Abstract
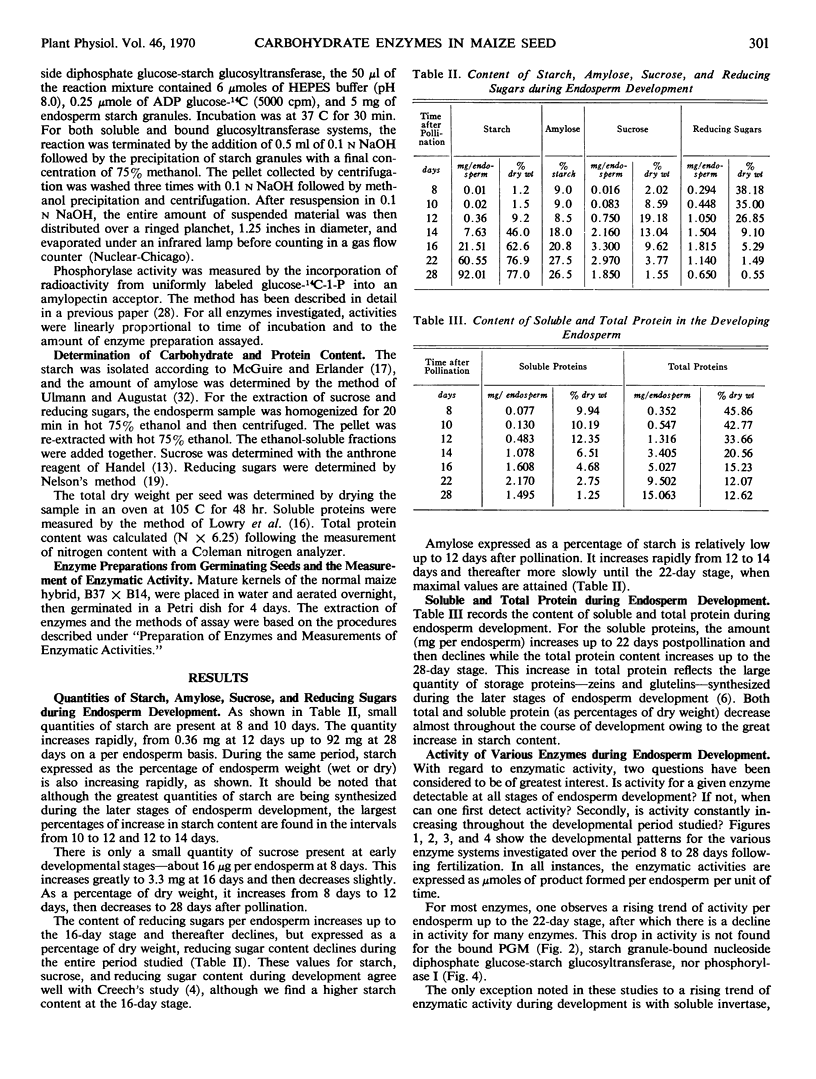
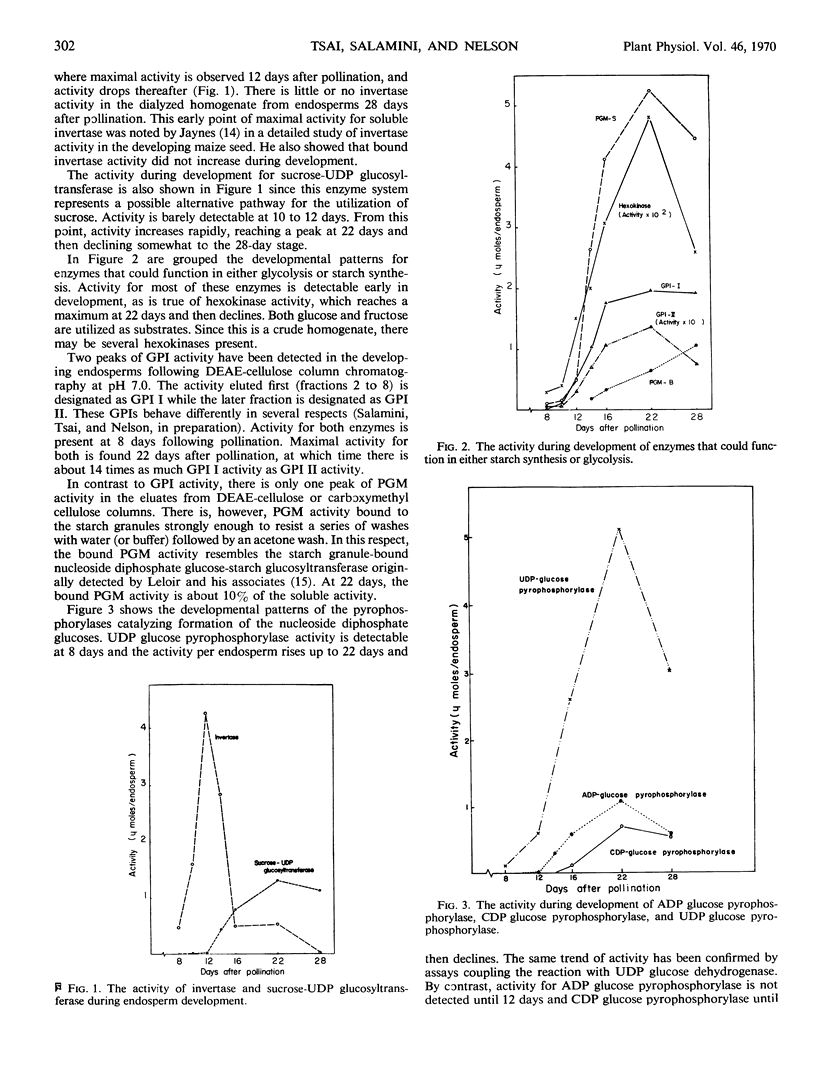
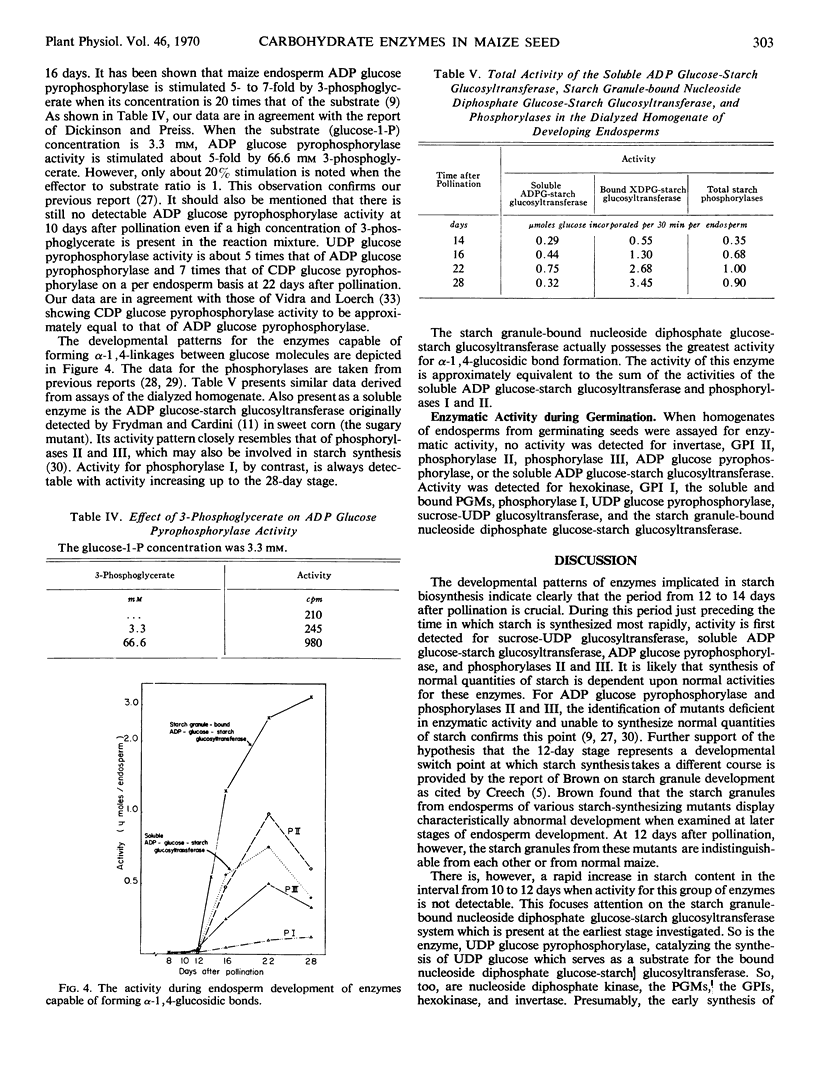
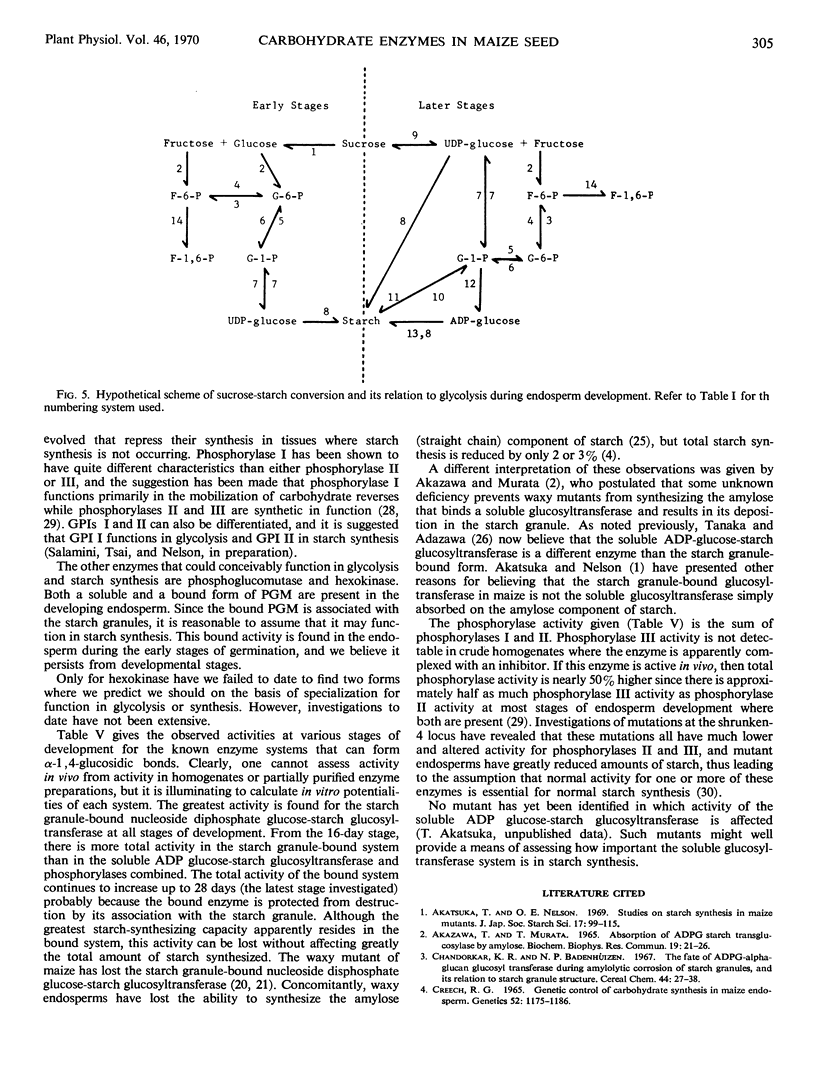
A number of enzymes presumably implicated in starch synthesis were assayed at various stages of endosperm development ranging from 8 days to 28 days after pollination. Activity for invertase, hexokinase, the glucose phosphate isomerases, the phosphoglucomutases, phosphorylase I, uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, and the starch granule-bound nucleoside diphosphate glucose-starch glucosyltransferase was present at the earliest stage of development (8 days) studied. Activity was detectable for phosphorylase III, the soluble adenosine diphosphate glucose-starch glucosyltransferase, adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, and sucrose-uridine diphosphate glucosyltransferase at 12 days. For phosphorylase II and cytidine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, activity was first detectable at the 14- and 16-day stages, respectively. Rapid increases in starch content are observed prior to detectable activity for adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, the soluble adenosine diphosphate glucose-starch glucosyltransferase and phosphorylases II and III. For all enzymes, except invertase, activity per endosperm rises to a peak at 22 or 28 days. Greatest activity for invertase is found at 12 days with a steady decline thereafter. The pattern of invertase activity in comparison with that of sucrose-uridine diphosphate glucosyltransferase supports previous suggestions, that the latter plays a key role in the conversion of sucrose to starch. In addition to phosphorylases I, II, and III, multiple forms of glucosephosphate isomerase and phosphoglucomutase were detected.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Creech R G. Genetic Control of Carbohydrate Synthesis in Maize Endosperm. Genetics. 1965 Dec;52(6):1175–1186. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.6.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. B., Preiss J. Presence of ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase in Shrunken-2 and Brittle-2 Mutants of Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jul;44(7):1058–1062. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.7.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman R. B., Cardini C. E. Biosynthesis of phytoglycogen from adenosine diphosphate D-glucose in sweet corn. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:353–357. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(64)80009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P., Preiss J. Adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase. A regulatory enzyme in the biosynthesis of starch in spinach leaf chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4491–4504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F., DE FEKETE M. A., CARDINI C. E. Starch and oligosaccharide synthesis from uridine diphosphate glucose. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Sugiyama T., Minamikawa T., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch synthesis in ripening rice grains. 3. Mechanism of the sucrose-starch conversion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jan;113(1):34–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON O. E., RINES H. W. The enzymatic deficiency in the waxy mutant of maize. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Oct 31;9:297–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON O. E., TSAI C. Y. GLUCOSE TRANSFER FROM ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE-GLUCOSE TO STARCH IN PREPARATIONS OF WAXY SEEDS. Science. 1964 Sep 11;145(3637):1194–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3637.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADINI A. C., LELOIR L. F. Studies on uridine-diphosphate-glucose. Biochem J. 1952 Jun;51(3):426–430. doi: 10.1042/bj0510426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressey R. Potato sucrose synthetase: purification, properties, and changes in activity associated with maturation. Plant Physiol. 1969 May;44(5):759–764. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.5.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONGINEDEFEKETE M. A., CARDINI C. E. MECHANISM OF GLUCOSE TRANSFER FROM SUCROSE INTO THE STARCH GRANULE OF SWEET CORN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:173–184. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Nelson O. E. Mutations at the shrunken-4 locus in maize that produce three altered phosphorylases. Genetics. 1969 Apr;61(4):813–821. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Nelson O. E. Phosphorylases I and II of Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1968 Jan;43(1):103–112. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Nelson O. E. Starch-deficient maize mutant lacking adenosine dephosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase activity. Science. 1966 Jan 21;151(3708):341–343. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3708.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Nelson O. E. Two additional phosphorylases in developing maize seeds. Plant Physiol. 1969 Feb;44(2):159–167. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Handel E. Direct microdetermination of sucrose. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):280–283. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidra J. D., Loerch J. D. A study of pyrophosphorylase activities in maize endosperm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 9;159(3):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



