Abstract
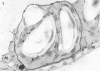
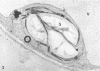
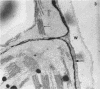
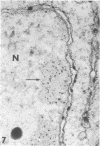
When samples of pea tendril tissue were incubated in the Wachstein-Meisel medium for the demonstration of adenosine triphosphatases, deposits of lead reaction product were localized between the membranes of the chloroplast envelope. The presence of Mg2+ was necessary for adenosine triphosphatase activity, and Ca2+ could not substitute for this requirement. Varying the pH of incubation to 5.5 or 9.4 inhibited enzyme activity, as did the addition of p-chloromercuribenzoic acid or N-ethylmaleimide. The adenosine triphosphatase was apparently inactivated or degraded when the plants were grown in the dark for 24 hours prior to incubation. The enzyme was substrate-specific for adenosine triphosphate; no reaction was obtained with adenosine diphosphate, uridine triphosphate, inosine triphosphate, p-nitrophenyl phosphate, and sodium β-glycerophosphate. Sites of nonspecific depositions of lead are described. The adenosine triphosphatase on the chloroplast envelope may be involved in the light-induced contraction of this organelle.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHWORTH C. T., LUIBEL F. J., STEWART S. C. The fine structural localization of adenosine triphosphatase in the small intestine, kidney, and liver of the rat. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:1–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTOSZEWICZ W., BARRNETT R. J. FINE STRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY IN THE URINARY BLADDER OF THE TOAD. J Ultrastruct Res. 1964 Jun;10:599–609. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(64)80033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. D., Altschul A. M. Glycoside-sensitive ATPase from Arachis hypogaea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Apr 22;15(5):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. D., Neucere N. J., Altschul A. M., Evans W. J. Activity patterns of purified ATPase from Arachis hypogaea. Life Sci. 1965 Jul;4(14):1439–1447. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carell E. F., Kahn J. S. Purification and properties of a Mg2+-dependent ATPase from chloroplasts of Euglena gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 9;131(3):571–579. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Padykula H. A. Cytochemical studies of adenosine triphosphatase activity in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):252–260. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M., Barrnett R. J. Fine structural cytochemical localizations of phosphatase activities of rat and guinea pig. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Nov;48(2):395–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman I. W., Heitkamp D. H. Electron microscopic localization of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase activity. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Oct;16(10):645–653. doi: 10.1177/16.10.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. H., Moudrianakis E. N. Function of the "quantasome" in photosynthesis: structure and properties of membrane-bound particle active in the dark reactions of photophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe M. J., Galston A. W. Physiological Studies on Pea Tendrils. III. ATPase Activity and Contractility Associated with Coiling. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jun;42(6):845–847. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.6.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHN J. S., JAGENDORF A. T. An enzyme from spinach chloroplasts catalyzing adenosine triphosphate-adenosine diphosphate exchange. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:940–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karu A. E., Moudrianakis E. N. Fractionation and comparative studies of enzymes in aqueous extracts of spinach chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Feb;129(2):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHESI V. T., BARRNETT R. J. The demonstration of enzymatic activity in pinocytic vesicles of blood capillaries with the electron microscope. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jun;17:547–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Palade G. E. The localization of Mg-Na-K-activated adenosine triphosphatase on red cell ghost membranes. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):385–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClurkin I. T., McClurkin D. C. Cytochemical demonstration of a sodium-activated and a potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase in loblolly pine seedling root tips. Plant Physiol. 1967 Aug;42(8):1103–1110. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.8.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani A., Barrnett R. J. Fine structural demonstration of phosphatase activity at pH 9. Nature. 1965 Jun 5;206(988):1001–1003. doi: 10.1038/2061001a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Rosenthal A. S., Beaver D. L., Schuffman S. S. Lead ion and phosphatase histochemistry. II. Effect of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by lead ion on the histochemical localization of adenosine triphosphatase activity. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Oct;14(10):702–710. doi: 10.1177/14.10.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Rosenthal A. S. Pitfalls in the use of lead ion for histochemical localization of nucleoside phosphatases. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Aug;16(8):530–539. doi: 10.1177/16.8.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIFAKH S. A., KAZAKOVA T. B. Actomyosin-like protein in mitochondria of the mouse liver. Nature. 1963 Mar 16;197:1106–1107. doi: 10.1038/1971106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVIKOFF A. B., HAUSMAN D. H., PODBER E. The localization of adenosine triphosphatase in liver: in situ staining and cell fractionation studies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1958 Jan;6(1):61–71. doi: 10.1177/6.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobel P. S. Chloroplast shrinkage and increased photophosphorylation in vitro upon illuminating intact plants of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 15;153(1):170–182. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobel P. S. Light-Induced Chloroplast Shrinkage in vivo Detectable After Rapid Isolation of Chloroplasts From Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol. 1968 May;43(5):781–787. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.5.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTERO VILARDEBO L. R., LANE N., GODMAN G. C. DEMONSTRATION OF MITOCHONDRIAL ATPASE ACTIVITY IN FORMALIN-FIXED COLONIC EPITHELIAL CELLS. J Cell Biol. 1963 Dec;19:647–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L., Deamer D. W., Crofts A. R. Conformational changes in chloroplasts. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1966;19:281–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S., Moses H. L., Beaver D. L., Schuffman S. S. Lead ion and phosphatase histochemistry. I. Nonenzymatic hydrolysis of nucleoside phosphates by lead ion. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Oct;14(10):698–701. doi: 10.1177/14.10.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tice L. W. Lead-adenosine triphosphate complexes in adenosine triphosphatase histochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Feb;17(2):85–94. doi: 10.1177/17.2.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WACHSTEIN M., MEISEL E. Histochemistry of hepatic phosphatases of a physiologic pH; with special reference to the demonstration of bile canaliculi. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 Jan;27(1):13–23. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/27.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]