Abstract
Cyanidium caldarium was grown at 20 and 55 C and harvested during exponential growth phase. Lipids were extracted and separated by silicic acid column and thin layer chromatography. The major glycolipids were identified as mono- and digalactosyl diglyceride and sulfolipid. Major phospholipids were identified as phosphatidyl choline and phosphatidyl ethanolamine. The cells grown at 20 C contained significantly larger quantities of these glycolipids and phospholipids than cells grown at 55 C.
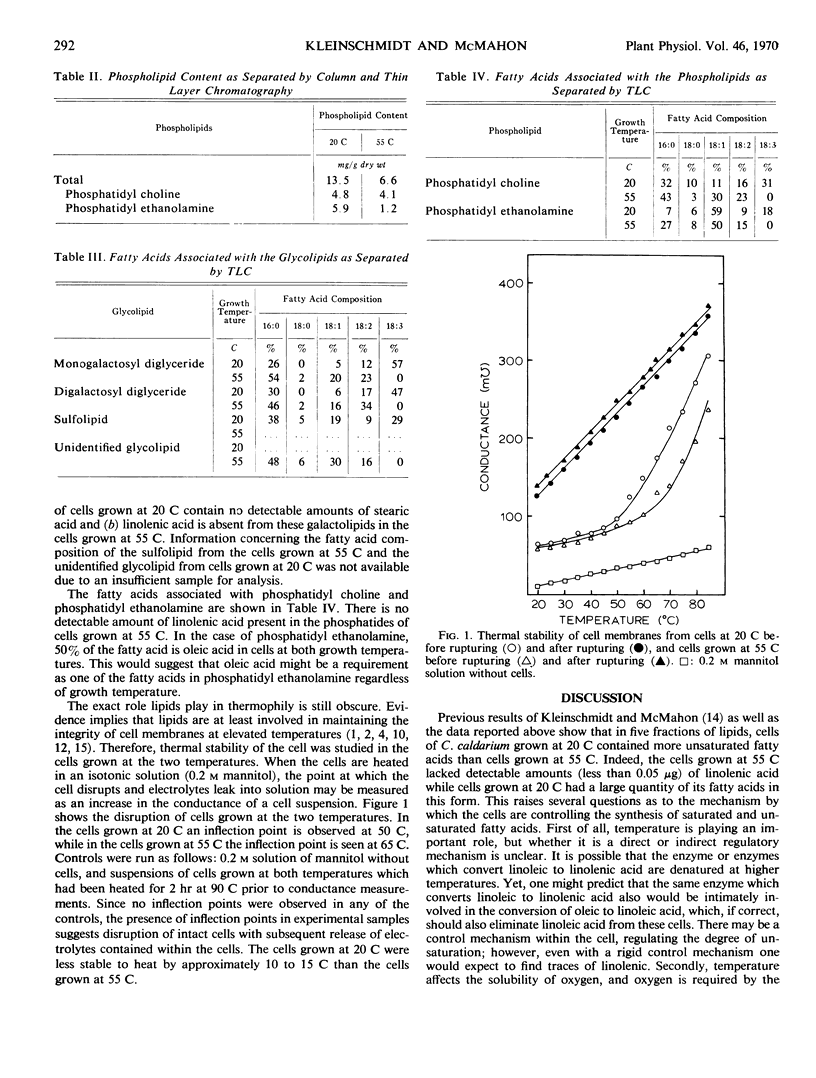
Fatty acid analysis showed that in all cases the cells grown at 20 C contained more unsaturated fatty acids than the cells grown at 55 C. Cells grown at 55 C were shown to lack linolenic acid, in contrast to cells grown at 20 C, which contained appreciable quantities in certain lipid components. For example, monogalactosyl diglyceride had 57% of its fatty acids in the form of linolenic acid. Cells grown at 55 C were 10 to 15 C more stable to disruption by heating than cells grown at 20 C. The greater thermostability of the latter was attributed to a higher degree of saturation of their membrane fatty acids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biezenski J. J. Efficient elution of rabbit liver and plasma phospholipids from thin-layer plates. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):409–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Life at high temperatures. Evolutionary, ecological, and biochemical significance of organisms living in hot springs is discussed. Science. 1967 Nov;158(3804):1012–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3804.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Rose A. H. Fatty-acid composition of Candida utilis as affected by growth temperature and dissolved-oxygen tension. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):371–378. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.371-378.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER H. E., JOHNSON P., WEBER E. J. GLYCOLIPIDS. Annu Rev Biochem. 1965;34:109–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.34.070165.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas T., Herodek S. The effect of environmental temperature on the fatty acid composition of crustacean plankton. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):369–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine H., Hagen P. N-methyl groups in bacterial lipids. 3. Phospholipids of hyphomicrobia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.367-375.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOFFLER H. Protoplasmic differences between mesophiles and thermophiles. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Dec;21(4):227–240. doi: 10.1128/br.21.4.227-240.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ongun A., Mudd J. B. Biosynthesis of galactolipids in plants. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1558–1566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Finkelstein A. Membrane biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:463–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughan P. G., Batt R. D. Quantitative analysis of sulfolipid (sulfoquinovosyl diglyceride) and galactolipids (monogalactosyl and digalactosyl diglycerides) in plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):74–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


