of the colonies that came from swabbed silver treated steering wheels revealed all of the isolates were members of the Bacillus genus (B. subtillis, B. sphaericus, B. firmus, B. megaterium, B. simplex).
Figure 4.
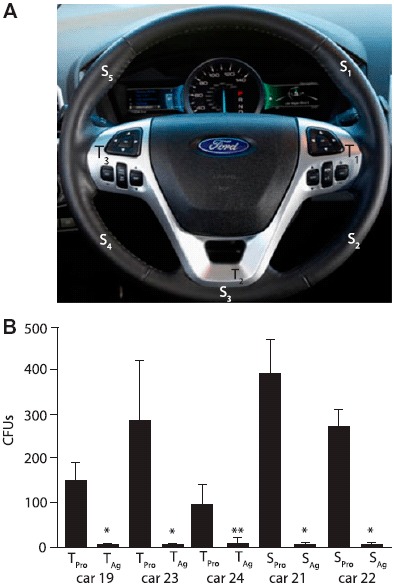
Analysis of CFUs present on production steering wheels vs silver treated steering wheels. (A) Locations of swabbing at hard trim piece locations (T1–3) or soft exterior locations (S1–5). (B) Number of CFUs isolated from swab locations from trim (T) or exterior steering wheel locations (S) from production (Pro) vs silver coated (Ag) steering wheels. *p < 0.005 vs the comparable production piece; **p < 0.05 vs the comparable production piece.
Discussion
Despite the fact that humans spend a significant amount of time inside automobiles, very little is known about the microbial ecology of car interiors and how this might impact the occupant's microbiome. In this study, bacterial communities of frequently touched car interior surfaces were enumerated and analyzed. These results indicate that the most highly colonized locations were areas that would be suspected to have frequent touching by the occupants, including locations on the steering wheel, the gear shifter, door handles and window switches, and the center console near the beverage holder (Figure 1). The bacterial communities of steering wheels, gear shifters, and the center console were analyzed by culture independent pyrosequencing and though this revealed novel populations at each site, two genera, viz. – Staphylococcus and Propionibacterium were the dominant members at most sites. Members of these genera commonly colonize human skin, which suggests the prevalent genera which are able to persist on car interior surfaces are deposited there by skin to surface contact.
Because several members of the staphylococcal genus are important human pathogens, the species present were determined and it was found that the most prevalent were S. epidermidis (43%), S. aureus (31%), and S. warneii (13%) (Table 2). A relatively high percentage (22.6%) of methicillin resistant S. aureus was also isolated from shared community driven cars (Table 3).
This analysis suggests that car interiors may be important environmental reservoirs that are capable of harboring antibiotic resistant S. aureus. This is of potential interest because colonization by S. aureus significantly increases the likelihood of a person developing several types of infections (Stenehjem & Rimland 2013). S. aureus can readily be transferred from fomites to people. Colonized individuals can shed the organism into the environment, contaminating surfaces, which would allow for transfer to other individuals. S. aureus infection is notable for its ability to repeatedly infect patients, especially at sites involving the skin (Kaplan 2005; Crum et al. 2006) and there are indications that transmission among household members is common (Begier et al. 2004; Miller & Diep 2008). Therefore, limiting skin exposures via fomites may be one useful strategy to reduce infection and spread in these scenarios.
In order to explore strategies that limit colonization by pathogenic microbes, plastics used in the production of car interiors were coated with antimicrobial silver formulations and tested for their ability to resist colonization by S. aureus. All silver treated surfaces displayed the ability to resist S. aureus colonization. However exposure to artificial weathering revealed that some treated surfaces (Agion) retained anti-colonization properties, while others lost the ability to resist colonization (Deurex MXAg9510 and Biosafe). It is unclear why weathering caused these differences.
Finally the ability of 5% Agion silver ion treated surfaces in the form of steering wheels and trim within steering wheels was examined for the ability to resist pathogen colonization when placed inside cars. Initial swabbing of non-antimicrobial production steering wheels revealed relatively high levels of bacteria colonization by CFU analysis and the presence of S. aureus and S. epidermidis on each steering wheel. These production steering wheels were replaced with steering wheels that had been treated with 5% Agion, and five months later swabbing revealed significantly fewer CFUs and the absence of all staphylococcal species. The only culturable microbes present on these surfaces were members of the spore-forming Bacillus genus.
Overall these results suggest bacteria present on frequently touched car interior surfaces likely originate from human skin. The deposit of some of these microbes on car interiors could have undesired consequences. For example, many skin microbes have the capacity to produce unpleasant odors (Dumas et al. 2009; Ara et al. 2013). Others, such as S. aureus, have the capacity to render more serious consequences and could potentially be a threat to human health. In addition, the presence of drug resistant S. aureus in cars used by multiple people could lead to the dissemination of this pathogen.
Environmental sources of S. aureus are clearly not isolated to cars. In hospitals, MRSA is frequently isolated from nurse workstations, bed spaces, pagers, and stethoscopes (Smith 1996; Singh et al. 2002; Hardy et al. 2006). Measures to control MRSA in these environments have likely contributed to limiting MRSA infections (Vriens et al. 2002; Meek 2004) and this success lends credence to the notion that environmental sources are an important component of MRSA pathogenesis. It is possible that strategies to reduce S. aureus car interior colonization, like those examined here, could reduce transmission, colonization and infection by this dangerous pathogen. It is proposed that individuals experiencing frequent S. aureus skin infections or those concerned about S. aureus carrier status consider the surfaces of car interiors as potential reservoirs for S. aureus.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant to BRB from Ford Motor Company. The authors would like to thank Jeff Scheu (Red Spot Paint) and Janice Gould (Red Spot Paint) for coordinating the development and formulation of antimicrobial coatings including preparation of all painted test plaques.
References
- Amend AS, Seifert KA, Samson R, Bruns TD. Indoor fungal composition is geographically patterned and more diverse in temperate zones than in the tropics. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 2010;107::13748–13753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000454107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ara K, Hama M, Akiba S, Koike K, Okisaka K, Hagura T, Kamiya T, Tomita F. Foot odor due to microbial metabolism and its control. Can J Microbiol. 2013;52::357–364. doi: 10.1139/w05-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey MT, Dowd SE, Parry NMA, Galley JD, Schauer DB, Lyte M. Stressor exposure disrupts commensal microbial populations in the intestines and leads to increased colonization by Citrobacter rodentium. Infect Immun. 2010;78::1509–1519. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00862-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begier EM, Frenette K, Barrett NL, Mshar P, Petit S, Boxrud DJ, Watkins-Colwell K, Wheeler S, Cebelinski EA, Glennen A, et al. A high-morbidity outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among players on a college football team, facilitated by cosmetic body shaving and turf burns. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39::1446–1453. doi: 10.1086/425313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bou G. linkspringercom. vol 391. Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; 2007. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) analysis and susceptibility testing of MRSA. pp. 29–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaway TR, Dowd SE, Edrington TS, Anderson RC, Krueger N, Bauer N, Kononoff PJ, Nisbet DJ. Evaluation of bacterial diversity in the rumen and feces of cattle fed different levels of dried distillers grains plus solubles using bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing. J Anim Sci. 2010;88::3977–3983. doi: 10.2527/jas.2010-2900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone KA, Dowd SE, Stamatas GN, Nikolovski J. Diversity of the human skin microbiome early in life. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131::2026–2032. doi: 10.1038/jid.2011.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Meth. 2010;7::335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum NF, Lee RU, Thornton SA, Stine OC, Wallace MR, Barrozo C, Keefer-Norris A, Judd S, Russell KL. Fifteen-year study of the changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Med. 2006;119::943–951. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas ER, Michaud AE, Bergeron C, Lafrance JL, Mortillo S, Gafner S. Deodorant effects of a supercritical hops extract: antibacterial activity against Corynebacterium xerosis and Staphylococcus epidermidis and efficacy testing of a hops/zinc ricinoleate stick in humans through the sensory evaluation of axillary deodorancy. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8::197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1473-2165.2009.00449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics. 2011;27::2194–2200. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster TJ. Colonization and infection of the human host by staphylococci: adhesion, survival and immune evasion. Vet Dermatol. 2009;20::456–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3164.2009.00825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grice EA, Segre JA. The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9::244–253. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handl S, Dowd SE, Garcia-Mazcorro JF, Steiner JM, Suchodolski JS. Massive parallel 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing reveals highly diverse fecal bacterial and fungal communities in healthy dogs and cats. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2011;76::301–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy KJ, Oppenheim BA, Gossain S, Gao F, Hawkey PM. Relationship between environmental contamination with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and patients’ acquisition of MRSA. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2006;27::127–132. doi: 10.1086/500622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan SL. Treatment of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24::457. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000164162.00163.9d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassem II. Chinks in the armor: the role of the nonclinical environment in the transmission of Staphylococcus bacteria. Am J Infect Control. 2011;39::539–541. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2010.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kembel SW, Jones E, Kline J, Northcutt D, Stenson J, Womack AM, Bohannan BJ, Brown GZ, Green JL. Architectural design influences the diversity and structure of the built environment microbiome. ISME J. 2012;6::1469–1479. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klepeis NE, Nelson KE, Ott WR, Robinson J, Tsang AM, Switzer P, Behar JV, Hern SC, Engelmann S. The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): a resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol. 2001;11::231–252. doi: 10.1038/sj.jea.7500165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Dumyati G, Townes JM, et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298::1763–1771. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.15.1763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: modified target sites. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2005;57::1471–1485. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2005.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339::520–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199808203390806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny JBH, Bohannan BJM, Brown JH, Colwell RK, Fuhrman JA, Green JL, Horner-Devine MC, Kane M, Krumins JA, Kuske CR, et al. Microbial biogeography: putting microorganisms on the map. Nature Rev Microbiol. 2006;4::102–112. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek C. Isolate patients, screen staff to fight MRSA. Can Med Assoc J. 2004;171::1158–1158. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1041611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller LG, Diep BA. Colonization, fomites, and virulence: rethinking the pathogenesis of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46::752–760. doi: 10.1086/526773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto M. MRSA virulence and spread. Cell Microbiol. 2012;14::1513–1521. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakarinen J, Hyvärinen A, Salkinoja-Salonen M, Laitinen S, Nevalainen A, Mäkelä MJ, Haahtela T, von Hertzen L. Predominance of Gram-positive bacteria in house dust in the low-allergy risk Russian Karelia. Environ Microbiol. 2008;10::3317–3325. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne DE, Martin NR, Parzych KR, Rickard AH, Underwood A, Boles BR. Tannic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus surface colonization in an IsaA-dependent manner. Infect Immun. 2013;81::496–504. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00877-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pynnonen M, Stephenson RE, Schwartz K, Hernandez M, Boles BR. Hemoglobin promotes Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7::e1002104. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rintala H, Pitkaranta M, Toivola M, Paulin L, Nevalainen A. Diversity and seasonal dynamics of bacterial community in indoor environment. BMC Microbiol. 2008;8::56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safdar N, Bradley EA. The risk of infection after nasal colonization with Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Med. 2008;121::310–315. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.07.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh D, Kaur H, Gardner WG, Treen LB. Bacterial contamination of hospital pagers. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2002;23::274–276. doi: 10.1086/502048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith MA. Contaminated stethoscopes revisited. Arch Intern Med. 1996;156::82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenehjem E, Rimland D. MRSA nasal colonization burden and risk of MRSA infection. Am J Infect Control. 2013;41::405–410. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2012.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tringe SG, Zhang T, Liu X, Yu Y, Lee WH, Yap J, Yao F, Suan ST, Ing SK, Haynes M, et al. The airborne metagenome in an indoor urban environment. PLoS ONE. 2008;3::e1862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vornhagen J, Stevens M, McCormick DW, Dowd SE, Eisenberg JNS, Boles BR, Rickard AH. Coaggregation occurs amongst bacteria within and between biofilms in domestic showerheads. Biofouling. 2013;29::53–68. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2012.744395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriens M, Blok H, Fluit A, Troelstra A, Werken CVD, Verhoef J. Costs associated with a strict policy to eradicate methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Dutch University Medical Center: a 10-year survey. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 2002;21::782–786. doi: 10.1007/s10096-002-0811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


