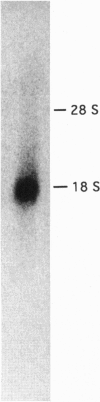
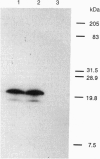
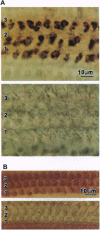
Abstract
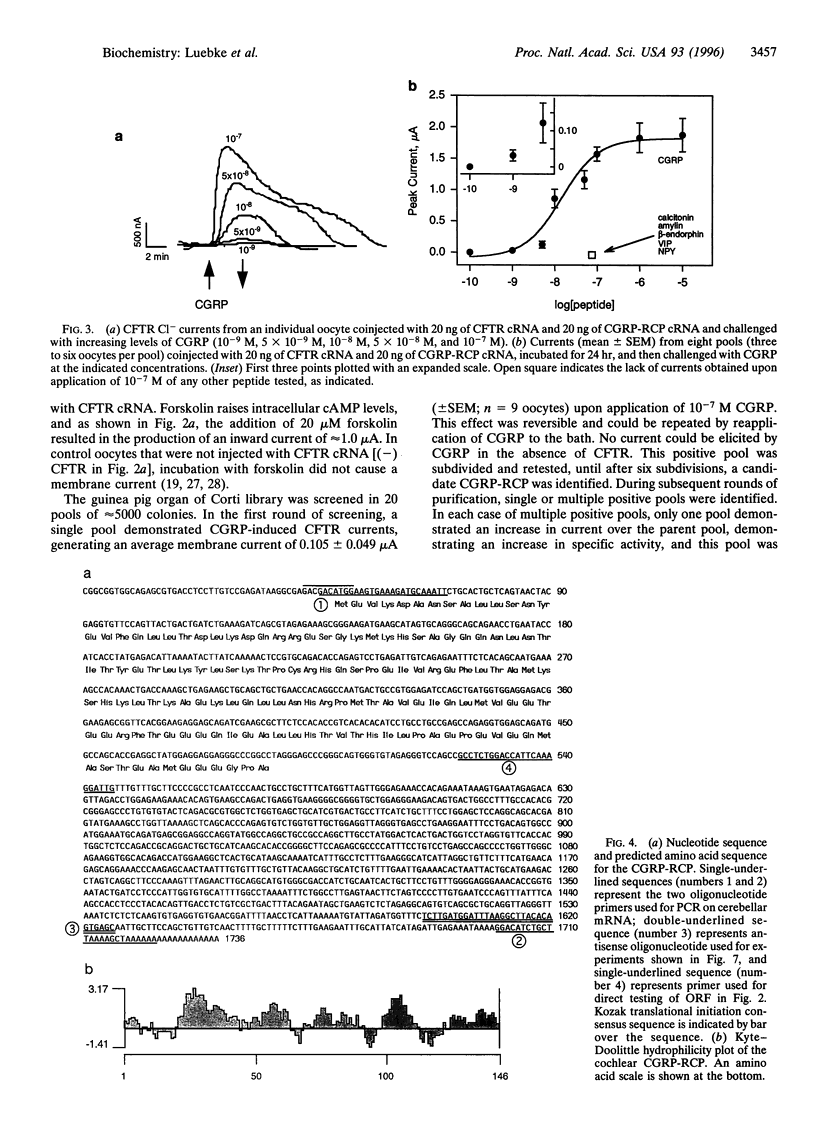
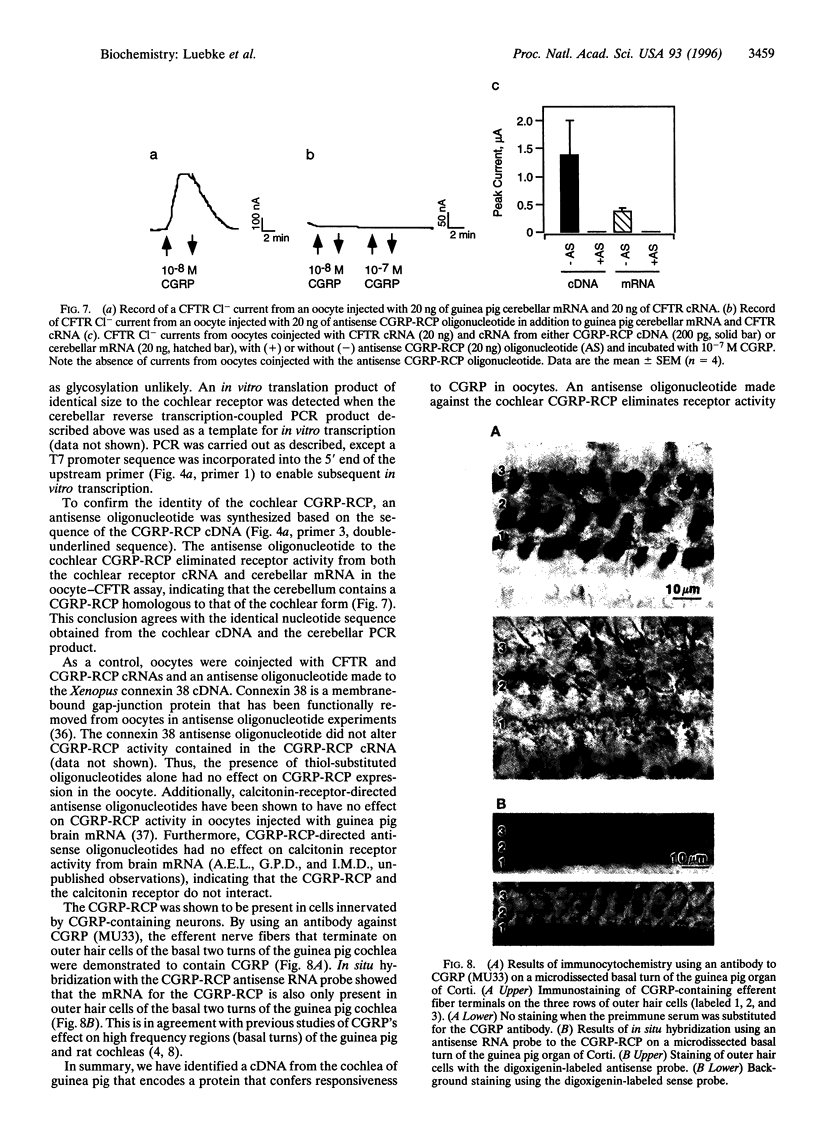
An expression-cloning strategy was used to isolate a cDNA that encodes a protein that confers calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) responsiveness to Xenopus laevis oocytes. A guinea pig organ of Corti (the mammalian hearing organ) cDNA library was screened by using an assay based on the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). The CFTR is a chloride channel that is activated upon phosphorylation; this channel activity was used as a sensor for CGRP-induced activation of intracellular kinases. A cDNA library from guinea pig organ of Corti was screened by using this oocyte-CFTR assay. A cDNA was identified that contained an open reading frame coding for a small hydrophilic protein that is presumed to be either a CGRP receptor or a component of a CGRP receptor complex. This CGRP receptor component protein confers CGRP-specific activation to the CFTR assay, as no activation was detected upon application of calcitonin, amylin, neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal peptide, or beta-endorphin. In situ hybridization demonstrated that the CGRP receptor component protein is expressed in outer hair cells of the organ of Corti and is colocalized with CGRP-containing efferent nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C., Mroz E. A., Sewell W. F. A possible neurotransmitter role for CGRP in a hair-cell sensory organ. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 1;419(1-2):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90606-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amara S. G., Jonas V., Rosenfeld M. G., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):240–244. doi: 10.1038/298240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrio L. C., Suchyna T., Bargiello T., Xu L. X., Roginski R. S., Bennett M. V., Nicholson B. J. Gap junctions formed by connexins 26 and 32 alone and in combination are differently affected by applied voltage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8410–8414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear C. E., Duguay F., Naismith A. L., Kartner N., Hanrahan J. W., Riordan J. R. Cl- channel activity in Xenopus oocytes expressing the cystic fibrosis gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19142–19145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum A. K., Wotta D. R., Law P. Y., Wilcox G. L. Functional expression of adrenergic and opioid receptors in Xenopus oocytes: interaction between alpha 2- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995 Jan;28(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)00185-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain S. D., Williams T. J., Tippins J. R., Morris H. R., MacIntyre I. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):54–56. doi: 10.1038/313054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee T. K., Fisher R. A. Multiple affinity forms of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor in rat cerebellum. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;39(6):798–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee T. K., Moy J. A., Cai J. J., Lee H. C., Fisher R. A. Solubilization and characterization of a guanine nucleotide-sensitive form of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;43(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossman D., McEwan J., MacDermot J., MacIntyre I., Dollery C. T. Human calcitonin gene-related peptide activates adenylate cyclase and releases prostacyclin from human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;92(4):695–701. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis T., Fournier A., Cadieux A., Pomerleau F., Jolicoeur F. B., St Pierre S., Quirion R. hCGRP8-37, a calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonist revealing calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor heterogeneity in brain and periphery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jul;254(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis T., Fournier A., St Pierre S., Quirion R. Structure-activity profile of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and brain tissues. Evidence for receptor multiplicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):718–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegerstrand A., Dalsgaard C. J., Jonzon B., Larsson O., Nilsson J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates proliferation of human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3299–3303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Takagi Y., Takata S., Fukuda Y., Yoshimi H., Fujita T. Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor in cultured vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):1113–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoi J., Murphy G. F., Egan C. L., Lerner E. A., Grabbe S., Asahina A., Granstein R. D. Regulation of Langerhans cell function by nerves containing calcitonin gene-related peptide. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):159–163. doi: 10.1038/363159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., McClain J., Barrezueta N. X., Aldrich T. H., Pan L., Li Y., Wiegand S. J., Friedman B., Davis S., Yancopoulos G. D. The alpha component of the CNTF receptor is required for signaling and defines potential CNTF targets in the adult and during development. Neuron. 1993 Jan;10(1):89–102. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90245-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapas S., Clark A. J. Identification of an orphan receptor gene as a type 1 calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Dec 26;217(3):832–838. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartner N., Hanrahan J. W., Jensen T. J., Naismith A. L., Sun S. Z., Ackerley C. A., Reyes E. F., Tsui L. C., Rommens J. M., Bear C. E. Expression of the cystic fibrosis gene in non-epithelial invertebrate cells produces a regulated anion conductance. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90498-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Taga T., Akira S. Cytokine signal transduction. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luebke A. E., Dickerson I. M., Muller K. J. In situ hybridization reveals transient laminin B-chain expression by individual glial and muscle cells in embryonic leech central nervous system. J Neurobiol. 1995 May;27(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/neu.480270102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Katada T., Murayama Y., Ui M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. A simple structure encodes G protein-activating function of the IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90116-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterlund M., Fontaine B., Devillers-Thiery A., Geoffroy B., Changeux J. P. Acetylcholine receptor expression in primary cultures of embryonic chick myotubes--I. Discoordinate regulation of alpha-, gamma- and delta-subunit gene expression by calcitonin gene-related peptide and by muscle electrical activity. Neuroscience. 1989;32(2):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Smith L. D. Reversible inhibition of translation by Xenopus oocyte-specific proteins. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):378–380. doi: 10.1038/309378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Dho S., Bear C. E., Kartner N., Kennedy D., Riordan J. R., Tsui L. C., Foskett J. K. cAMP-inducible chloride conductance in mouse fibroblast lines stably expressing the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7500–7504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Mermod J. J., Amara S. G., Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Rivier J., Vale W. W., Evans R. M. Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):129–135. doi: 10.1038/304129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell-Harde D., Pu H., Betts M., Harkins R. N., Perez H. D., Croze E. Reconstitution of a high affinity binding site for type I interferons. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 3;270(44):26033–26036. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.44.26033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Hiroshima O., Yuzuriha T., Yamato C., Saito A., Kimura S., Hirabayashi T., Goto K. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-binding sites of porcine cardiac muscles and coronary arteries: solubilization and characterization. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1919–1924. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliwinska-Kowalska M., Parakkal M., Schneider M. E., Fex J. CGRP-like immunoreactivity in the guinea pig organ of Corti: a light and electron microscopy study. Hear Res. 1989 Oct;42(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(89)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stangl D., Born W., Fischer J. A. Characterization and photoaffinity labeling of a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor solubilized from human cerebellum. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8605–8611. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uezono Y., Bradley J., Min C., McCarty N. A., Quick M., Riordan J. R., Chavkin C., Zinn K., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Receptors that couple to 2 classes of G proteins increase cAMP and activate CFTR expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Receptors Channels. 1993;1(3):233–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter D. E., Adams J. C., Mugnaini E. Chemically distinct rat olivocochlear neurons. Synapse. 1991 Jan;7(1):21–43. doi: 10.1002/syn.890070104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackym P. A., Popper P., Ward P. H., Micevych P. E. Cell and molecular anatomy of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat vestibular system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991 Oct;105(4):493–510. doi: 10.1177/019459989110500401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Han C., Fiscus R. R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) causes endothelium-dependent cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP and vasorelaxant responses in rat abdominal aorta. Neuropeptides. 1991 Oct;20(2):115–124. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90061-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox E. R., Fex J. Construction of a cDNA library from microdissected guinea pig organ of Corti. Hear Res. 1992 Sep;62(1):124–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(92)90208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimalawansa S. J., Gunasekera R. D., Zhang F. Isolation, purification, and characterization of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor. Peptides. 1993 Jul-Aug;14(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(93)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. L., Sachs M. B. Effect of electrical stimulation of the crossed olivocochlear bundle on auditory nerve response to tones in noise. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Apr;57(4):1002–1021. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.4.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]