Abstract
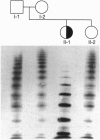
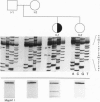
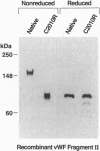
The same heterozygous T -> C transition at nt 8567 of the von Willebrand factor (vWF) transcript was found in two unrelated patients with type III) von Willebrand disease, with no other apparent abnormality. In one family, both alleles were normal in the parents and one sister; thus, the mutation originated de novo in the proposita. The second patient also had asymptomatic parents who, however, were not available for study. The structural consequences of the identified mutation, resulting in the CyS2010 -> Arg substitution, were evaluated by expression of the vWF carboxyl-terminal domain containing residues 1366-2050. Insect cells infected with recombinant baculovirus expressing normal vWF sequence secreted a disulfide linked dimeric molecule with an apparent molecular mass of 150 kDa before reduction, yielding a single band of 80 kDa after disulfide bond reduction. In contrast, cells expressing the mutant fragment secreted a monomeric molecule of apparent molecular mass of 80 kDa, which remained unchanged after reduction. We conclude that CyS2010 is essential for normal dimerization of vWF subunits through disulfide bonding of carboxyl-terminal domains and that a heterozygous mutation in the corresponding codon is responsible for defective multimer formation in type III) von Willebrand disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma H., Dent J. A., Sugimoto M., Ruggeri Z. M., Ware J. Independent assembly and secretion of a dimeric adhesive domain of von Willebrand factor containing the glycoprotein Ib-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12342–12347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma H., Hayashi T., Dent J. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Ware J. Disulfide bond requirements for assembly of the platelet glycoprotein Ib-binding domain of von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2821–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz S. D., Dent J., Roberts J., Fujimura Y., Plow E. F., Titani K., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Epitope mapping of the von Willebrand factor subunit distinguishes fragments present in normal and type IIA von Willebrand disease from those generated by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):524–531. doi: 10.1172/JCI112843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Bosak J. O. An ELISA test for the binding of von Willebrand antigen to collagen. Thromb Res. 1986 Aug 1;43(3):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budowle B., Chakraborty R., Giusti A. M., Eisenberg A. J., Allen R. C. Analysis of the VNTR locus D1S80 by the PCR followed by high-resolution PAGE. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):137–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacheris P. M., Nichols W. C., Ginsburg D. Molecular characterization of a unique von Willebrand disease variant. A novel mutation affecting von Willebrand factor/factor VIII interaction. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13499–13502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A., Berkowitz S. D., Ware J., Kasper C. K., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of a cleavage site directing the immunochemical detection of molecular abnormalities in type IIA von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6306–6310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J. A., Galbusera M., Ruggeri Z. M. Heterogeneity of plasma von Willebrand factor multimers resulting from proteolysis of the constituent subunit. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):774–782. doi: 10.1172/JCI115376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Fretto L. J., Hamilton K. K., Erickson H. P., McKee P. A. Substructure of human von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1491–1500. doi: 10.1172/JCI112129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fretto L. J., Fowler W. E., McCaslin D. R., Erickson H. P., McKee P. A. Substructure of human von Willebrand factor. Proteolysis by V8 and characterization of two functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15679–15689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Kostel P., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. A heparin-binding domain of human von Willebrand factor. Characterization and localization to a tryptic fragment extending from amino acid residue Val-449 to Lys-728. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1734–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaucher C., Diéval J., Mazurier C. Characterization of von Willebrand factor gene defects in two unrelated patients with type IIC von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1994 Aug 15;84(4):1024–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Konkle B. A., Gill J. C., Montgomery R. R., Bockenstedt P. L., Johnson T. A., Yang A. Y. Molecular basis of human von Willebrand disease: analysis of platelet von Willebrand factor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Sadler J. E. von Willebrand disease: a database of point mutations, insertions, and deletions. For the Consortium on von Willebrand Factor Mutations and Polymorphisms, and the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Feb 1;69(2):177–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Chopek M. W., Titani K., Davie E. W. Limited proteolysis of human von Willebrand factor by Staphylococcus aureus V-8 protease: isolation and partial characterization of a platelet-binding domain. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3156–3163. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M., MACPHERSON J. C. A one-stage factor VIII (antihaemophilic globulin) assay and its use on venous and capillary plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 May 15;7:215–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill F. G., Enayat M. S., George A. J. Investigation of a kindred with a new autosomal dominantly inherited variant type von Willebrand's disease (possible type IID). J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jun;38(6):665–670. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.6.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita S., Harrison J., Lazerson J., Abildgaard C. F. A new variant of dominant type II von Willebrand's disease with aberrant multimeric pattern of factor VIII-related antigen (type IID). Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1369–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroner P. A., Friedman K. D., Fahs S. A., Scott J. P., Montgomery R. R. Abnormal binding of factor VIII is linked with the substitution of glutamine for arginine 91 in von Willebrand factor in a variant form of von Willebrand disease. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19146–19149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legaz M. E., Schmer G., Counts R. B., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of human Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3946–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe T., Sharefkin J., Yang S. Q., Dieffenbach C. W. A computer program for selection of oligonucleotide primers for polymerase chain reactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1757–1761. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch D. C., Williams R., Zimmerman T. S., Kirby E. P., Livingston D. M. Biosynthesis of the subunits of factor VIIIR by bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons S. E., Bruck M. E., Bowie E. J., Ginsburg D. Impaired intracellular transport produced by a subset of type IIA von Willebrand disease mutations. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4424–4430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane D. E., Stibbe J., Kirby E. P., Zucker M. B., Grant R. A., McPherson J. Letter: A method for assaying von Willebrand factor (ristocetin cofactor). Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Sep 30;34(1):306–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Tuley E. A., Westfield L. A., Lester-Mancuso T. L., Le Beau M. M., Sorace J. M., Sadler J. E. Human von Willebrand factor gene and pseudogene: structural analysis and differentiation by polymerase chain reaction. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):253–269. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti T., Rösselet S. J., Titani K., Walsh K. A. Identification of disulfide-bridged substructures within human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8099–8109. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier C., Parquet-Gernez A., Goudemand M. Dosage de l'antigéne lié au facteur VIII par la technique ELISA. Intérêt dans l'étude de la maladie de Willebrand. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1977 Dec;25 (Suppl):18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke C. H., Jr, Kaneshiro M. M., Maher I. A., Weiner J. M., Rapaport S. I. The standardized normal Ivy bleeding time and its prolongation by aspirin. Blood. 1969 Aug;34(2):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., Cronberg S. A severe haemorrhagic disorder with prolonged bleeding time due to a plasma defect but with normal factor VIII. Acta Med Scand. 1968 Sep;184(3):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb02441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz I., Tuley E. A., Mancuso D. J., Randi A. M., Firkin B. G., Howard M. A., Sadler J. E. von Willebrand disease type B: a missense mutation selectively abolishes ristocetin-induced von Willebrand factor binding to platelet glycoprotein Ib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9846–9849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Nilsson I. M., Lombardi R., Holmberg L., Zimmerman T. S. Aberrant multimeric structure of von Willebrand factor in a new variant of von Willebrand's disease (type IIC). J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1124–1127. doi: 10.1172/JCI110700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Ware J. von Willebrand factor. FASEB J. 1993 Feb 1;7(2):308–316. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.2.8440408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1140–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):895–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. E. A revised classification of von Willebrand disease. For the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost. 1994 Apr;71(4):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneppenheim R., Plendl H., Budde U. Luminography--an alternative assay for detection of von Willebrand factor multimers. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneppenheim R., Thomas K. B., Krey S., Budde U., Jessat U., Sutor A. H., Zieger B. Identification of a candidate missense mutation in a family with von Willebrand disease type IIC. Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;95(6):681–686. doi: 10.1007/BF00209487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Kumar S., Takio K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Ashida K., Walsh K. A., Chopek M. W., Sadler J. E., Fujikawa K. Amino acid sequence of human von Willebrand factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3171–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuley E. A., Gaucher C., Jorieux S., Worrall N. K., Sadler J. E., Mazurier C. Expression of von Willebrand factor "Normandy": an autosomal mutation that mimics hemophilia A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6377–6381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorberg J., Fontijn R., van Mourik J. A., Pannekoek H. Domains involved in multimer assembly of von willebrand factor (vWF): multimerization is independent of dimerization. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):797–803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Lawrence S. O., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Fay P. J., Marder V. J. Topology and order of formation of interchain disulfide bonds in von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells. Identification of a large precursor polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2065–2067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Marder V. J. Biosynthesis of von Willebrand protein by human endothelial cells: processing steps and their intracellular localization. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Dent J. A., Azuma H., Sugimoto M., Kyrle P. A., Yoshioka A., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of a point mutation in type IIB von Willebrand disease illustrating the regulation of von Willebrand factor affinity for the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Dent J. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Nannini L. H. Subunit composition of plasma von Willebrand factor. Cleavage is present in normal individuals, increased in IIA and IIB von Willebrand disease, but minimal in variants with aberrant structure of individual oligomers (types IIC, IID, and IIE). J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):947–951. doi: 10.1172/JCI112394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]