Abstract
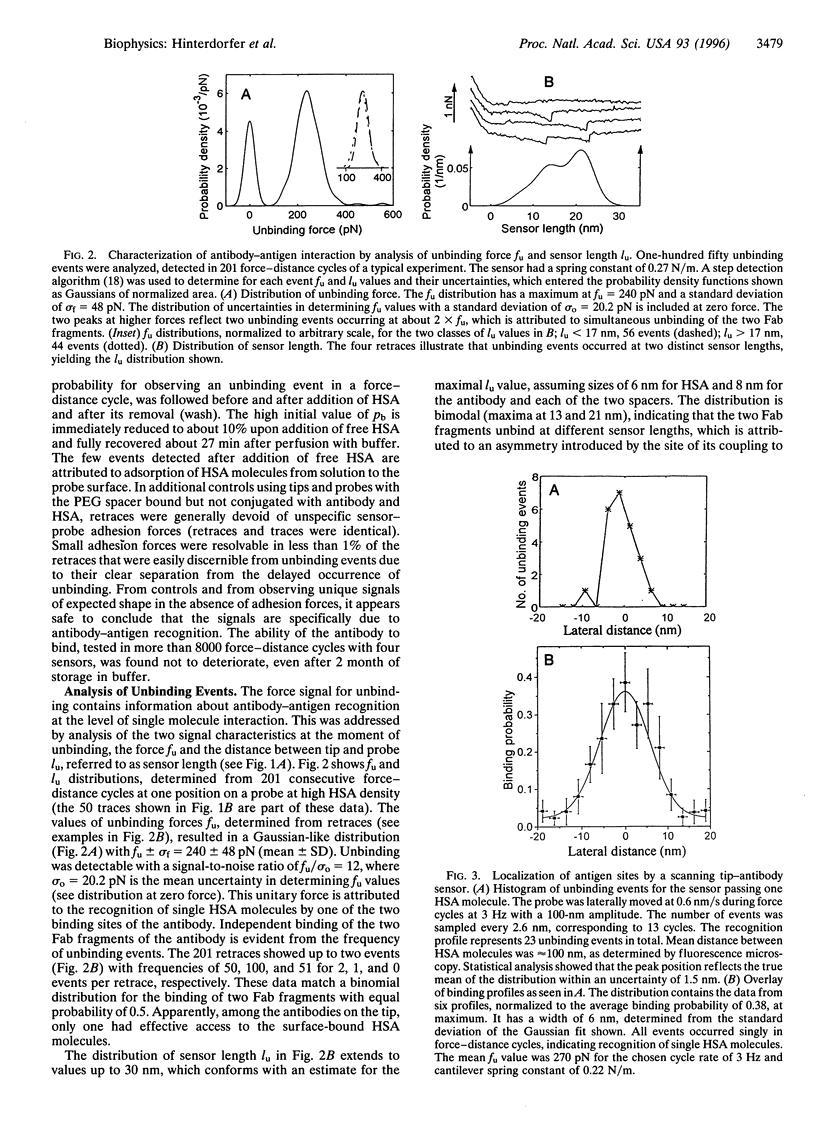
A methodology has been developed for the study of molecular recognition at the level of single events and for the localization of sites on biosurfaces, in combining force microscopy with molecular recognition by specific ligands. For this goal, a sensor was designed by covalently linking an antibody (anti-human serum albumin, polyclonal) via a flexible spacer to the tip of a force microscope. This sensor permitted detection of single antibody-antigen recognition events by force signals of unique shape with an unbinding force of 244 +/- 22 pN. Analysis revealed that observed unbinding forces originate from the dissociation of individual Fab fragments from a human serum albumin molecule. The two Fab fragments of the antibody were found to bind independently and with equal probability. The flexible linkage provided the antibody with a 6-nm dynamical reach for binding, rendering binding probability high, 0.5 for encounter times of 60 ms. This permitted fast and reliable detection of antigenic sites during lateral scans with a positional accuracy of 1.5 nm. It is indicated that this methodology has promise for characterizing rate constants and kinetics of molecular recognition complexes and for molecular mapping of biosurfaces such as membranes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science. 1978 May 12;200(4342):618–627. doi: 10.1126/science.347575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland T., Ratner B. D. Direct measurement of hydrogen bonding in DNA nucleotide bases by atomic force microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5297–5301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Berk D., Leung A. Detachment of agglutinin-bonded red blood cells. I. Forces to rupture molecular-point attachments. Biophys J. 1991 Apr;59(4):838–848. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82296-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florin E. L., Moy V. T., Gaub H. E. Adhesion forces between individual ligand-receptor pairs. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.8153628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrübler T., Amerstorfer A., Schindler H., Gruber H. J. Synthesis and applications of a new poly(ethylene glycol) derivative for the crosslinking of amines with thiols. Bioconjug Chem. 1995 May-Jun;6(3):242–248. doi: 10.1021/bc00033a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal R., John S. A. Biological applications of atomic force microscopy. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 1):C1–21. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. U., Chrisey L. A., Colton R. J. Direct measurement of the forces between complementary strands of DNA. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):771–773. doi: 10.1126/science.7973628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moy V. T., Florin E. L., Gaub H. E. Intermolecular forces and energies between ligands and receptors. Science. 1994 Oct 14;266(5183):257–259. doi: 10.1126/science.7939660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D. J., Schabert F. A., Büldt G., Engel A. Imaging purple membranes in aqueous solutions at sub-nanometer resolution by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1681–1686. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80345-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup S. H., Erickson H. P. Kinetics of protein-protein association explained by Brownian dynamics computer simulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3338–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T., Schütz G. J., Baumgartner W., Gruber H. J., Schindler H. Imaging of single molecule diffusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 2;93(7):2926–2929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.7.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shao Z., Yang J. Progress in high resolution atomic force microscopy in biology. Q Rev Biophys. 1995 May;28(2):195–251. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]