Abstract
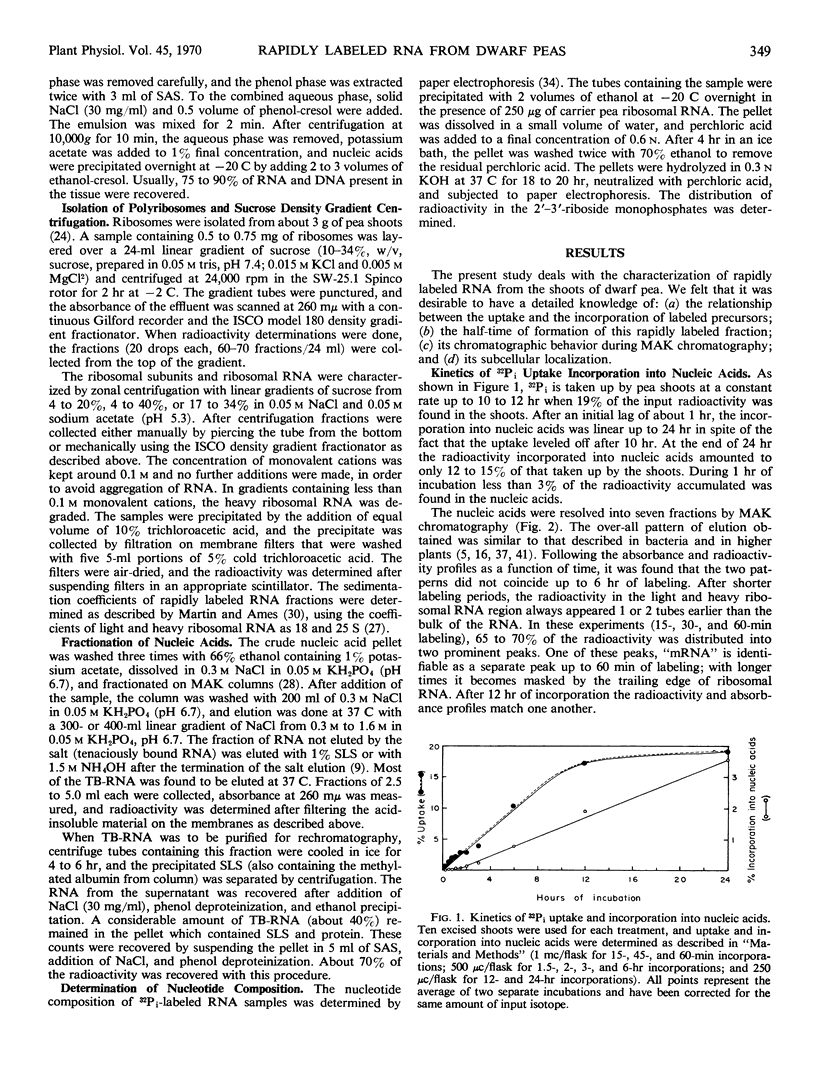
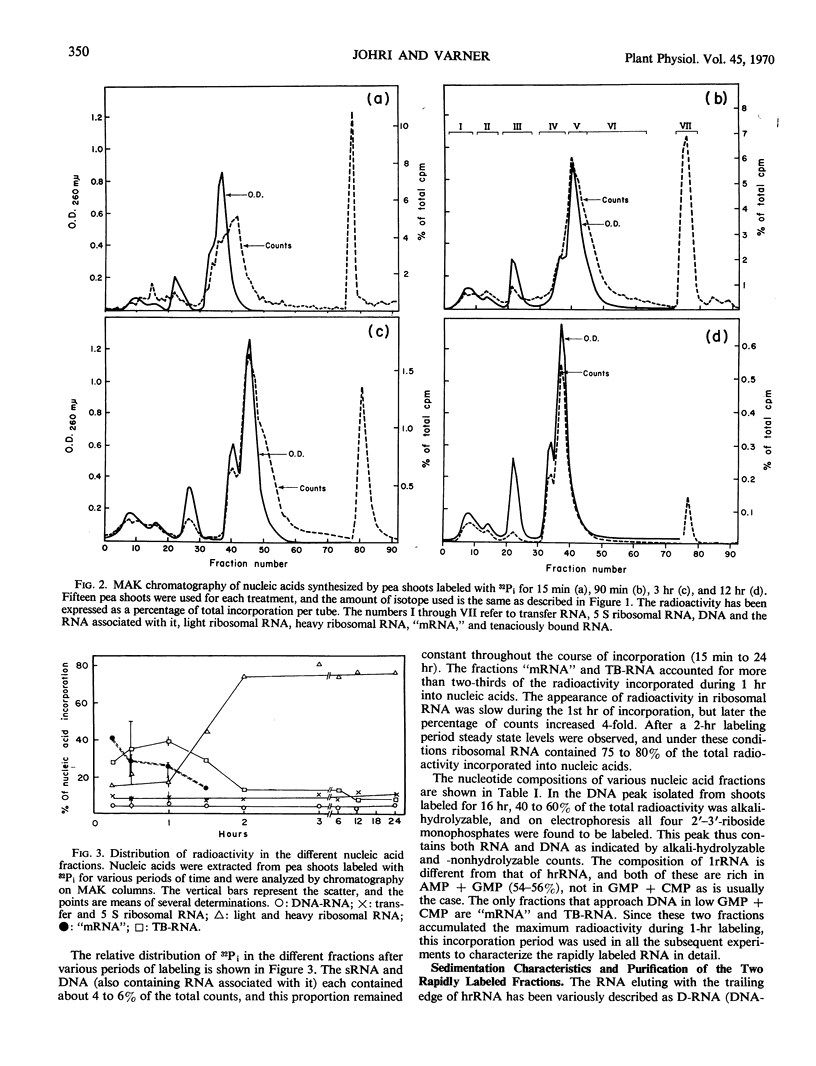
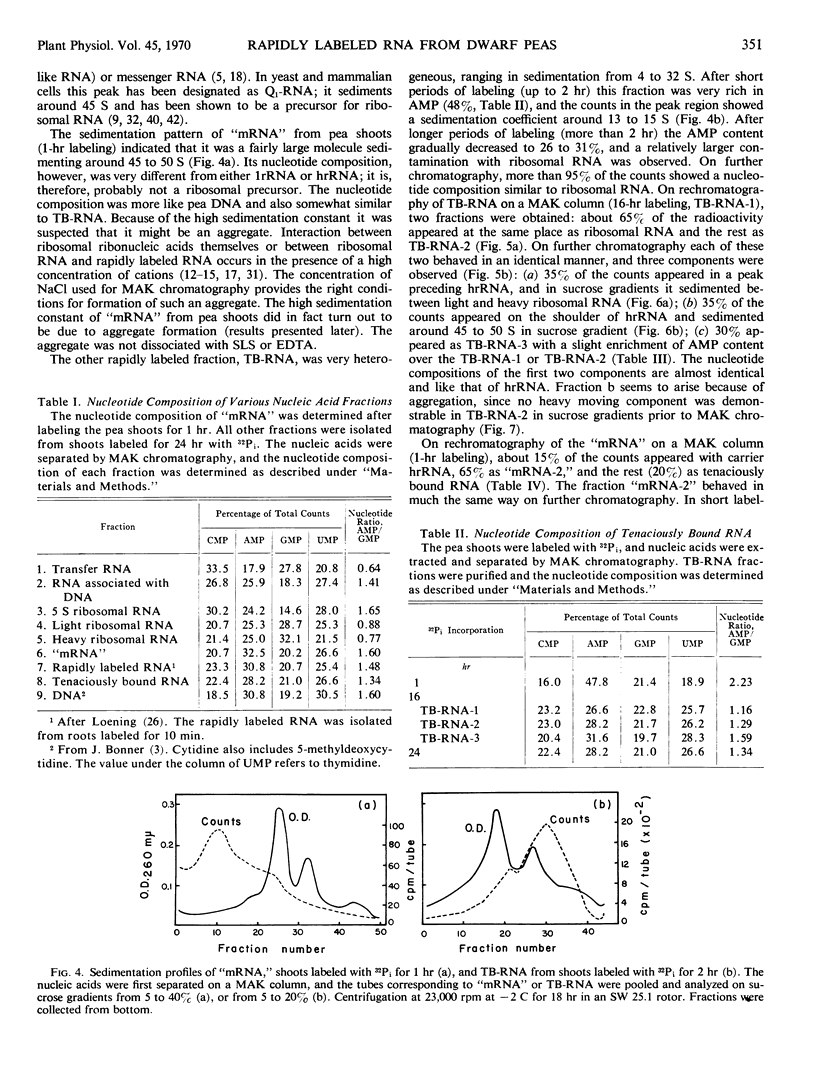
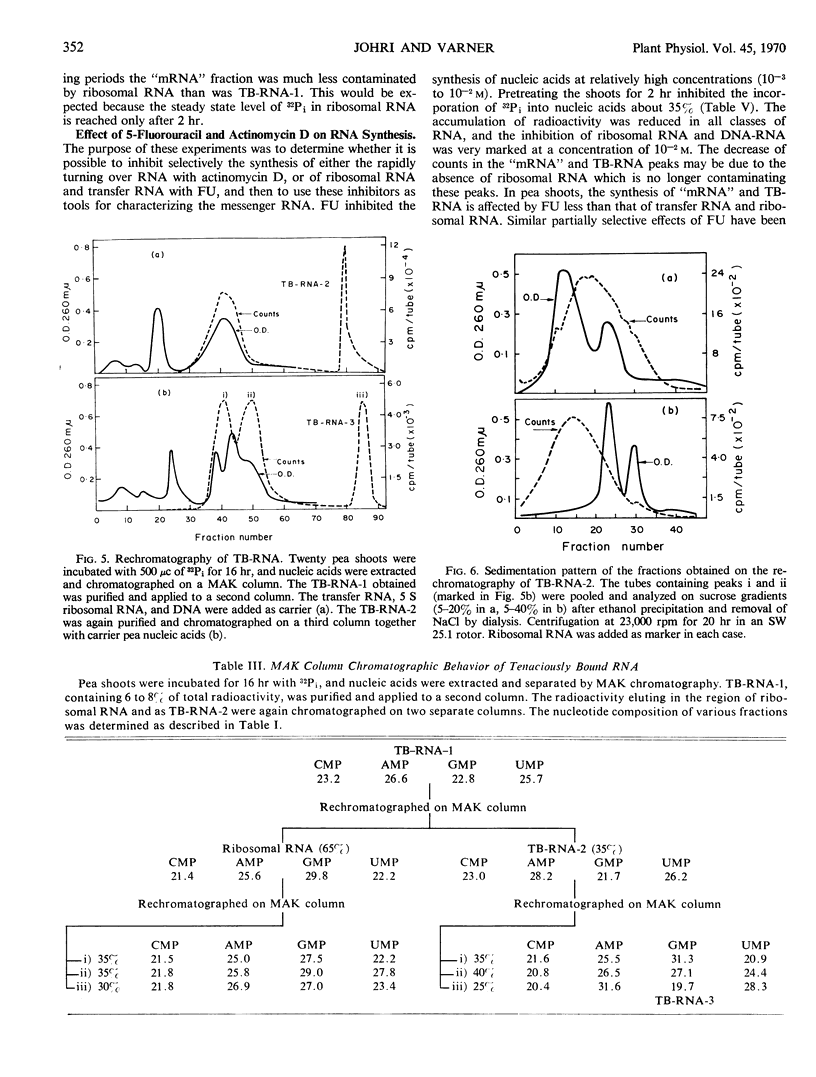
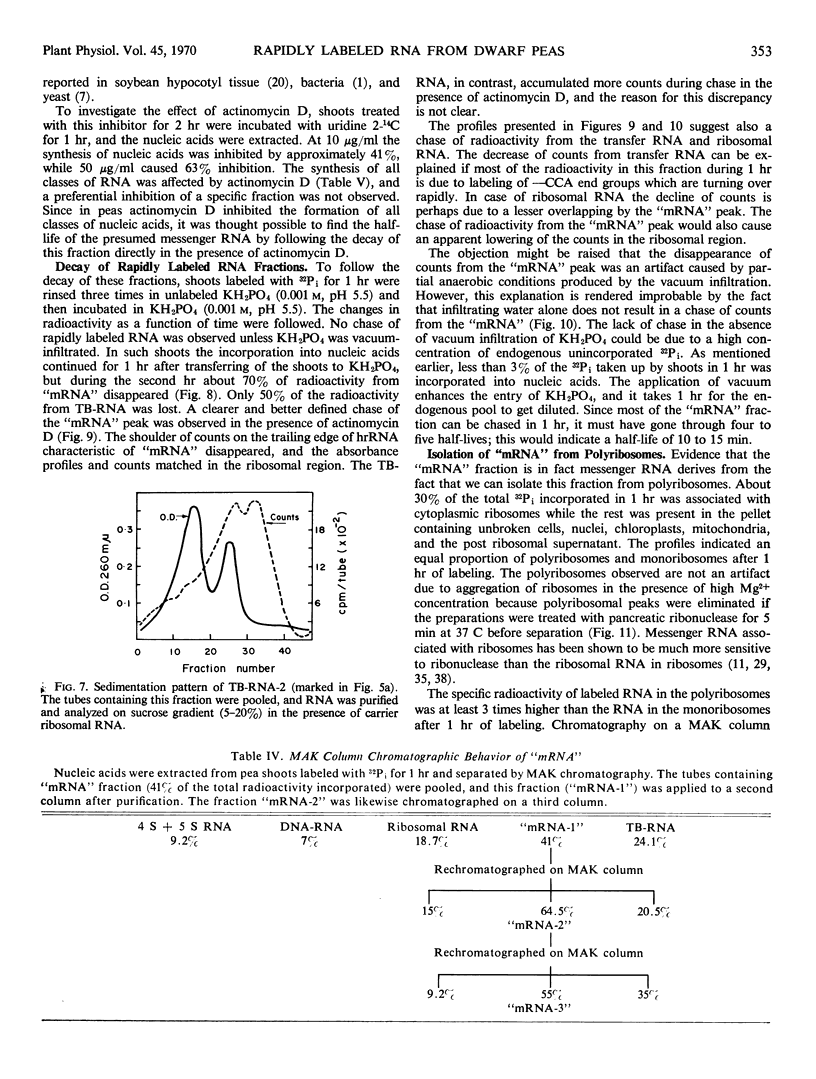
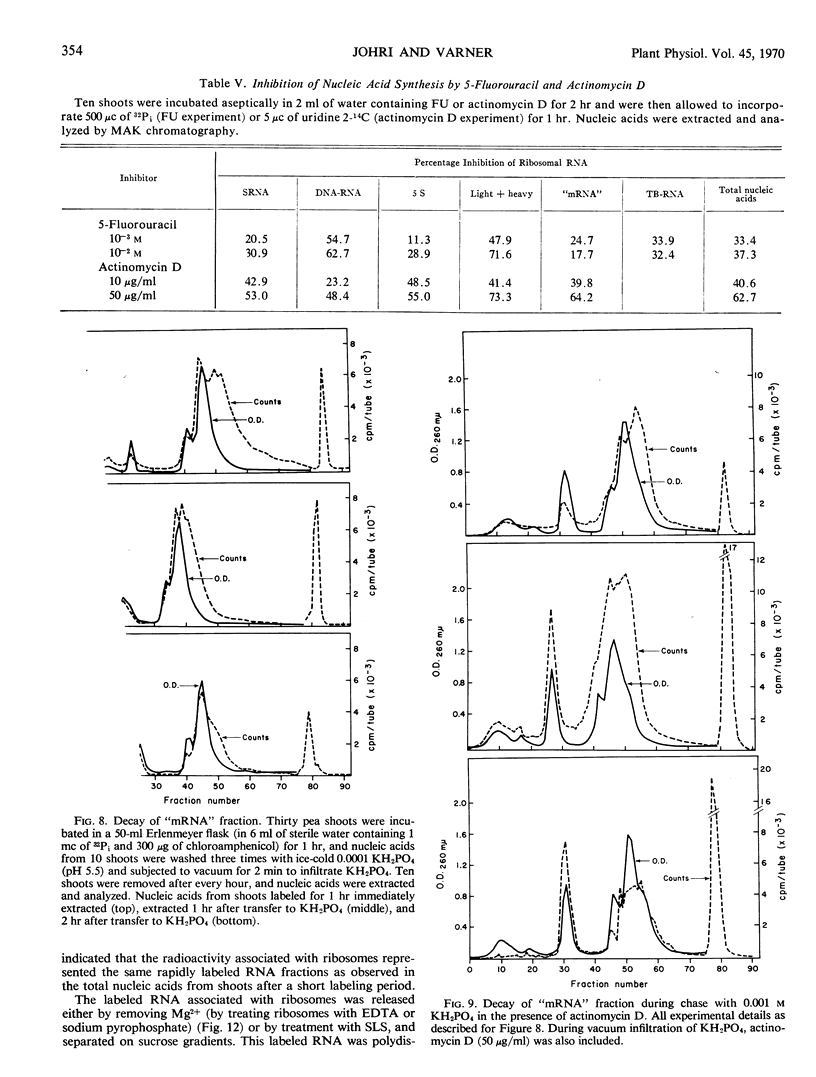
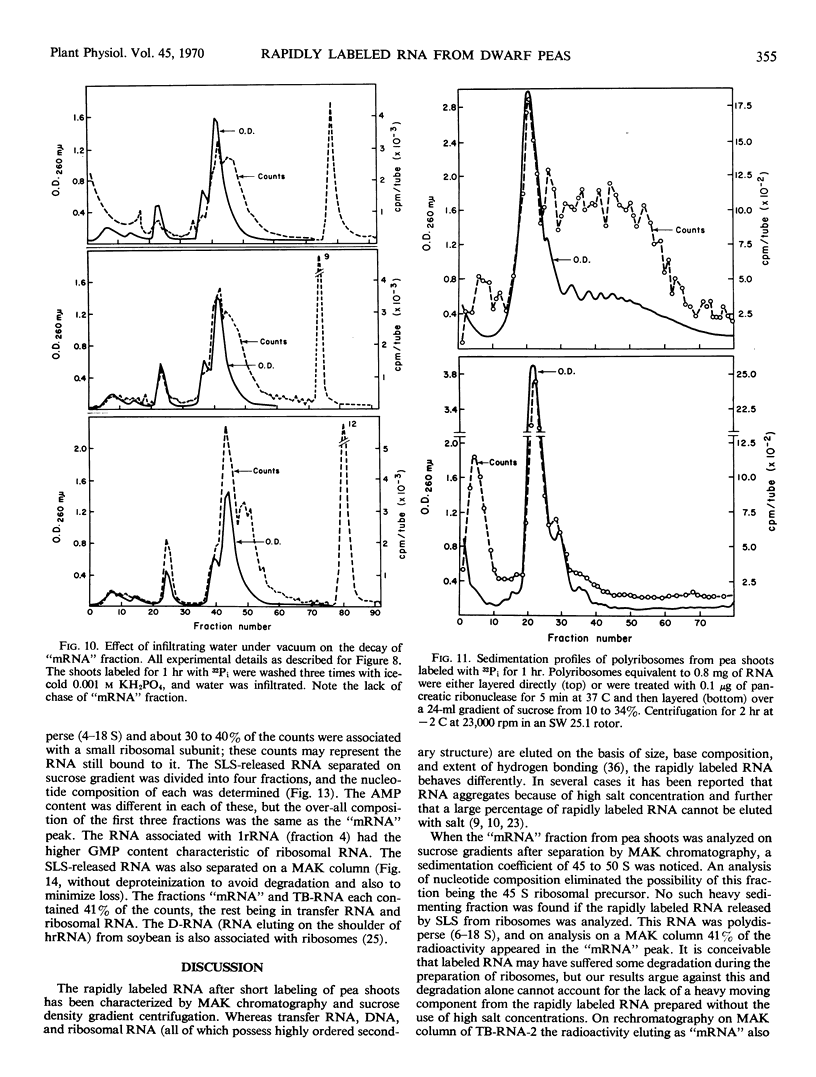
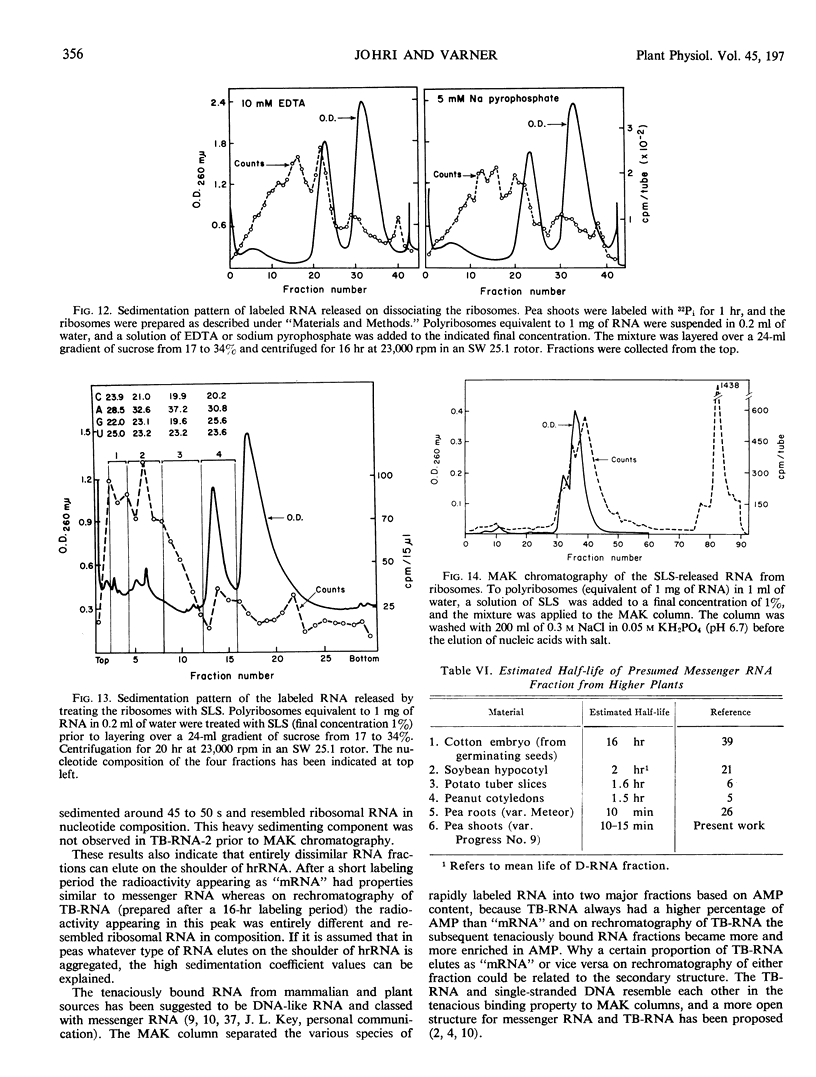
The ribonucleic acid synthesized by excised shoots of dwarf pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Progress No. 9) during short labeling periods has been characterized. Thirty percent of the total 32Pi incorporated in 1 hour is found in the ribosomal fraction. This labeled RNA was polydisperse (6-18 Svedberg units) and after chromatography on a methylated albumin-kieselguhr column about 80% of the radioactivity appeared in two peaks. One of these appeared on the shoulder of heavy ribosomal RNA (“mRNA”) while the other was tenaciously bound to the column (TB-RNA). In the presence of high NaCl concentration, about half of the polydisperse RNA interacted with ribosomal RNA and eluted as “mRNA” while the remainder eluted as TB-RNA. This interaction in the presence of salt seems to result in the alteration of secondary structure because the “mRNA” fraction had a high sedimentation coefficient (45-50 Svedberg units). The polydisperse RNA approaches DNA in low cytidylate and guanylate content. After short periods of labeling TB-RNA showed higher adenylate content than “mRNA.” The radioactivity from the “mRNA” peak can be chased, and these counts may represent a class of shortlived messenger RNA molecules with an average half-life of 10 to 15 minutes. The other component, TB-RNA, could not be chased and accumulated radioactivity during the chase period.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARONSON A. I. The effect of 5-fluorouracil on bacterial protein and ribonucleic acid synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:98–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90873-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano K. Size heterogeneity of T2 messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chroboczek H., Cherry J. H. Characterization of nucleic acids in peanut cotyledons. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):28–37. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Click R. E., Hackett D. P. Functional stability of messenger RNA to potato tuber slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 18;142(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90621-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBIN D. T., ELKORT A. T. SOME ABNORMAL PROPERTIES OF CHLORAMPHENICOL RNA. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:508–518. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellem K. A., Sheridan J. W. Tenacious binding of the bulk of the DNA-like RNA of metazoan cells to methylated albumin columns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Aug 11;16(6):505–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellem K. A. Some properties of mammalian DNA-like RNA isolated by chromatography on methylated bovine serum albumin-kieselguhr columns. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(2):283–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIERER A. Function of aggregated reticulocyte ribosomes in protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1963 Feb;6:148–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. R., Parish J. H., Kirby K. S., Cook E. A. Sedimentation of rapidly labelled RNA from rat liver in different gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):603–605. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes D. H., Grunberg-Manago M., Guérin M. F. Interactions between homopolyribonucleotides and bacterial ribonucleic acid in solutions of high ionic strength. I. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):477–498. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes D. H., Hayes F., Guérin M. F. Association of rapidly labelled bacterial RNA with ribosomal RNA in solutions of high ionic strength. II. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):499–515. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao T. C., Segel W., Tang C. L. Apparent aggregation of 28-S ribosomal RNA of Zea mays. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 21;157(3):640–643. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGLE J., KEY J. L., HOLM R. E. DEMONSTRATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A DNA-LIKE RNA IN EXCISED PLANT TISSUE. J Mol Biol. 1965 Apr;11:730–746. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle J., Key J. L. A comparative evaluation of the synthesis of DNA-like RNA in excised and intact plant tissues. Plant Physiol. 1965 Nov;40(6):1212–1219. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.6.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle J., Key J. L. A re-evaluation of the fractionation of high molecular weight RNA by MAK chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Mar 27;30(6):711–716. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90571-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johri M. M., Varner J. E. Enhancement of RNA synthesis in isolated pea nuclei by gibberellic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):269–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:266–269. doi: 10.1042/bj0960266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH G., KUBINSKI H. ZUR DARSTELLUNG UND FRAKTIONIERUNG VON HOCHMOLEKULARER RIBONUCLEINSAEURE. Z Naturforsch B. 1964 Aug;19:683–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Barnett N. M., Lin C. Y. RNA and protein biosynthesis and the regulation of cell elongation by auxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Aug 9;144(1):49–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb34000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Ingle J. REQUIREMENT FOR THE SYNTHESIS OF DNA-LIKE RNA FOR GROWTH OF EXCISED PLANT TISSUE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52(6):1382–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaver C. J., Key J. L. Polyribosome formation and RNA synthesis during aging of carrot-root tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1338–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. Y., Key J. L., Bracker C. E. Association of D-RNA with Polyribosomes in the Soybean Root. Plant Physiol. 1966 Jun;41(6):976–982. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.6.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E., Ingle J. Diversity of RNA components in green plant tissues. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):363–367. doi: 10.1038/215363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Synthesis of messenger ribonucleic acid in excised pea-seedling root segments. Separation of the messenger from microsomes by electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):125–133. doi: 10.1042/bj0970125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbaix G., Burny A. Separation of the messenger RNA of reticulocyte polyribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Aug 11;16(6):522–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish J. H., Kirby K. S. Reagents which reduce interactions between ribosomal RNA and rapidly labelled RNA from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERRER K., LATHAM H., DARNELL J. E. Demonstration of an unstable RNA and of a precursor to ribosomal RNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Feb 15;49:240–248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEBRING E. D., SALZMAN N. P. AN IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR MEASURING THE DISTRIBUTION OF P32O4--AMONG THE NUCLEOTIDES OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Anal Biochem. 1964 May;8:126–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAEHELIN T., BRINTON C. C., WETTSTEIN F. O., NOLL H. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF E. COLI ERGOSOMES. Nature. 1963 Aug 31;199:865–870. doi: 10.1038/199865a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., CHENG T. Y. Fractionation of nucleic acids with the methylated albumin column. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tester C. F., Dure L. S., 3rd Nucleic acid synthesis during the hormone-stimulated growth of excised oat coleoptiles. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2532–2538. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Rich A., Hall C. E. Electron Microscope Studies of Ribosomal Clusters Synthesizing Hemoglobin. Science. 1962 Dec 28;138(3548):1399–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3548.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Dure L. S., 3rd Ribonucleic acid synthesis in germinating cotton seeds. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Loening U., Willems M., Penman S. Acrylamide gel electrophoresis of HeLa cell nucleolar RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1088–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANKOFSKY S. A., SPIEGELMAN S. Distinct cistrons for the two ribosomal RNA components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:538–544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa-Fukada M., Fukada T., Kawade Y. Characterization of rapidly labeled ribonucleic acid of animal cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 15;103(3):383–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kloet S. R., Strijkert P. J. Selective inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis by 5-fluorouracil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Apr 6;23(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


