Abstract
The nuclear DNAs from a number of angiosperm species were tested for hybridization to the RNAs contained in 70 S (chloroplastic) and 80 S (cytoplasmic) ribosomes. All of the DNAs contained regions complementary to RNAs from chloroplastic as well as cytoplasmic ribosomes. DNAs from closely related plants varied widely in their proportion of coding for these RNAs. About 0.15% of the DNAs from a number of different species of Nicotiana were found to be complementary to the RNAs of each kind of ribosome; however, DNAs from some other members of this genus had more than three times this proportion of coding for ribosomal RNAs. These and other data suggest that hybridization percentage for ribosomal RNA is not a familial or generic characteristic.
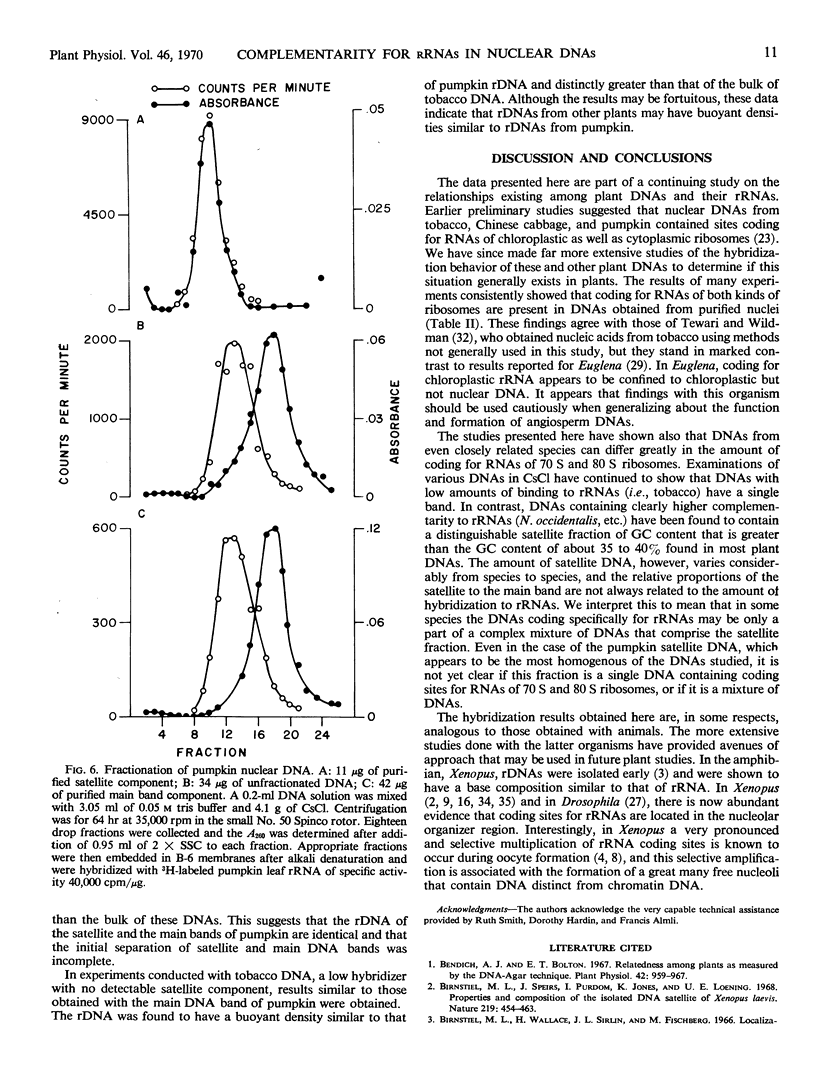
DNAs with high amounts of coding for ribosomal RNAs have thus far been found to contain satellite DNAs of base composition more like ribosomal RNA than the main DNA component. The satellite DNA from pumpkin has been isolated and shown to contain cistrons for both chloroplastic and cytoplasmic ribosomal RNAs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendich A. J., Bolton E. T. Relatedness Among Plants as Measured by the DNA-Agar Technique. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jul;42(7):959–967. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.7.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M., Speirs J., Purdom I., Jones K., Loening U. E. Properties and composition of the isolated ribosomal DNA satellite of Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1968 Aug 3;219(5153):454–463. doi: 10.1038/219454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Dawid I. B. Specific gene amplification in oocytes. Oocyte nuclei contain extrachromosomal replicas of the genes for ribosomal RNA. Science. 1968 Apr 19;160(3825):272–280. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3825.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIPCHASE M. I., BIRNSTIEL M. L. ON THE NATURE OF NUCLEOLAR RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1101–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigner J., Doty P. The native, denatured and renatured states of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):549–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIERER A., SCHRAMM G. Infectivity of ribonucleic acid from tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1956 Apr 14;177(4511):702–703. doi: 10.1038/177702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G. Differential synthesis of the genes for ribosomal RNA during amphibian oögenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):553–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Pardue M. L. Formation and detection of RNA-DNA hybrid molecules in cytological preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):378–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIAO T. C. CHARACTERISTICS OF RIBOSOMES ISOLATED FROM ROOTS OF ZEA MAYS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 16;91:598–605. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingle J. Synthesis and Stability of Chloroplast Ribosomal-RNA's. Plant Physiol. 1968 Sep;43(9):1448–1454. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.9.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John H. A., Birnstiel M. L., Jones K. W. RNA-DNA hybrids at the cytological level. Nature. 1969 Aug 9;223(5206):582–587. doi: 10.1038/223582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupila S., Bryan A. M., Stern H. Extractability of DNA & its determination in tissues of higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1961 Mar;36(2):212–215. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.2.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E., Ingle J. Diversity of RNA components in green plant tissues. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):363–367. doi: 10.1038/215363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Feeley J. ACTIVATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN THE IMBIBITION PHASE OF SEED GERMINATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51(6):1075–1079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda K., Siegel A. Hybridization of plant ribosomal RNA to DNA: the isolation of a DNA component rich in ribosomal RNA cistrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):673–680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra B. D., Mahler H. R. Characterization of some unusual DNAs from the mitochondria from certain "petite" strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):685–703. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Bishop J. O. Hybridization between rat liver DNA and complementary RNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 28;40(1):117–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITOSSA F. M., SPIEGELMAN S. LOCALIZATION OF DNA COMPLEMENTARY TO RIBOSOMAL RNA IN THE NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZER REGION OF DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:737–745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., CHENG T. Y. Fractionation of nucleic acids with the methylated albumin column. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., MARMUR J., DOTY P., 2nd Dependence of the density of deoxyribonucleic acids on guanine-cytosine content. Nature. 1959 May 23;183(4673):1429–1431. doi: 10.1038/1831429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N. S., Smillie R. M. Evidence for the direction of chloroplasts ribosomal RNA synthesis by chloroplast DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):598–603. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D., Whitfeld P. R. The nature of the ribonucleic acid of isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Nov;117(2):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Function of chloroplast DNA. I. Hybridization studies involving nuclear and chloroplast DNA with RNA from cytoplasmic (80S) and chloroplast (70S) ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):569–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewavas A. J., Gibson I. Ribosomal RNA nucleotide sequence homologies in plants. Plant Physiol. 1968 Mar;43(3):445–447. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE J. M., TS'O P. O. Nucleotide composition of various ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jun 2;5:125–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace H., Birnstiel M. L. Ribosomal cistrons and the nucleolar organizer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):296–310. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]