Abstract
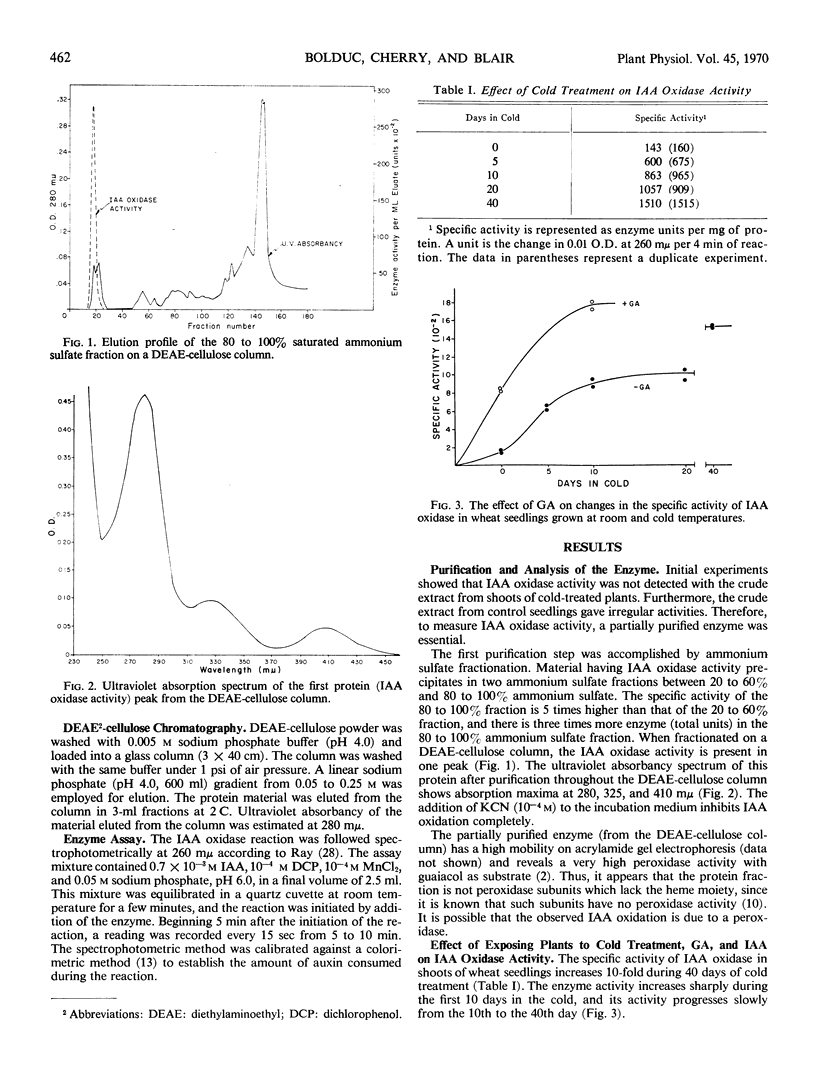
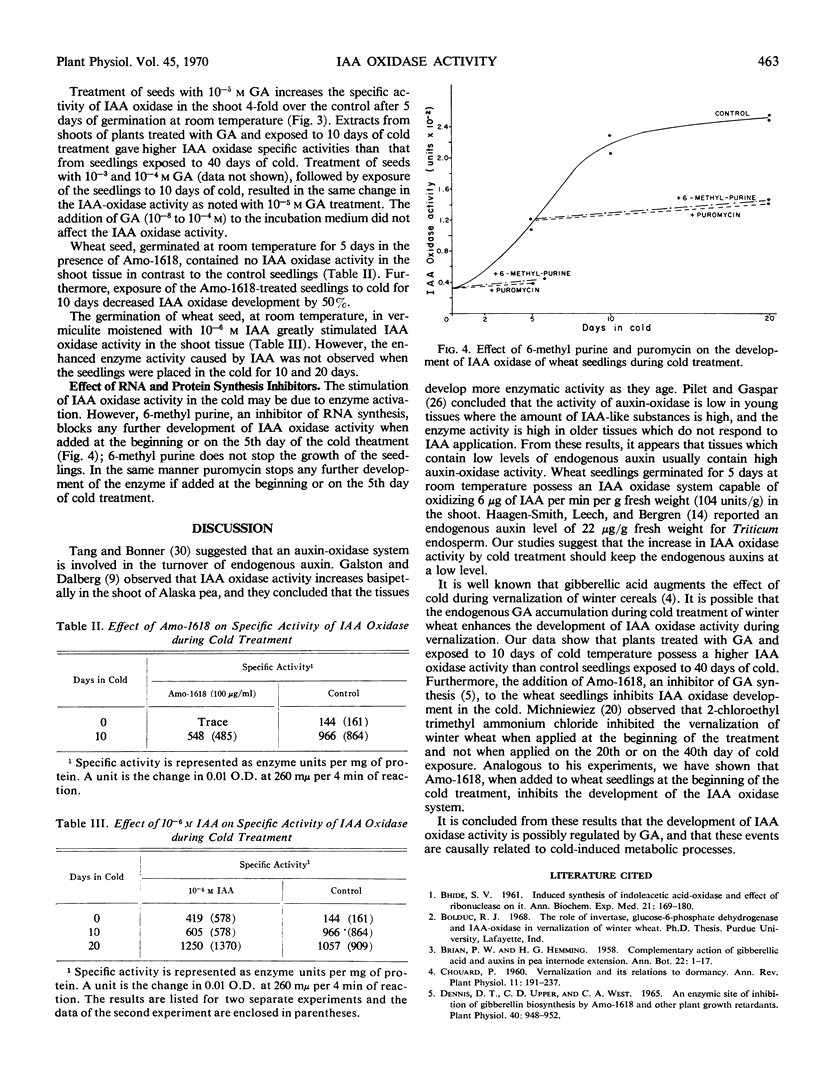
The activity of indoleacetic acid oxidase increased 10-fold during 40 days of cold treatment of winter wheat seedlings. Puromycin and 6-methyl purine inhibited indoleacetic acid oxidase development in the cold. Addition of gibberellic acid stimulated indoleacetic acid oxidase development during germination at room temperature and during cold treatment. Amo-1618 inhibited indoleacetic acid oxidase development before and during cold treatment. Indoleacetic acid treatment increased indoleacetic acid oxidase activity during germination at room temperature while no significant effect on activity was observed during cold treatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dennis D. T., Upper C. D., West C. A. An enzymic site of inhibition of gibberellin biosynthesis by Amo 1618 and other plant growth retardants. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):948–952. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang S. C., Bourke J. B., Stevens V. L., Butts J. S. Influences of Gibberellic Acid on Metabolism of Indoleacetic Acid, Acetate, and Glucose in Roots of Higher Plants. Plant Physiol. 1960 Mar;35(2):251–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALSTON A. W., BONNER J., BAKER R. S. Flavoprotein and peroxidase as components of the indoleacetic acid oxidase system of peas. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Feb;42(2):456–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galston A. W., Warburg H. An Analysis of Auxin-gibberellin Interaction in Pea Stem Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1959 Jan;34(1):16–22. doi: 10.1104/pp.34.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy A. H. Interaction of Growth-retarding Compounds and Gibberellin on Indoleacetic Acid Oxidase and Peroxidase of Cucumber Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1963 Nov;38(6):731–737. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen W. A. The Histochemical Localization of Peroxidase in Roots and Its Induction by Indoleacetic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1955 Sep;30(5):426–432. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.5.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockerse R., Siegel B. Z., Galston A. W. Hormone-induced repression of a peroxidase isozyme in plant tissue. Science. 1966 Jan 28;151(3709):452–453. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3709.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILET P. E. Action des gibberellines sur l'activité auxines-oxydasique de tissus cultivés in vitro. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1957 Oct 14;245(16):1327–1328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY P. M. The destruction of indoleacetic acid. II. Spectrophotometric study of the enzymatic reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Sep;64(1):193–216. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel B. Z., Galston A. W. Indoleacetic acid oxidase activity of apoperoxidase. Science. 1967 Sep 29;157(3796):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3796.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGENKNECHT A. C., BURRIS R. H. Indoleacetic acid inactivating enzymes from bean roots and pea seedlings. Arch Biochem. 1950 Jan;25(1):30–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe R., Stutz R. E. Effect of Gibberellic Acid and Photoperiod on Indoleacetic Acid Oxidase in Lupinus Albus L. Plant Physiol. 1960 May;35(3):359–361. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


