Abstract
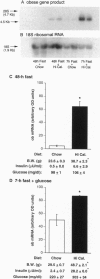
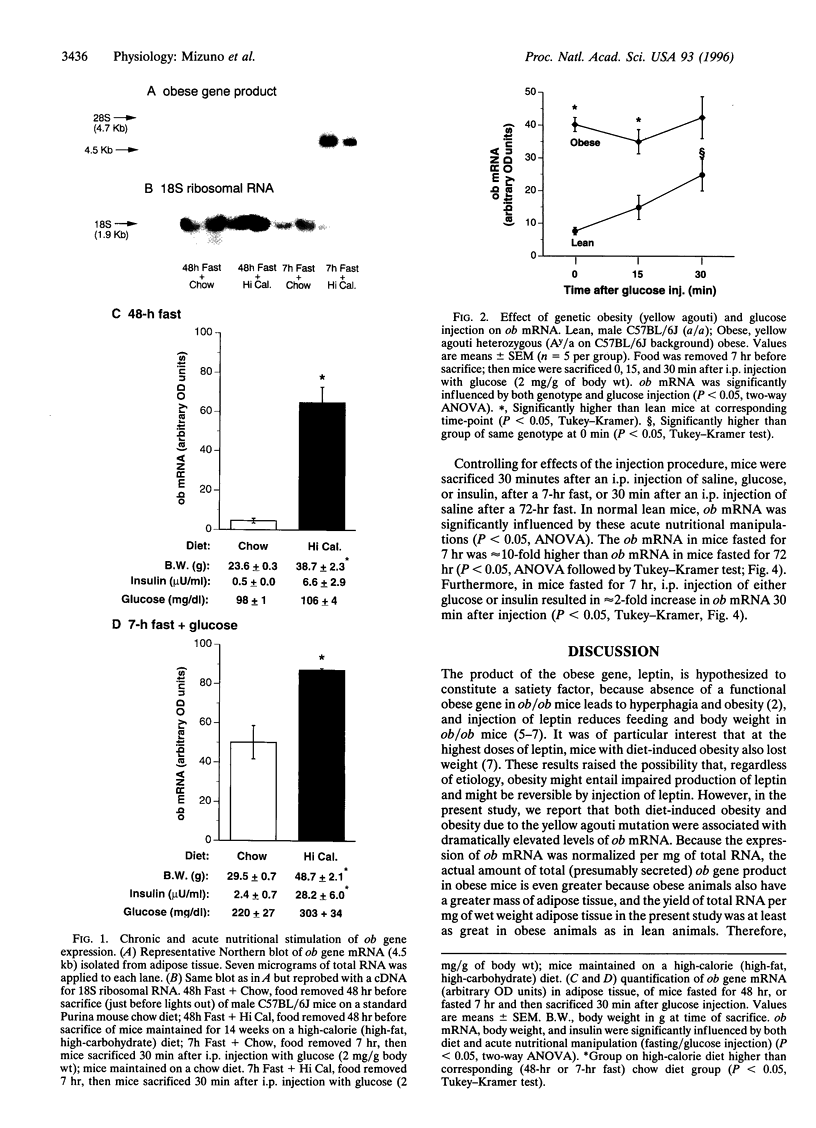
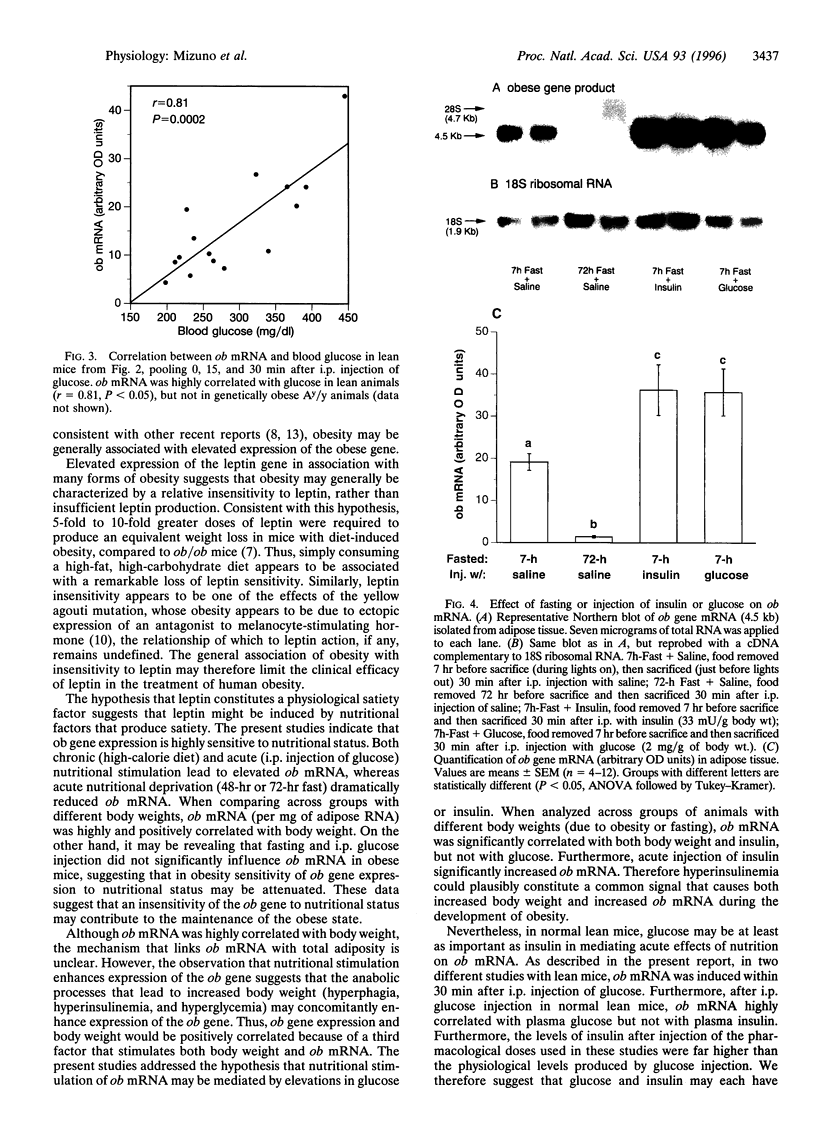
Mutations in the obese (ob) gene lead to obesity. This gene has been recently cloned, but the factors regulating its expression have not been elucidated. To address the regulation of the ob gene with regard to body weight and nutritional factors, Northern blot analysis was used to assess ob mRNA in adipose tissue from mice [lean, obese due to diet, or genetically (yellow agouti) obese] under different nutritional conditions. ob mRNA was elevated in both forms of obesity, compared to lean controls, correlated with elevations in plasma insulin and body weight, but not plasma glucose. In lean C57BL/6J mice, but not in mice with diet-induced obesity, ob mRNA decreased after a 48-hr fast. Similarly, in lean C57BL/6J controls, but not in obese yellow mice, i.p. glucose injection significantly increased ob mRNA. For up to 30 min after glucose injection, ob mRNA in lean mice significantly correlated with plasma glucose, but not with plasma insulin. In a separate study with only lean mice, ob mRNA was inhibited >90% by fasting, and elevated approximately 2-fold 30 min after i.p. injection of either glucose or insulin. These results suggest that in lean animals glucose and insulin enhance ob gene expression. In contrast to our results in lean mice, in obese animals ob mRNA is elevated and relatively insensitive to nutritional state, possibly due to chronic exposure to elevated plasma insulin and/or glucose.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks P. J., Kaplitt M. G., Kleopoulos S. P., Funabashi T., Mobbs C. V., Pfaff D. W. Detection of messenger RNA and low-abundance heteronuclear RNA with single-stranded DNA probes produced by amplified primer extension labeling. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993 Dec;41(12):1761–1766. doi: 10.1177/41.12.8245424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campfield L. A., Smith F. J., Guisez Y., Devos R., Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.7624778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen N. G., Romsos D. R. Enhanced sensitivity of pancreatic islets from preobese 2-week-old ob/ob mice to neurohormonal stimulation of insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1995 Feb;136(2):505–511. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.2.7835283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L. Effects of parabiosis of obese with diabetes and normal mice. Diabetologia. 1973 Aug;9(4):294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01221857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Considine R. V., Considine E. L., Williams C. J., Nyce M. R., Magosin S. A., Bauer T. L., Rosato E. L., Colberg J., Caro J. F. Evidence against either a premature stop codon or the absence of obese gene mRNA in human obesity. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jun;95(6):2986–2988. doi: 10.1172/JCI118007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaas J. L., Gajiwala K. S., Maffei M., Cohen S. L., Chait B. T., Rabinowitz D., Lallone R. L., Burley S. K., Friedman J. M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.7624777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Gardner L. B., Barrett E. J. Insulin and glucose suppress hepatic glycogenolysis by distinct enzymatic mechanisms. Metabolism. 1993 Dec;42(12):1546–1551. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90149-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D., Willard D., Patel I. R., Kadwell S., Overton L., Kost T., Luther M., Chen W., Woychik R. P., Wilkison W. O. Agouti protein is an antagonist of the melanocyte-stimulating-hormone receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 27;371(6500):799–802. doi: 10.1038/371799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maffei M., Fei H., Lee G. H., Dani C., Leroy P., Zhang Y., Proenca R., Negrel R., Ailhaud G., Friedman J. M. Increased expression in adipocytes of ob RNA in mice with lesions of the hypothalamus and with mutations at the db locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6957–6960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelleymounter M. A., Cullen M. J., Baker M. B., Hecht R., Winters D., Boone T., Collins F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):540–543. doi: 10.1126/science.7624776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath E. A., Thenen S. W. Use of tritiated water for measurement of 24-hour milk intake in suckling lean and genetically obese (ob/ob) mice. J Nutr. 1979 May;109(5):840–847. doi: 10.1093/jn/109.5.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Kahn A. Transcriptional control of metabolic regulation genes by carbohydrates. FASEB J. 1994 Jan;8(1):28–35. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.1.8299888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. T., Gill A. M., Frigeri L. G., Barsh G. S., Wolff G. L. Obesity, diabetes, and neoplasia in yellow A(vy)/- mice: ectopic expression of the agouti gene. FASEB J. 1994 May;8(8):479–488. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.8.8181666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., Friedman J. M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):425–432. doi: 10.1038/372425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]