Abstract
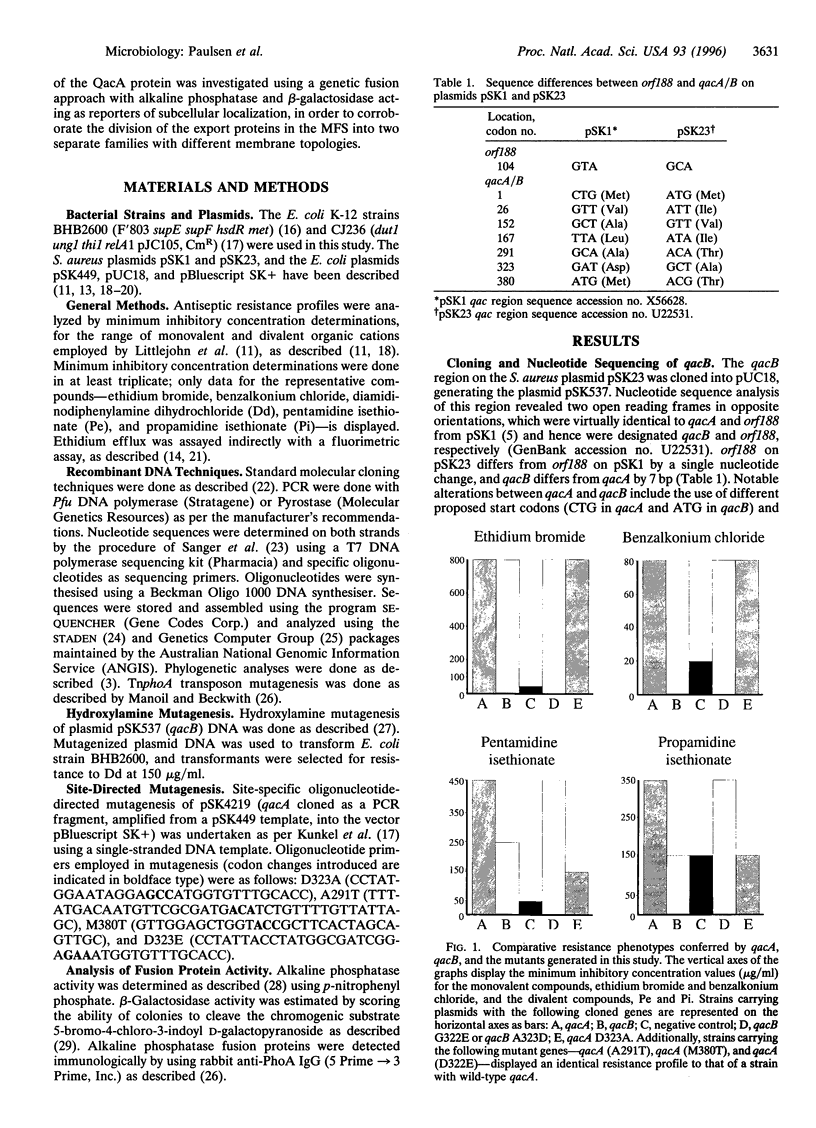
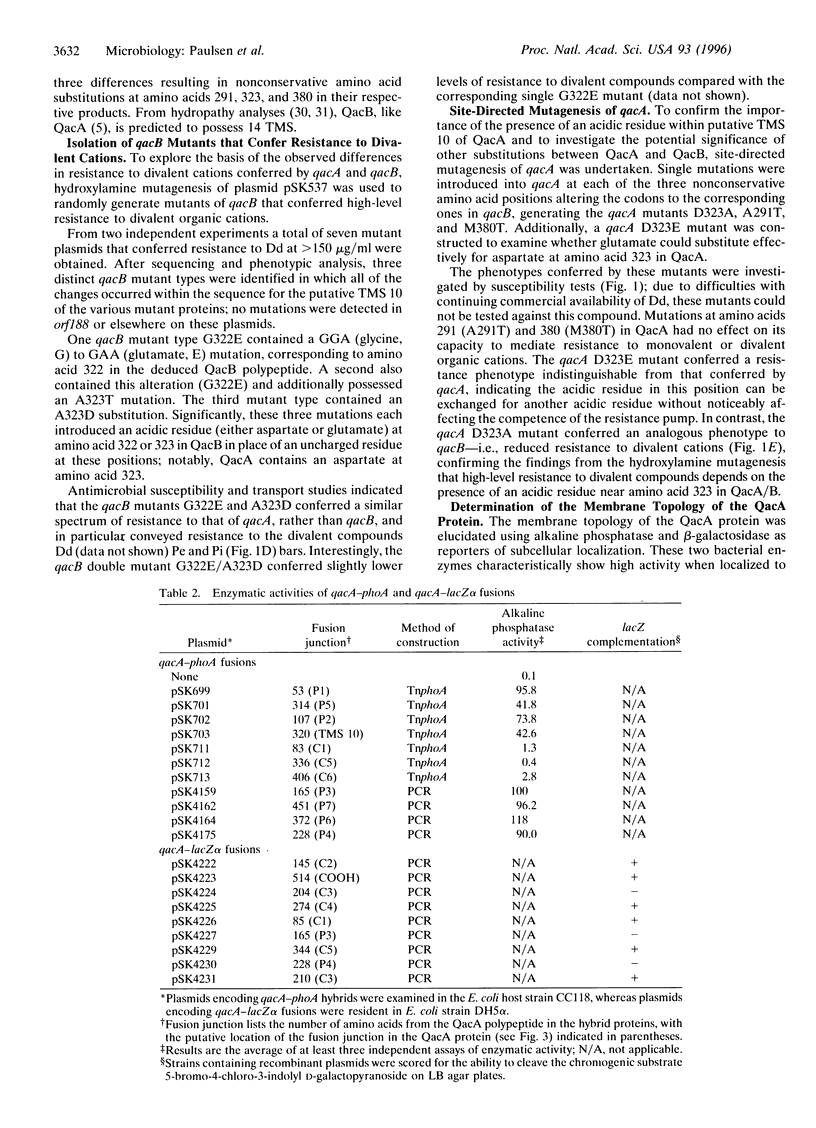
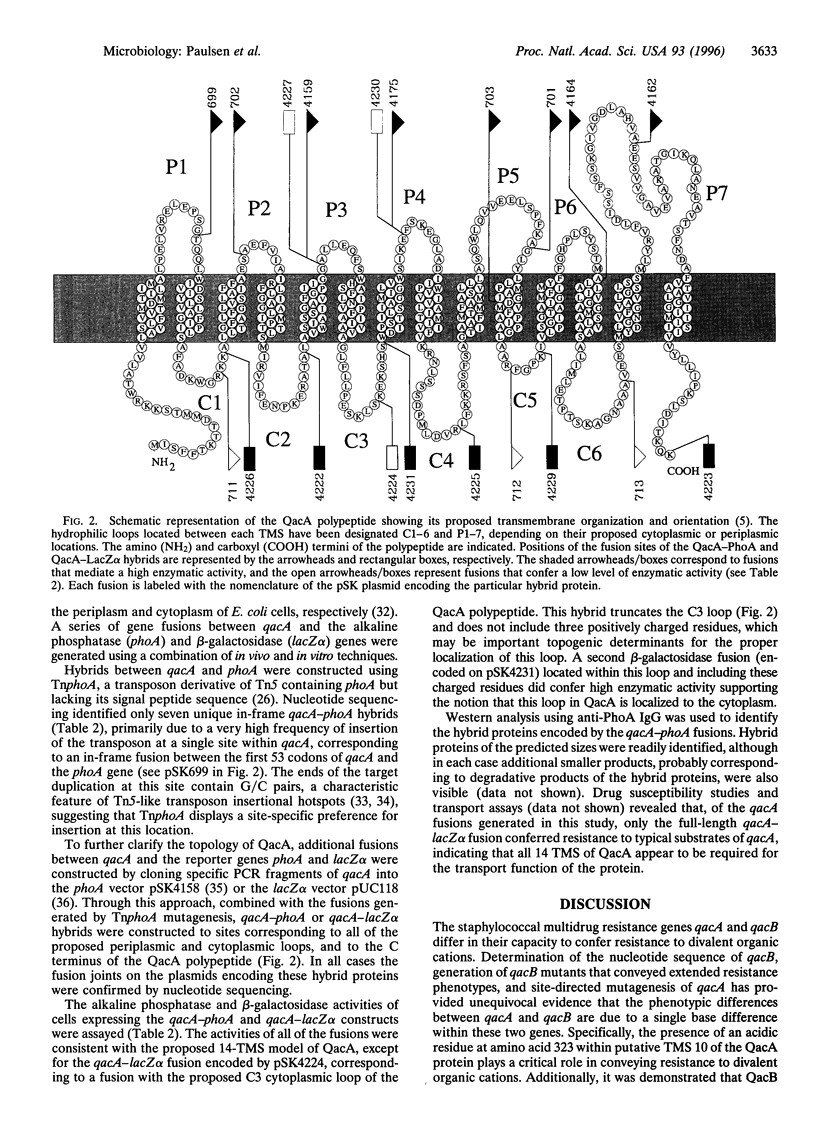
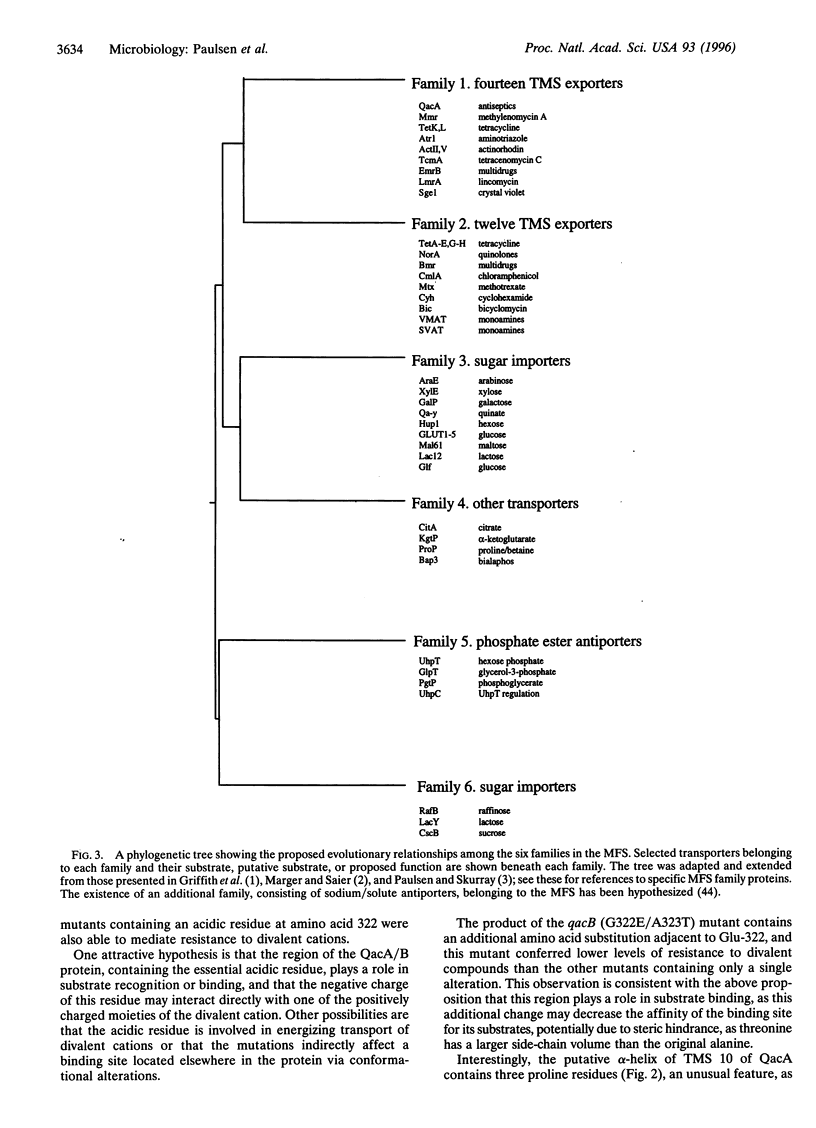
The closely related multidrug efflux pumps QacA and QacB, from the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus, both confer resistance to various toxic organic cations but differ in that QacB mediates lower levels of resistance to divalent cations. Cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the qacB gene revealed that qacB differs from qacA by only seven nucleotide substitutions. Random hydroxylamine mutagenesis of qacB was undertaken, selecting for variants that conferred increased resistance to divalent cations. Both QacA and the QacB mutants capable of conferring resistance to divalent cations contain an acidic residue at either amino acid 322 or 323, whereas QacB contains uncharged residues in these positions. Site-directed mutagenesis of qacA confirmed the importance of an acidic residue within this region of QacA in conferring resistance to divalent cations. Membrane topological analysis using alkaline phosphatase and beta-galactosidase fusions indicated that the QacA protein contains 14 transmembrane segments. Thus, QacA represents the first membrane transport protein shown to contain 14 transmembrane segments, and confirms that the major facilitator superfamily contains a family of proteins with 14 transmembrane segments.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard J. D., Bertrand K. P. Sequence of a class E tetracycline resistance gene from Escherichia coli and comparison of related tetracycline efflux proteins. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4554–4560. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4554-4560.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Deber C. M. Hypothesis about the function of membrane-buried proline residues in transport proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):917–921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickman E., Beckwith J. Analysis of the regulation of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase synthesis using deletions and phi80 transducing phages. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 5;96(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calamia J., Manoil C. lac permease of Escherichia coli: topology and sequence elements promoting membrane insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson T. J., Staden R. An X windows and UNIX implementation of our sequence analysis package. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Jul;7(3):398–398. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.3.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. K., Baker M. E., Rouch D. A., Page M. G., Skurray R. A., Paulsen I. T., Chater K. F., Baldwin S. A., Henderson P. J. Membrane transport proteins: implications of sequence comparisons. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):684–695. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90090-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K., Stoffel W. PROFILEGRAPH: an interactive graphical tool for protein sequence analysis. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Aug;8(4):331–337. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.4.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hresko R. C., Kruse M., Strube M., Mueckler M. Topology of the Glut 1 glucose transporter deduced from glycosylation scanning mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20482–20488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A., Smith H. R., Anderson E. S. Mutagenesis of plasmid DNA with hydroxylamine: isolation of mutants of multi-copy plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Apr 23;145(1):101–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00331564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leelaporn A., Paulsen I. T., Tennent J. M., Littlejohn T. G., Skurray R. A. Multidrug resistance to antiseptics and disinfectants in coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1994 Mar;40(3):214–220. doi: 10.1099/00222615-40-3-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B. Active efflux mechanisms for antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):695–703. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis K. Multidrug resistance pumps in bacteria: variations on a theme. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Mar;19(3):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlejohn T. G., Paulsen I. T., Gillespie M. T., Tennent J. M., Midgley M., Jones I. G., Purewal A. S., Skurray R. A. Substrate specificity and energetics of antiseptic and disinfectant resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Aug 15;74(2-3):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90439-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. D., Kadner R. J. Topology of the Escherichia coli uhpT sugar-phosphate transporter analyzed by using TnphoA fusions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):1688–1693. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.1688-1693.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. K., Berg D. E. Mutations that affect Tn5 insertion into pBR322: importance of local DNA supercoiling. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5956–5960. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5956-5960.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. K., Weston-Hafer K., Berg D. E. Transposon Tn5 target specificity: preference for insertion at G/C pairs. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):645–650. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya O., Lewis K. Emr, an Escherichia coli locus for multidrug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8938–8942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Analysis of plasmids in nosocomial strains of multiple-antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):817–826. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., Skurray R. Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus: genetic basis. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):88–134. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.88-134.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Bacterial transporters. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;6(4):571–582. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marger M. D., Saier M. H., Jr A major superfamily of transmembrane facilitators that catalyse uniport, symport and antiport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90081-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley M. The phosphonium ion efflux system of Escherichia coli: relationship to the ethidium efflux system and energetic studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):3187–3193. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-3187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyfakh A. A., Bidnenko V. E., Chen L. B. Efflux-mediated multidrug resistance in Bacillus subtilis: similarities and dissimilarities with the mammalian system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4781–4785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Prevention of drug access to bacterial targets: permeability barriers and active efflux. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):382–388. doi: 10.1126/science.8153625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen I. T., Brown M. H., Dunstan S. J., Skurray R. A. Molecular characterization of the staphylococcal multidrug resistance export protein QacC. J Bacteriol. 1995 May;177(10):2827–2833. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.10.2827-2833.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen I. T., Skurray R. A. Topology, structure and evolution of two families of proteins involved in antibiotic and antiseptic resistance in eukaryotes and prokaryotes--an analysis. Gene. 1993 Feb 14;124(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90755-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr A functional superfamily of sodium/solute symporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 29;1197(2):133–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouch D. A., Cram D. S., DiBerardino D., Littlejohn T. G., Skurray R. A. Efflux-mediated antiseptic resistance gene qacA from Staphylococcus aureus: common ancestry with tetracycline- and sugar-transport proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2051–2062. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seol W., Shatkin A. J. Membrane topology model of Escherichia coli alpha-ketoglutarate permease by phoA fusion analysis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):565–567. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.2.565-567.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Banks J. L., Snavely M. D., Maguire M. E. Sequence and topology of the CorA magnesium transport systems of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Identification of a new class of transport protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14071–14080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennent J. M., Lyon B. R., Gillespie M. T., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Cloning and expression of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid-mediated quaternary ammonium resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):79–83. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennent J. M., Lyon B. R., Midgley M., Jones I. G., Purewal A. S., Skurray R. A. Physical and biochemical characterization of the qacA gene encoding antiseptic and disinfectant resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jan;135(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxler B., Boyd D., Beckwith J. The topological analysis of integral cytoplasmic membrane proteins. J Membr Biol. 1993 Feb;132(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00233047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane protein structure prediction. Hydrophobicity analysis and the positive-inside rule. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90934-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




