Abstract
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies in human females in the world. One protein that has elevated enzymatic lipase activity in breast cancers in vitro is phospholipase D (PLD), which is also involved in cell migration. We demonstrate that the PLD2 isoform, which was analyzed directly in the tumors, is crucial for cell invasion that contributes critically to the growth and development of breast tumors and lung metastases in vivo. We used three complementary strategies in a SCID mouse model and also addressed the underlying molecular mechanism. First, the PLD2 gene was silenced in highly metastatic, aggressive breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231) with lentivirus-based shRNA, which were xenotransplanted in SCID mice. The resulting mouse primary mammary tumors were reduced in size (65%, p<0.05) and their onset delayed when compared to control tumors. Second, we stably overexpressed PLD2 in low-invasive breast cancer cells (MCF-7) with a biscistronic MIEG retroviral vector and observed that these cells were converted into a highly aggressive phenotype, as primary tumors that formed following xenotransplantation were larger, grew faster and developed lung metastases more readily. Third, we implanted osmotic pumps into SCID xenotransplanted mice that delivered two different small-molecule inhibitors of PLD activity (FIPI and NOPT). These inhibitors led to significant (>70%, p<0.05) inhibition of primary tumor growth, metastatic axillary tumors and lung metastases. In order to define the underlying mechanism, we determined that the machinery of PLD-induced cell invasion is mediated by phosphatidic acid (PA), WASp, Grb2 and Rac2 signaling events that ultimately affect actin polymerization and cell invasion. In summary, this study shows that PLD has a central role in the development, metastasis and level of aggressiveness of breast cancer, raising the possibility that PLD2 could be used as a new therapeutic target.
Keywords: Cell signaling, human breast cancer, PLD, cell invasion and metastasis, SCID mice, xenotransplant
INTRODUCTION
Breast cancer is globally the most common malignancy affecting greater than one million human females per year in 145 countries surveyed (1, 2). Breast cancer metastasis, which is the primary cause of death in patients, is a complex process that involves cell proliferation, invasion through basement membrane and vessel walls, diapedesis into capillaries or lymphatic vessels and further establishment of new colonies in other tissues (3–5). Cell invasion and metastasis need the interaction of a developmental regulatory program, called epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), for transformed epithelial cells to several malignant attributes that enable them to systematically invade adjacent tissues (6). Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) secretion, which requires the full function of the actin-based motility machinery of the cell, is involved in metastasis and is mediated by phospholipase D (PLD), which contributes to in vitro tumor cell invasion (7–12).
Phosphatidic acid (PA)-dependent PLD is required for actin polymerization and ruffle formation, chemotaxis and phagocytosis and elevated PLD activity has been found in colorectal, renal, gastric and breast cancers, as well as melanoma (13–22). PLD confers rapamycin resistance and survival signals in human cancer cells with activated H-Ras or K-Ras (19, 23). There is also a requirement for normal PLD catalytic activity in H-RasV12-induced transformation of normal Rat-2 fibroblasts (24). Elevation of either PLD or especially the PLD2 isoform has the potential to transform both murine and rat fibroblasts (25–27). The potential exists for stimulation of PLD activity to directly contribute to cell proliferation, which further compounds the formation of a fully malignant phenotype (28–30). Recently, two powerful inhibitors of PLD enzymatic activity derived from halopemide have been described: 5-fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI) and N-[2-(4–oxo-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triazaspiro[4,5]dec-8-yl)ethyl]-2-naphthalenecarboxamide (NOPT) (31–33).
A commonly used animal model is the immunodeficient CB17/IcrHsd-Prkdc-Scid mouse model (34), which is deficient in B and T cells, thus allowing engraftment of allogeneic and xenogeneic cells. Additionally, the mammary fat pad (mfp) can be targeted by viral, chemical and physical carcinogens and will yield unique and complex models for neoplastic development. A SCID tumor model based on implantation of human MDA-MD-231 breast cancer cells into the mfp progresses rapidly (<4 weeks until primary tumor onset) after xenotransplantation (35, 36).
PLD couples survival and migration in tumor cell lines (37). Overexpression of wild-type PLD2 has been implicated in EL4 lymphoma metastasis in vivo, while overexpression of catalytically inactive PLD2 generated fewer liver metastases compared to control cells (38). Recently, Chen et al. examined the in vivo role of PLD1 in melanoma growth and metastasis, showing that administration of the inhibitor FIPI into wild-type mice or the loss of PLD1 via PLD1 knockout mice led to a significant reduction of tumor metastases. These results implicate the importance of PLD1 in the tumor microenvironment, which aids in tumor growth/metastasis (39). However, in that work, PLD was not analyzed directly in the tumors or whether the other mammalian isoform, PLD2, contributed towards tumor growth.
In the present study, we demonstrate that PLD2 plays a role in breast cancer invasion and tumorigenesis in vivo. PLD2 stably silenced in highly invasive breast cancer cells led to tumors derived from these cells being only mildly invasive in SCID mice. Conversely, when PLD2 was overexpressed in low invasive breast cancer cells and xenotransplated into SCID mice, more substantial breast tumors arose. Moreover, implanting micro-osmotic pumps containing PLD-specific inhibitors into SCID mice led to a reduction of breast tumors and metastasis following xenotransplantation. Lastly, we determined the mechanism of mammary tumor cell invasion and metastasis seen following PLD2 overexpression as being mediated by PA, Grb2 and Rac2. We advance here the concept that PLD2 is a key factor for cell invasion that contributes critically to growth and metastasis of breast tumors in vivo. The results from this study will have clear pharmacological implications in humans.
RESULTS
Knocking down PLD deters invasion of highly aggressive cancer cells
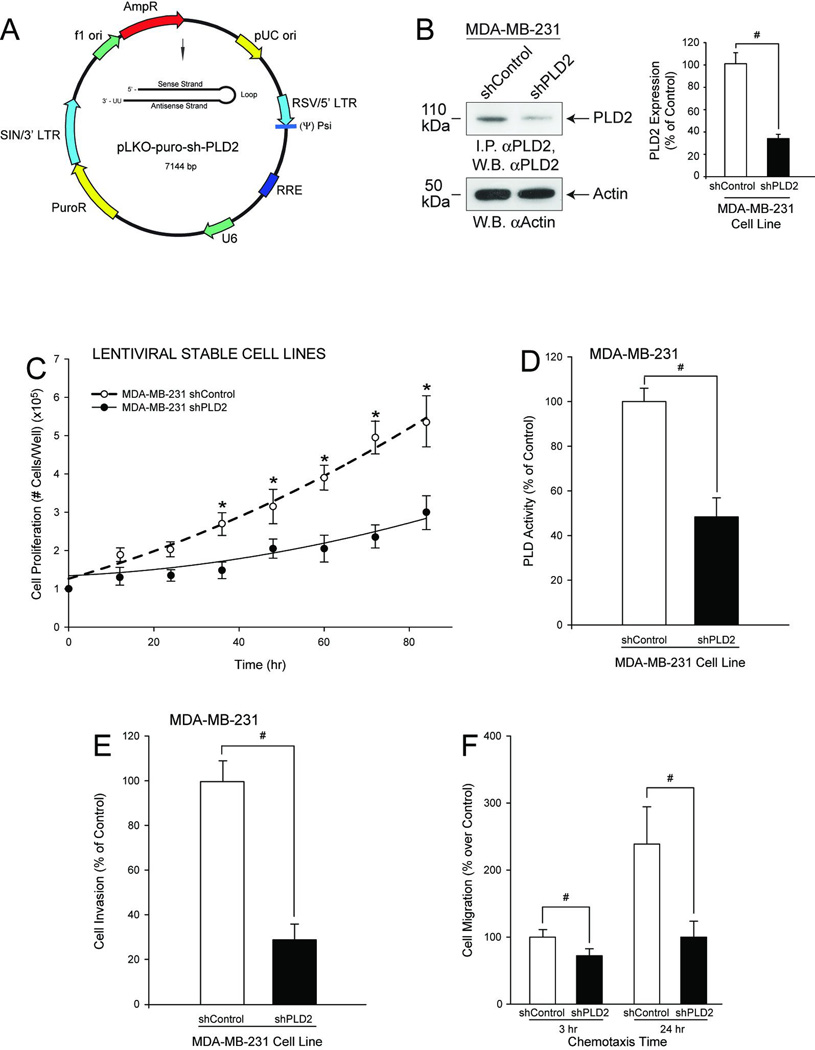
It is known that MDA-MB-231 cells are highly invasive and metastatic cancer cells, and some reasons could be due to high PLD activity found in these cells and PLD’s involvement in cancer cell survival (37). We reasoned that if this were the case, inhibiting PLD2 expression would diminish the highly invasive potential of these cells. To test this hypothesis, we knocked down PLD2 using a targeted lentiviral shRNA. We created two stable MDA-MB-231 cell lines, one that stably silenced PLD2 expression (MDA-MB-231 shPLD2) (Figure 1A) and one infected with an appropriate negative control (MDA-MB-231 shControl). Figure 1B represents the overall effectiveness of PLD2-knockdown, as shown using Western-blot analysis.
Figure 1. A stably silenced PLD2 MDA-MB-231 cell line using lentiviral shRNA shows decreased cancer cell invasion.
A, Vector map of pKLO-shPLD2. B, Western-blot analysis of cell lysates from MDA-MB-231 shControl or shPLD2 cells, with anti-PLD2 antibody. B inset, Quantification of PLD2 silencing from Western-blot analysis of cell lysates from MDA-MB-231 shControl or shPLD2 cells. C, Cell proliferation of puromycin-resistant, stable MDA-MB-231 pKLO cells expressing shPLD2. D, PLD activity. E–F, Negative effect of PLD silencing on physiological functions (cell invasion and chemotaxis, respectively). Triplicate results are mean ± SEM. The symbols * and # denote statistically significant (p<0.05) differences (increases or decreases, respectively) between samples and controls.
As shown in Figure 1C, we found that cell proliferation of shPLD2-silenced MDA-MB-231 cells decreased as a function of time and a concomitant decrease in PLD catalytic activity (Figure 1D), cell invasion (Figure 1E) and chemotaxis (Figure 1F) were observed. Thus, these highly aggressive cancer cells have been rendered low-invasive by PLD2 expression that was knocked-down by ~70% and resulted in PLD activity that was decreased by ~55%, which underscores the crucial importance of this molecule in cell invasion.
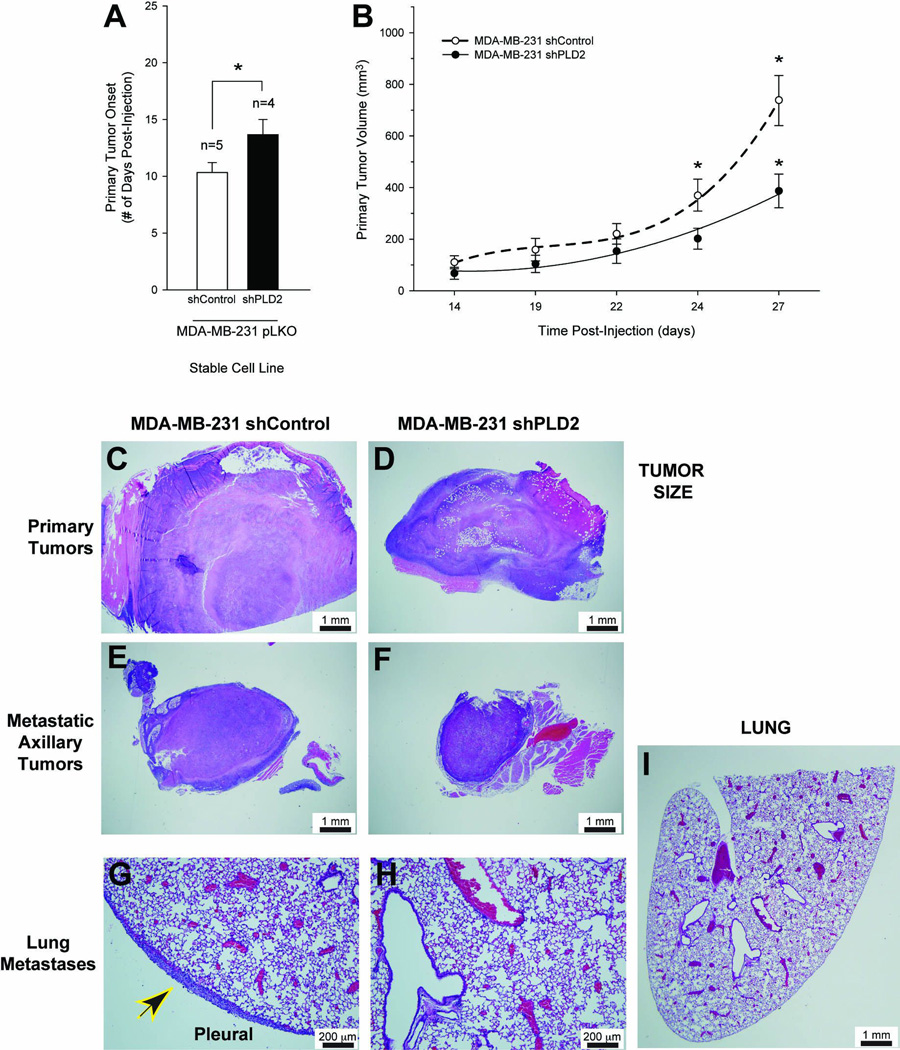
We next tested if this decrease in aggressiveness was observed in an in vivo mouse model: SCID mice were injected with MDA-MB-231 shControl or shPLD2 cancer cells. We found a statistically significant 4-day delay in the onset of measurable primary breast tumor formation in mice injected with MDA-MB-231·pLKO-shPLD2 silenced cells when compared to mice that were injected with the negative MDA-MB-231 shControl cells (Figure 2A). Primary tumor volume was decreased by 65% after 27 days post-injection (Figure 2B). This difference in primary tumor size was corroborated by the histology of these samples (Figure 2C–D, respectively).
Figure 2. PLD2 silencing of SCID mouse metastastic breast cancer model decreases tumor size.
Metastatic breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231-shPLD2 were implanted into the mammary fat pad of immunodeficient 8 week old female SCID mice. Mammary tumor growth and lung metastasis were determined after the duration of the study (at least 5 weeks). A, Primary tumor onset (# days post-injection) for SCID mice injected with MDA-MB-231 pKLO (either shControl or shPLD2) stable cell lines. B, Growth curves of primary tumor volume (mm3). Representative histology images of primary (C–D) and metastatic tumor sections (E–F) and lung sections (G, H, I) detected by hematoxylin-eosin staining of 3–4 different cross sections (7–10 µm- thick) of tissue from at least 3 different mice from each group at 10× magnification, respectively. C, E, G, Histology of SCID mice injected with MDA-MB-231 shControl cells. D, F, H, I, Histology of SCID mice injected with MDA-MB-231 shPLD2 cells. Black and yellow arrowhead denotes presence of pleural carcinoma. I, 2× magnification. G–H, Scale bar = 200 µm. C–F, I, Scale bar = 1 mm.
Large subcutaneous solid carcinomas of differing size with central necrosis developed in both sets of mice at the site of tumor injection (primary tumors) (Figure 2C,D), while metastatic tumors of differing size presented as nodules in well circumscribed subcutaneous lymph glands (Figure 2E,F). However, we identified metastatic carcinomas with associated neutrophilic infiltration on the pleural surface of the lungs in ~20% of MDA-MB-231 shControl mice (Figure 2G, arrowhead), whereas mice injected with MDA-MB-231 shPLD2 cells had no lesions within the lungs (Figure 2H) or on the pleural surface (Figure 2I). If by eliminating PLD2, damage is reduced or eliminated, then it can be inferred that is presence of PLD2 was conducive to the metastatic phenotype.
PLD expression changes low-invasive MCF-7 cells to a high-invasive phenotype
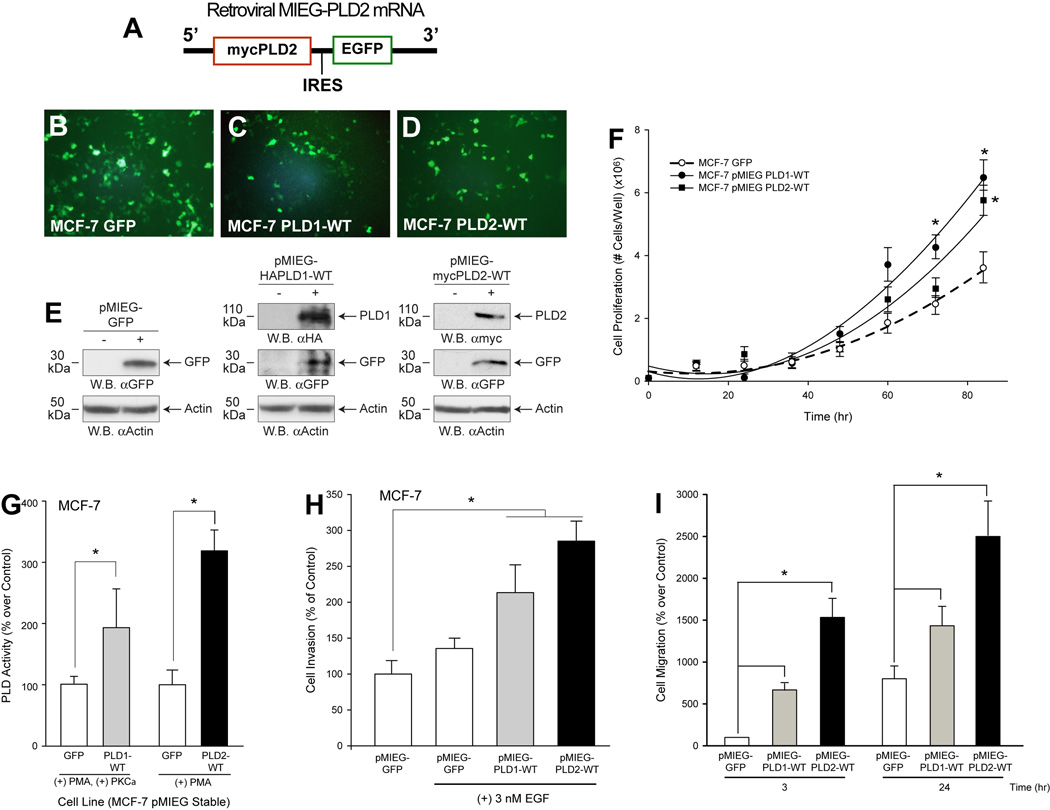
Contrary to silencing PLD2 in a highly invasive breast cancer cell line, as just discussed, we sought to perform the opposite experimentation, i.e., overexpression of PLD in MCF-7, a low-invasive and low metastatic cell line (40, 41). As the pMIEG vector used to deliver the PLD genes also contained a downstream GFP construct (Fig. 3A), we were able to visually verify stable PLD-overexpressing MCF-7 cells following puromycin selection (Figure 3B–D) and verified PLD2 induction using Western-blot analysis (Figure 3E). We found that cell proliferation of PLD1- or PLD2-overexpressing MCF-7 cells was increased ~2-fold when compared to the MCF-7·pMIEG-control cells (Figure 3F), concomitantly with increases in PLD catalytic activity (Figure 3G), cell invasion (Figure 3H) and chemotaxis (Figure 3I).
Figure 3. A MCF-7 Cancer Cell Line Stably Overexpressing Recombinant Human PLD2 shows enhanced cancer cell invasion.
A, Simplified scheme of MIEG-PLD2 mRNA. B–D, Immunofluorescence of GFP in puromycin-resistant, stable MCF-7·pMIEG cells overexpressing either GFP vector, PLD1 or PLD2. E, Western-blot analyses of cell lysates. F, Effect of PLD overexpression on cell proliferation. G, Effect of PLD overexpression on PLD activity. H-I, Effect of PLD overexpression on physiological functions (cell invasion and chemotaxis, respectively). Triplicate results are mean ± SEM. * denotes statistically significant (p<0.05) increases respect to controls.
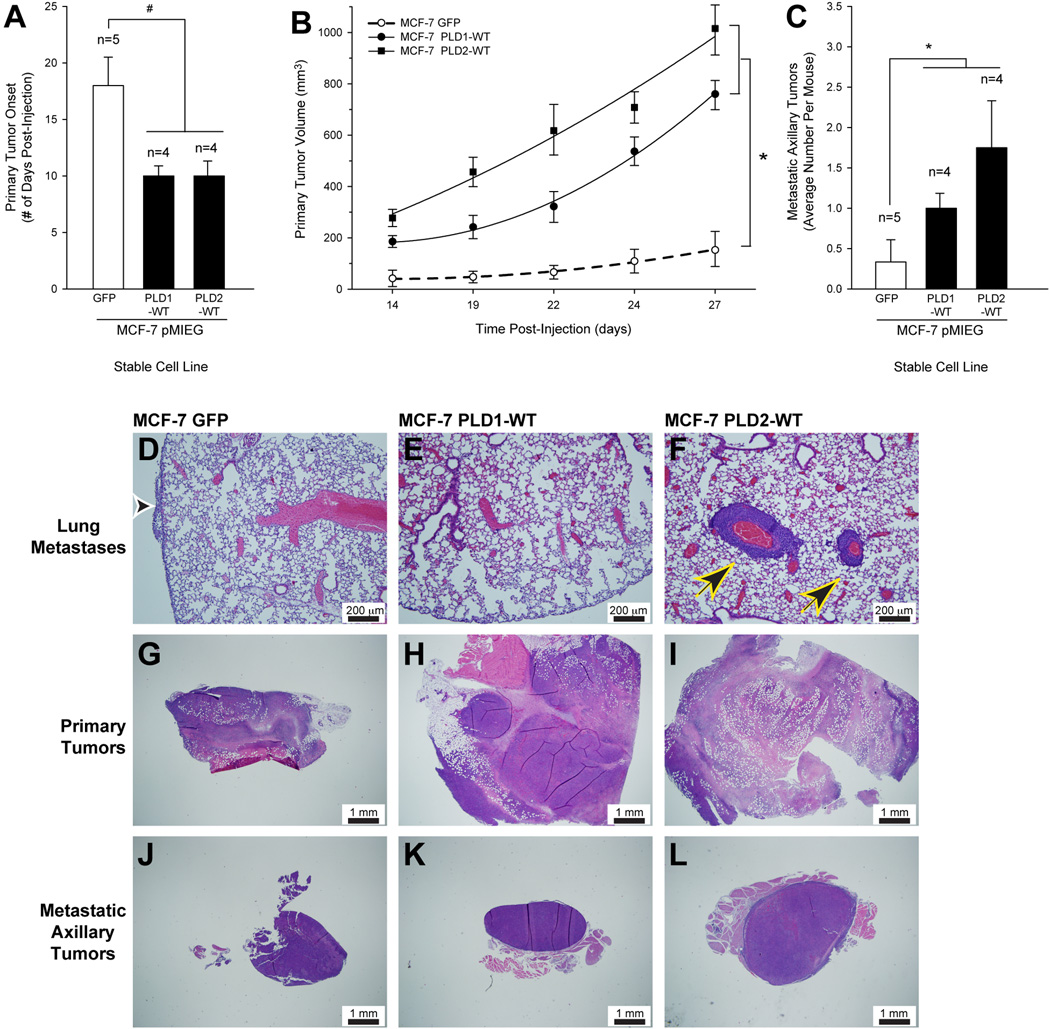
SCID mice were injected with MCF-7·pMIEG-PLD overexpressing cancer cells. The presence of PLD1/2 accelerated the onset of detectable primary tumors by ~ 7 days (10 days versus 17 days) compared with the negative control mice that received MCF-7·pMIEG-GFP cells (Figure 4A). Primary tumor volume was increased 7–10-fold in the MCF-7·pMIEG-PLD injected mice when compared to controls (Figure 4B). Remarkably, PLD overexpression increased the number of metastatic axillary tumors generated in the SCID mice injected with MCF-7·pMIEG stable cells by a factor of 4 to 6 when compared to the negative control GFP vector mice (Figure 4C).
Figure 4. PLD2 overexpression of SCID mouse metastastic breast cancer model increases tumor size.
Metastatic breast cancer cells MCF-7·pMIEG were implanted into the mammary fat pad of SCID mice. A, Primary tumor onset (# days post-injection) of SCID mice injected with MCF-7·pMIEG (either GFP, PLD1 or PLD2) stable cell lines. B, Effect of PLD overexpression on growth curves of primary tumor volume (mm3) in the PLD-xenotransplanted SCID mice. C, Increase in the number of metastatic tumors generated in PLD-xenotransplanted SCID mice. The symbols * and # denote statistically significant (p<0.05) differences (increases or decreases, respectively) between samples and controls. D–L, Representative histology images of lung sections (D–F), primary tumor sections (G–I) or metastatic axillary tumor sections (J-L) detected by hematoxylin-eosin staining of 3–4 different cross sections (7–10 µm- thick) of tissue from at least 3 different mice from each group at 10× magnification, respectively. D, G, J, Histology of SCID mice injected with MCF-7·pMIEG GFP cells. E, H, K, Histology of SCID mice injected with MCF-7·pMIEG PLD1 cells. F, I, L, Histology of SCID mice injected with MCF-7·pMIEG PLD2 cells. Black and white arrowhead denotes presence of pleural carcinoma (D); black and yellow arrowheads point at multifocal perivascular metastatic carcinomas in the lung parenchyma (F). D–F, Scale bar = 200 µm. G-L, Scale bar = 1 mm.
Hematoxylin-eosin stained cross-sections revealed the presence of tumors generated in the PLD-overexpressing MCF-7 cells. Negative control mice showed small carcinoma infiltration on the pleural surface (Figure 4D, arrowhead), whereas mice injected with breast cancer that overexpressed PLD2 had multifocal moderate sized perivascular metastatic carcinomas in the lung parenchyma (Figure 4F, arrowheads). Large subcutaneous solid carcinomas with central necrosis developed in both sets of PLD overexpressing mice at the site of tumor injection (primary tumors) (Figure 4H, I, respectively) and were significantly increased in size when compared to the medium-sized carcinoma generated in negative control MCF-7·pMIEG-GFP mice (Figure 4G).
Secondary tumors also presented as nodules in well-circumscribed subcutaneous metastases in axillary lymph nodes (Figure 4J–L) with the largest metastatic tumors being generated in the PLD2 overexpressing mice (Figure 4L) when compared to control and PLD1 overexpressing mice (Fig. 4J,K).
PLD inhibitors decrease cancer cell invasion in vitro
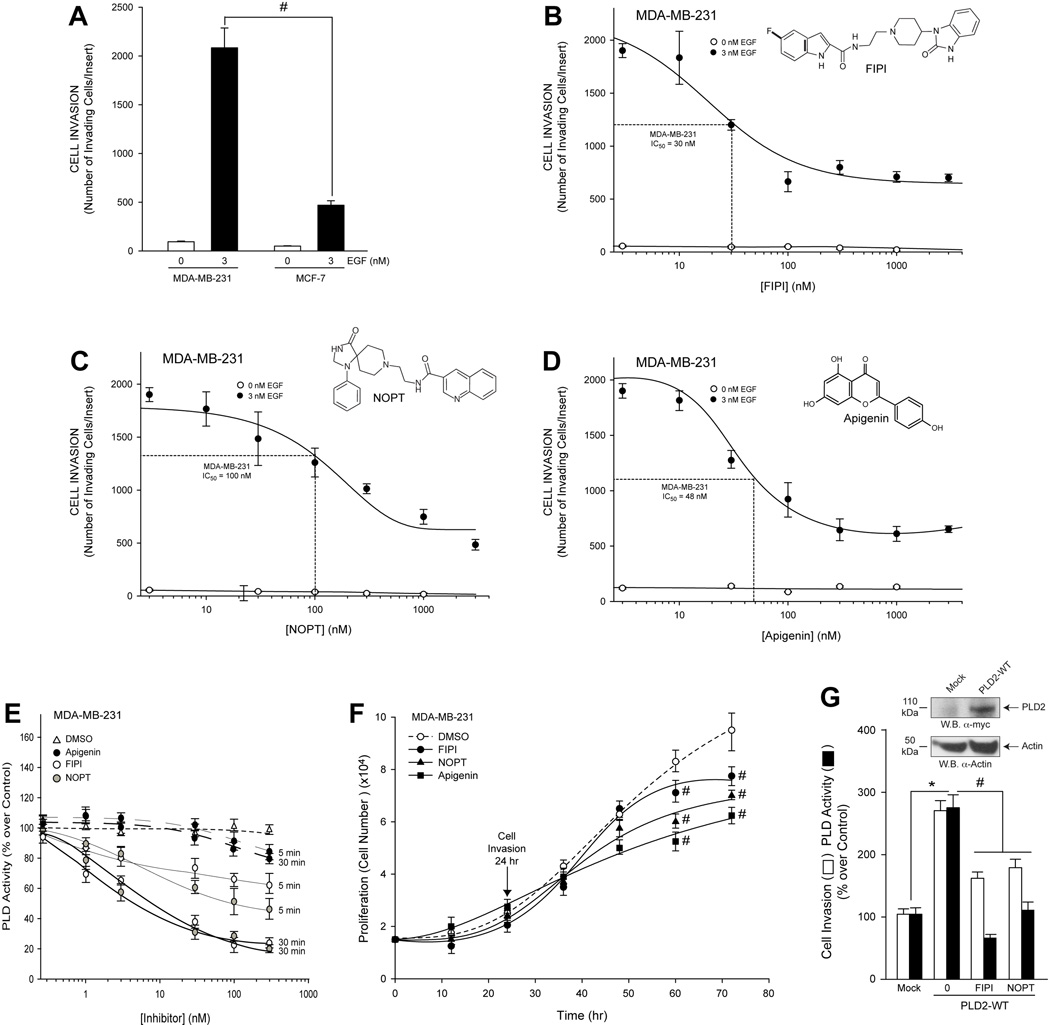
Recently described PLD inhibitors, FIPI and NOPT, were used to examine invasion through matrigel matrix of both MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells 29,30. MDA-MB-231 cancer cells were much more responsive to cell invasion through matrigel matrix (Figure 5A) when compared to MCF-7 cells after epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation. We determined that the number of MDA-MB-231 (Figure 5B–D) cells that invaded in response to 3 nM EGF decreased in proportion to increasing inhibitor concentration compared to the non-stimulated cells. Accordingly, we determined the optimal concentration of FIPI, NOPT and apigenin (Figure 5B–D insets, respectively) necessary to inhibit 50% of chemotactic MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in response to EGF (apigenin is not a PLD inhibitor, but it was used here as a positive control for cell invasion).
Figure 5. Small-molecule inhibitors, FIPI, NOPT and apigenin, inhibit cell invasion of two breast cancer cell lines, which correlates to a decreased PLD2 activity independent of cell proliferation.
Exponentially growing cells in culture were used for these experiments. A, Relative difference of cell invasiveness of highly invasive MDA-MB-231 compared to less invasive MCF-7 cells in response to 3 nM EGF. B–D, Effect of small molecule inhibitors on cell invasion. B, FIPI dose response. C, NOPT dose response. D, Apigenin dose response. Triplicate results are mean ± SEM. B inset, FIPI schematic. C inset, NOPT schematic. D inset, Apigenin inset. E, Time dependent effect of FIPI or NOPT on endogenous PLD activity after incubation for 5 min or for 30 min with the inhibitors prior to the enzymatic assay. F, Time dependent effects of small molecule inhibitors (300 nM concentration of each) on MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation. G, Effect of 300 nM concentration of each inhibitor on cell invasion or lipase assay (at 30 min) of MDA-MB-231 cancer cells overexpressing recombinant PLD2-WT. Triplicate results are mean ± SEM. The symbols * and # denote statistically significant (p<0.05) differences (increases or decreases, respectively) between samples and controls.
The results from Figure 5E show that the endogenous PLD activity of MDA-MB-231 cells were more sensitive to the negative effect of the dual PLD inhibitor, FIPI, and the PLD2-specific inhibitor, NOPT, as a function of time when compared to that of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, apigenin. The decreases in MDA-MB-231 cell invasion and PLD2 activity due to PLD inhibition were not a result of a decrease in cell proliferation of the MDA-MB-231 cells, as there was no alteration in proliferation when cell invasion measurements were performed (24 hours) (Figure 5F). However, treatment of cells with the small-molecule inhibitors for ≥36 hours resulted in a gradual decrease in cell proliferation indicating an anti-proliferation effect of the PLD inhibitors. Further, we determined that MDA-MB-231 cancer cells that overexpress recombinant PLD2-WT were significantly less invasive (Figure 5G, open bars) in the presence of the small molecule inhibitors with a concomitant and greater decrease in PLD2 activity (Figure 5G, filled bars), which supports the data presented in Figure 5E.
PLD inhibitors robustly inhibit tumor size and metastases formation in vivo
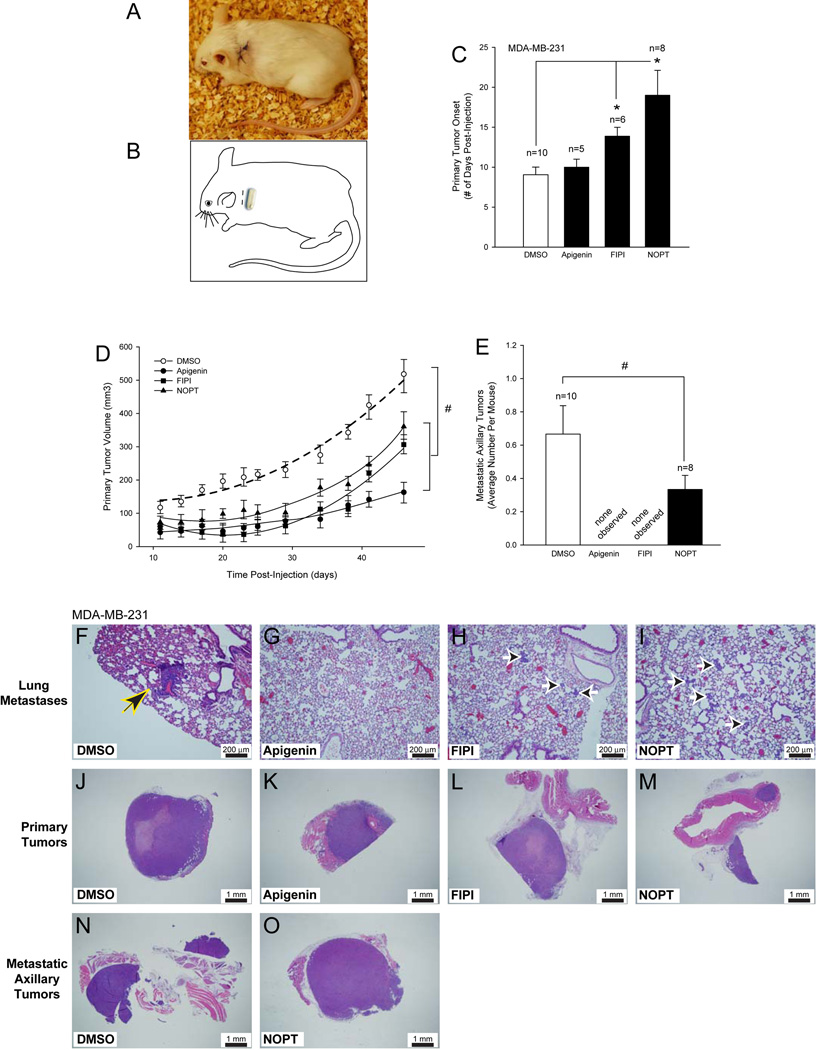
To test the PLD inhibitors in vivo, SCID mice were implanted with an Alzet micro- osmotic pump containing an inhibitor (Figure 6A) in the left dorsal thoracic area (Figure 6B), and were subsequently xenotransplanted with MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. There was a significant delay (~ 1.2–2-fold) in the onset of primary breast tumors in FIPI- and NOPT-treated mice (Figure 6C) and a significant decrease in the volume of primary tumors from the FIPI- and NOPT-treated mice (Figure 6D) (~30% and 40%, respectively).
Figure 6. Small-molecule inhibitors reduce tumor size on SCID mouse metastastic breast cancer model.
A, Schematic drawing of Alzet pump implantation in SCID mice. B, Photographic representation of surgical area on SCID mice after Alzet pump implantation. C, Delayed primary tumor onset (# days post-injection) for SCID mice xenotransplanted with MDA-MB-231 cells in the presence of small molecule inhibitors. D, Decreased primary tumor volume (mm3) following dosing of xenotransplanted SCID mice with small molecule inhibitors. E, Reduction in the number of secondary tumors of xenotransplanted SCID mice in the presence of inhibitors. Triplicate results are mean ± SEM. The symbols * and # denote statistically significant (p<0.05) differences (increases or decreases, respectively) between samples and controls. F–O, Representative histology images of lung sections (F–I), primary tumor sections (J–M) or secondary tumor sections (N–O) detected by hematoxylin-eosin staining of 3–4 different cross sections (7–10 µm- thick) of tissue from at least 3 different mice from each group at 10× or 2× magnification, respectively. Black and yellow arrowhead denotes presence of small focal metastatic perivascular lung carcinomas (F); black and white arrow heads point at small 2–20 cell carcinoma emboli in the alveolar walls (H–I). F-I, Scale bar = 200 µm. J–O, Scale bar = 1 mm.
Additionally, the presence of the small-molecule PLD inhibitors drastically reduced the number of metastatic axillary tumors generated in the SCID mice (Figure 6E). The mice that received NOPT had ~ 50% fewer metastatic axillary tumors when compared to the DMSO only negative control mice, while no secondary tumors were observed in the mice that received FIPI or apigenin.
Pathological studies indicated that MDA-MB-231 xenotransplanted SCID mice that received vehicle only (DMSO) had small focal metastatic perivascular lung carcinomas (Figure 6F, arrowhead), while mice that received either PLD2 inhibitor (FIPI or NOPT) generated small 2–20 cell carcinoma emboli in the alveolar walls (Figure 6H–I, arrowheads, respectively). Mice that received apigenin did not form metastatic lung lesions (Figure 6G).
MDA-MB-231 xenotransplanted SCID mice that received DMSO only had primary tumors that were large subcutaneous solid carcinomas with central necrosis invading the mammary fat pad and adjacent skeletal muscle (Figure 6J), while mice that received small-molecule inhibitors had primary tumors that were medium to small size subcutaneous solid carcinomas invading adjacent musculature (Figure 6K,M) or medium size subcutaneous solid carcinoma with central necrosis (FIPI, Figure 6L). Thus, PLD inhibitors robustly inhibited tumor onset, tumor size and lung metastasis once again underscoring the cell signaling molecule PLD as crucial in tumor progression.
Mechanism of PLD-derived enhancement of cell invasion and metastasis
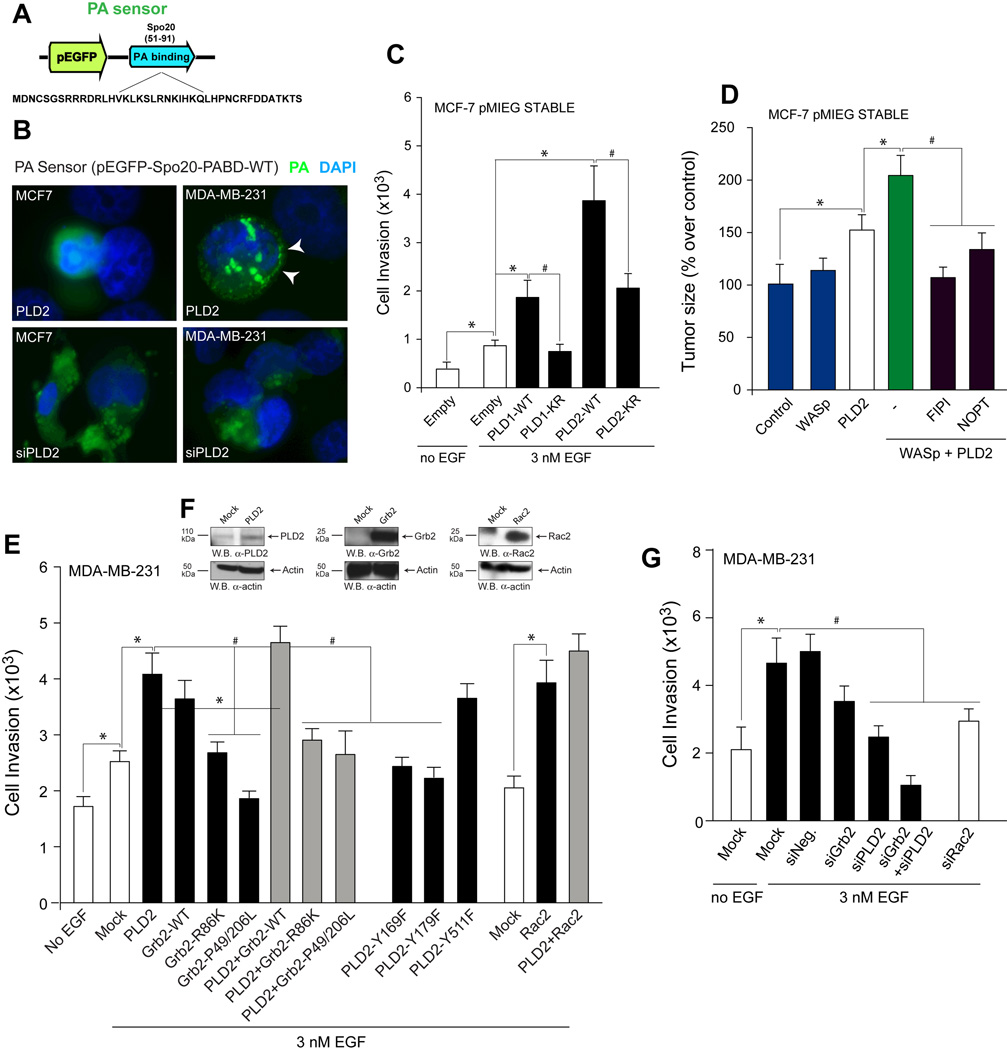
In this study, we examined breast cancer cells to determine the underlying mechanism that regulates PLD-mediated cell invasion and metastasis and found that it involves PA, the product of PLD enzymatic activity. In addition to this, PLD could also associate with other signaling molecules that could contribute to the invasive, metastatic phenotype, as described below. In the first approach, to examine for PLD activity, we used a PA sensor (EGFP-PA-binding domain of Spo) (32, 42, 43) to detect in vivo the presence of PA (Figure 7A). We observed that the PA sensor was recruited to a membranous surface in the MDA-MB-231 cells that overexpressed PLD2 but remained nuclear in the MCF-7 that also overexpressed PLD2. The PA sensor was also redistributed to cytoplasmic localizations in silenced cells when compared to cells that overexpressed PLD2 (Figure 7B). These data suggest a lack of PA availability to bind to membrane surfaces under conditions where PLD2 is silenced in cells in general or where PLD2 is endogenously expressed to a lesser extent in the less invasive MCF-7 cells compared to the highly invasive MDA-MB-231 cells. Additionally, when lipase-inactive PLD1 (PLD1-K866R) or PLD2 (PLD2-K758R) constructs were stably overexpressed in MCF-7 cells, invasion was significantly reduced due to a lack of PA production by the transfected recombinant PLDs compared to expression of wild-type PLDs (Figure 7C).
Figure 7. The mechanism that regulates PLD-mediated cell invasion and metastasis involves PA, Rac2 and Grb2.
A, PA sensor used for transfection into MDA-MB-231 or MCF-7 cells. B, Immunofluorescence of PA sensor expression. White arrowheads denote PA sensor localized to a membranous surface that contained PA. C, Cell invasion of MCF-7 cells stably expressing lipase-inactive constructs (PLD1-K866R or PLD2-K758R). D, Tumor size of mice injected with MCF-7 cells stably expressing PLD2, a WASp construct or a combination of the two. E, EGF-mediated cell invasion in cells that overexpress PLD2, Grb2 and Rac2 constructs (WT and SH2-binding deficient). F, PLD2, Grb2 and Rac2 protein expression in MDA-MB-231 cells. G, EGF-mediated cell invasion in cells silenced with siRNA for Grb2 and/or PLD2 or with siRNA for Rac2.
In an earlier study from our lab, we found that Wiscott-Aldrich Syndrome protein (WASp) was involved in PLD2-mediated phagocytosis via interaction with the growth receptor bound protein 2 (Grb2), which acted as the docking protein between PLD2 and WASp (13). Considering this earlier finding, we explored the mechanistic importance of WASp to our in vivo SCID mouse model using transient overexpression of WASp into MCF-7 cells that stably overexpressed PLD2, which were then xenotransplanted into SCID mice. Tumor size at the inject site of mice xenotransplanted with MCF-7 cells expressing PLD2, transient overexpression of a WASp-WT construct or a combination of the two indicate a role for WASP possibly aiding PLD2 in tumorigenesis, which was prevented by PLD inhibitors FIPI and NOPT (Figure 7D).
Additionally, we also discovered that once PLD activity is elevated following binding to Grb2-SH2 via PLD2-Y169, PLD2 cooperates with Rac2, and these three proteins are then able to stimulate actin polymerization and subsequent membrane ruffle formation (44). Taking this information into consideration, we determined that PLD2 lipase-independent interactions with Grb2 and Rac2 also underlie MDA-MB-231 cell invasion, as overexpression of either Grb2 or Rac2 alone or in combination with PLD2 overexpression significantly increased cell invasion of cancer cells (Figure 7E), while overexpression of Grb2 mutants that do not bind to PLD2 or WASp significantly reduced invasion (Figure 7E). In contrast, knockdown of Grb2 in conjunction with knockdown of PLD2 virtually abrogated invasion, as did knockdown of Rac2 gene expression (Figure 7G).
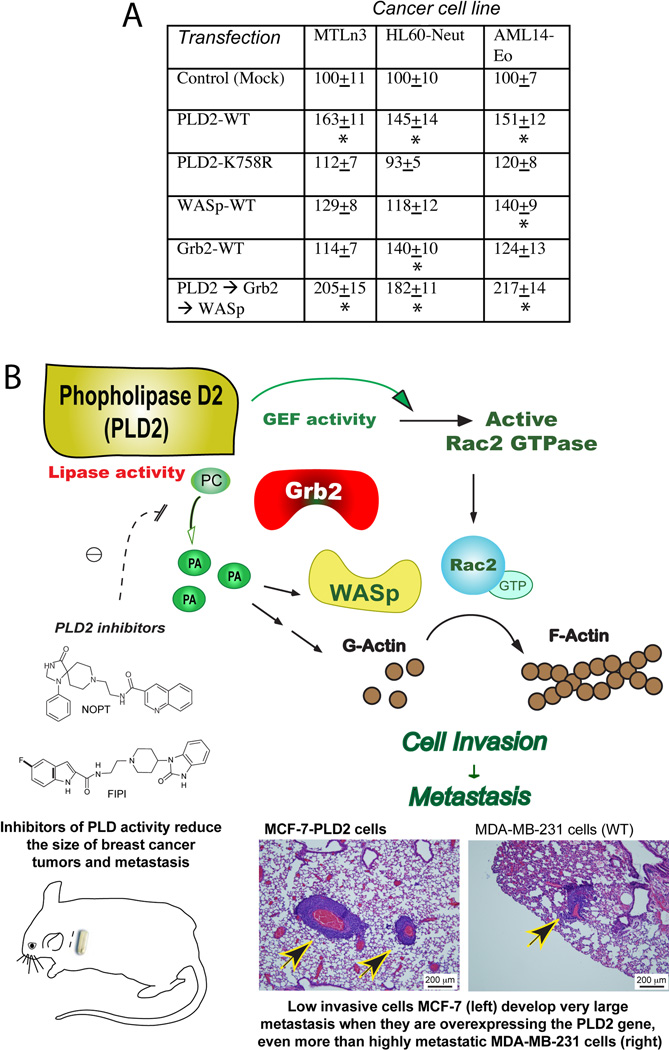
In addition to breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7, we sought to investigate if our findings were relevant to other cell lines. The data presented in Figure 8A show that MTLn3 (41) (rat breast cancer cells) demonstrate elevated cell invasion particularly with the overexpression of PLD2, Grb2 and WASP. Two other cancer cell lines, AML14-eosinophils (AML-14-Eo)(45) and HL-60 neutrophilic (HL60-neut), both leukemic, also displayed similar patterns. Thus, the mechanistic findings could be extrapolated to other cell lines.
Figure 8. Model for the mechanism that regulates PLD-mediated metastasis.
A, Cell invasion (MTLn3) or cell migration (HL60 and AML14) following overexpression of signaling molecules in three cancer cell lines other than MDA’s or MCF’s. Astericks represent significant increase (p<0.05). B, Model that summarizes graphically the findings of this study (histological samples are from Figs. 4F and 6F).
A summary of the study findings is presented in Figure 8B, incorporating the chemical inhibitors, in vitro and in vivo studies. Further, we have found that the mechanism of PLD2-mediated mammary tumor metastasis relies on both PA generated by PLD2 and on the interaction with protein binding partners, such as WASp, Grb2 and Rac2 that serve to upregulate actin polymerization and increase cell invasion.
DISCUSSION
The present study provides evidence that the signaling protein PLD2 is integral for human breast cancer progress in vivo by leading to increased tumor cell growth and invasion. We conducted a controlled study in SCID mice and the pathology examinations showed that PLD contributes to growth, invasion and metastases in vivo.
Using the metastatic model of SCID mice, we investigated the effects of short hairpin RNA (shRNA) as a means to constitutively silence PLD2 expression in highly invasive cancer cells (MDA-MD-231) and stable over-expression of PLD in low invasive cancer cells (MCF-7). We found that PLD2 knockdown in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells significantly abrogated tumor growth and lung metastases in SCID mice, while stable transduction of PLD2 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells significantly augmented tumor growth in SCID mice. Overexpression of lipase active PLD2 in lymphoma cells has been documented in the generation of liver metastases in vivo, while overexpression of lipase-inactive PLD2 inhibited liver metastases compared to control lymphoma cells (38). This report and the data herein support the importance of catalytically active PLD2 to the metastatic process.
Additionally, it has been documented in Pld1−/− mice that tumor vascularization of mouse melanoma or lung carcinoma was significantly abrogated as a result of PLD downregulation in the tumor environment (i.e. host cells) (39), but these injected tumor cells had PLD1 and PLD2 expression. In the study reported herein, the environment has normal expression of PLD (i.e. wild-type mice), but we are studying PLD expression (or the lack of) directly in the tumor, as the injected cells have been engineered to overexpress or suppress PLD2. Both of these studies ((39) and here) complement each other and give a more complete picture of the key role of PLD1 and PLD2 in tumorigenesis and metastasis.
We also studied the effects of small-molecule PLD inhibitors on tumor growth and the development of lung metastasis. FIPI is a derivative of halopemide that inhibits both PLD isoforms and interferes with PLD regulation of F-actin cytoskeleton reorganization, cell spreading and chemotaxis (31, 32). The other PLD enzymatic activity inhibitor, NOPT, inhibits the PLD2 isoform, both in vitro and in cells and is also effective as a PLD1 inhibitor at higher concentrations (33). In vitro, NOPT strongly inhibits the invasive migration of breast cancer cells in Transwell assays, shown the first time by (33). Very interestingly, Scott et al. present PLD as an useful target in blocking tumor cell invasion (33), which is what we have achieved in the present study in both in vitro cell invasion and in in vivo situations.
Chen et al. (39) showed elegantly that administration of FIPI to PLD1−/− mice inhibited tumor growth and metastasis. In the present study, we found that PLD inhibitory compounds deterred cell invasion, tumor growth and the incidence of metastatic tumors in xenotransplanted SCID mice, and that the novel approaches of deletion or overexpression of the PLD isoform PLD2 and follow up in vivo, demonstrates a crucial bearing of PLD2 on tumorigenesis. We advance here the concept that PLD2 is a key factor for cell invasion that contributes critically to growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells in vivo, which has potential clinical utility in human breast cancer treatment.
PLD confers rapamycin resistance (19) and survival signals in human cancer cells with activated H-Ras or K-Ras (23), possibly due to PA involvement. We have seen that the mechanism of PLD-mediated tumor invasion and metastasis involves PA and the association of PLD2 with Rac2 and actin. Support of PLD’s role in non-catalytic functions has been presented whereby PLD2 can still act as an adaptor protein for the Grb2 (13), binds onto Rac2 and affect cell membrane ruffling and cell growth (44, 46). We propose that PLD-synthesized PA is directly involved in regulating actin polymerization of invasive mesenchymal cells. As known, cancer cells escape the initial tumor when the tumor reaches a certain size, becoming invasive and highly motile and gain entry into the systemic circulation by reaching a nearby capillary or lymph vessel. Since in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, cancer cells become amoeboid, free-floating and highly mobile like leukocytes, our knowledge amassed in the last 5–7 years on PLD-derived chemotaxis action will be directly implicated in cell invasion in vivo.
Our laboratory (13, 44, 47, 48) and others (49–53) have provided ample evidence of PA-related actin polymerization. The implication of novel molecules such as Grb2, Sos, Wasp and Rac2 on cell migration has been previously reviewed (30, 54). Although we acknowledge that PLD1 is involved in increased tumor cell invasion and tumorigenesis in our model that relied on overexpression of PLD1 in the less invasive MCF-7 cells, we did not focus on any mechanistic control of PLD1 in this study, as our primary focus was on that of PLD2.
In conclusion, this study documents the first proof of a role for PLD2 in breast tumor progression and metastasis and has provided insight into the mechanism of action. PLD2 could be a marker of metastatic progression (38, 55, 56) and a viable target for anti-breast tumor therapy. This report provides the foundation for further studies of the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which PLD2 mediates tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in vivo. Our results also provide evidence that targeting PLD is a good candidate for future therapeutic and clinical applications aimed at reducing human breast cancer metastasis.
METHODS
Cells and cell culture
MDA-MB-231 cells were obtained from ATCC. MCF-7 cells were from Dr. Steven J. Berberich (Wright State University). GP2-293 retroviral packaging cells, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS). Cells were maintained at 37°C in an incubator with a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2.
Lentiviral production of MDA-MB-231 Cell Line to Stably Silence PLD2
Lentivirus was produced by the co-transfection of 293FT cells with a pLenti vector (pKLO-shControl or pKLO-shPLD2) and lentiviral packaging mix (Invitrogen), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Lentivirus-containing supernatant was harvested 48 hours post-transfection, purified by centrifugation and stored at −80°C. For viral transductions, 1 mL of the pKLKO-shControl or pPLKO-shPLD2 lentiviruses was incubated with MDA-MB-231 mammalian cells in the presence of 4 μg/mL polybrene overnight at 37°C in a humidified cell culture incubator. Twenty-four hours post-infection, cells were screened for target expression using a final concentration of 300 ng/mL puromycin for 7 days at which time mock MDA-MB-231·pKLO-shControl or PLD2-silenced MDA-MB-231·pKLO-shPLD2, puromycin-resistant cells were cultured in complete media (DMEM, 10% FCS, pen-strep). After 1 month of stable growth in complete media, verification of target cells was conducted by Western-blot analysis.
Cloning and Production of a MCF-7 Cancer Cell Line Stably Overexpressing Recombinant Human PLD2
To create the stable overexpression of recombinant PLD protein, a 5’ SalI and a 3’ HindIII sites were introduced in a pcDNA3.1-mycPLD2-WT PLD2 template. The PCR product was amplified with Pfu DNA polymerase. A pMIEG retroviral vector was prelinearized from the manufacturer and was recombined with the PCR product of interest using the In-Fusion Dry-Down PCR Cloning Kit and sequenced to ascertain expression of the correct DNA sequence. GFP only, PLD1 or PLD2 cloned into the MIEG retroviral vector were referred to as either “pMIEG-GFP”, “pMIEG-PLD1” or “pMIEG-PLD2” and were used to generate replication-deficient retroviral particles in vitro. The pMIEG vectors (GFP, HAPLD1 or mycPLD2) were transfected into GP2-293 mammalian cells in the presence of the pVSV-G vector. Cell culture supernatants containing the replication-deficient viral particles were harvested. Retrovirus was incubated with MCF-7 human breast cancer cells to produce stable cell lines overexpressing PLD or only the negative control GFP vector in the presence of 4 μg/mL polybrene. Verification of target cells overexpressing PLD was confirmed using Western-blot analysis.
Cell invasion assays
MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells were serum-starved for 2 hours and resuspended at a concentration 1.5 × 106 cells/mL in chemotaxis buffer (DMEM + 0.5 % bovine serum albumin). Approximately 3 × 105 cells were applied to the upper chambers of 8 μm PET matrigels (24–well format) with a 6.5 mm diameter membrane. Final concentration of chemoattractant used was 0 or 3 nM EGF in 500 μL of chemotaxis buffer placed in the lower wells of 24-well plates. Cell invasion assays were incubated for 6 hours (MDA-MB-231) or overnight (MCF-7) at 37°C in a humidified 5 % CO2 cell culture incubator. Cells were scraped from the matrigel insert and then stained for 1 hour with hematoxylin.
Cell migration assay
Cells were resuspended at a density of 5 × 105 cells/mL in chemotaxis buffer (DMEM with 0.1% BSA). A total of 200 µL was placed in the upper chambers (or inserts) of transwell inserts that were separated from the lower wells by a 6.5-mm diameter, 8-µm-pore-size polycarbonate membrane. For the study of chemotaxis, EGF was prepared fresh the day of the experiment in 1× PBS–0.1% BSA, pH, 7.2, at a stock concentration of 1 µM. When ready for chemotaxis, EGF was diluted to a 3 nM working concentration in 500 µL of chemotaxis buffer and placed into the lower wells of 24-well plates. Cell migration inserts were incubated for 1 hr at 37°C under a 5% CO2 atmosphere. The number of cells that migrated to the lower wells was calculated by placing 10-µL aliquots on a hemocytometer and counting four fields in duplicate.
Cell proliferation assay
MDA-MB-231 cells were plated into 24-well plates 24 hr prior to use. If relevant, then duplicate wells were untreated (DMSO) or treated with 300 nM FIPI or 300 nM NOPT. After incubation, cells were washed 2× with PBS and trypsinized with the final volume brought up to 1 mL/well using complete DMEM containing 10% FCS. Cell proliferation in the absence of inhibitors was determined for puromycin-resistant MDA-MB-231 cells stably silencing PLD2 (MDA-MB-231·pKLO-shPLD2) or MCF-7 cells stably overexpressing PLD (MCF-7·pMIEG-HA-PLD1 or MCF-7·pMIEG–mycPLD2). Duplicate wells of cells were plated into 24-well plates, incubated and trypsinized; viable cells counted/mL cells.
PLD activity assay
MDA-MB-231 cell lysates in the absence or presence of small-molecule inhibitors were processed for PLD activity in PC8 liposomes and [3H]n-butanol beginning with the addition of the following reagents (final concentrations): 3.5 mM PC8 phospholipid, 45 mM HEPES (pH 7.8), and 1.0 μCi [3H]n-butanol in a liposome form, to accomplish the transphosphatidylation reaction of PLD. Samples were incubated for 20 minutes at 30°C with continuous shaking. Addition of 0.3 mL ice-cold chloroform/methanol (1:2) stopped the reactions. Lipids were then isolated and resolved by thin layer chromatography. The amount of [3H]-PBut that co-migrated with PBut standards (Rf=0.45–0.50) was measured by scintillation spectrometry.
SCID mice
Eight week old female B- and T lymphocyte-deficient SCID/CB17 mice (C.B117/IcrHsd-Prkdc-Scid) were purchased form Harlan Laboratories (Indianapolis, IN). Mice were given a week to acclimate to the animal facility before they were studied. To minimize the risk of any exogenous infection, the SCID mice were maintained and cared for in sterile, static micro-isolation cages. Mice received irradiated food (Harlan Teklad 2920X, Harlan Laboratories) and sterile water ad libitum. All animal procedures and housing occurred in a facility accredited by AAALAC International, and all experimental procedures involving animals were reviewed and approved by Wright State University’s Institutional Laboratory Animal Care and Use committee.
Alzet miniature osmotic pumps
In experiments studying the effects of PLD inhibitors, Alzet miniature osmotic pumps (Durect Corp., Cupertino, CA) were used as an inhibitor-delivery system. The pumps were aseptically filled with either the vehicle (50% DMSO) or inhibitory compound at a concentration that would deliver 1.8 mg/kg/day of apigenin, FIPI, or NOPT at a rate of 0.11 μL/hr. for 4–5 weeks. For FIPI, this concentration is equivalent to ~300 nM given a 5.5 hr. half-life and 18% bioavailability (31), which exerts full inhibition on PLD2 (32). For NOPT, the current half-life is not available from the literature, but it should be sufficient to inhibit PLD2, especially since the IC50 for PLD1 is in the micromolar range and is much greater than PLD2 (33). The half-life of apigenin is not currently known in mice, but it is >12 hours in humans (57). Therefore, 1.8 mg/kg/day for each inhibitor should yield full inhibition of PLD or tyrosine kinases. Filled pumps were equilibrated in sterile 0.9% saline at room temp for 18 hours to reach steady state and optimal pump performance prior to implantation. After equilibration, pumps were aseptically implanted subcutaneously on the left dorsal thoracic area of the SCID mice while under isoflurane anesthesia. Carprofen (5 mg/kg) was administered for analgesia one time subcutaneously at the time of surgery.
Xenotransplants of SCID mice and metastastic breast cancer models
SCID mice that were xenotransplanted with cell lines that either over- or under-expressed PLD only in the absence of the small molecule inhibitors were injected with 4–6 × 106 cells (either MDA-MB-231·pKLO-shControl, MDA-MB-231·pKLO-shPLD2, MCF-7·pMIEG-GFP, MCF-7·pMIEG-HAPLD1 or MCF-7·pMIEG-mycPLD2) in sterile HBSS + 0.5% BSA in the left mammary fat pad with the mice under isoflurane anesthesia. Tumors were measured every 2–3 days throughout the study with a digital caliper and volume values were calculated with the formula V=(L)(w2)/2 (64). Approximately 4 weeks after injection of cancer cells, mice were humanely euthanized. The primary breast tumor, lung and any metastatic axillary tumors were surgically excised and final dimensions measured. The tissues were then fixed and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. For SCID mice that received delivery of small molecule inhibitors via implanted alzet pumps, mice were xenotransplanted one day after implantation. Approximately 4–6 × 106 MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in sterile HBSS + 0.5% BSA were injected into the left mammary fat pad with the mice under isoflurane anesthesia.
GFP-based PA Sensor
Sporulation-specific protein 20 (Spo20) is a yeast protein required for the fusion of exocytic vesicles with the plasma membrane during yeast sporulation through its interactions with the SNARE complex (58–60), which contains an inhibitory region that sequesters the protein in the nucleus (60, 61) and a positive regulatory region that binds to phospholipids (especially PA) in the cell membrane, termed the PA binding domain (PABD). Cloning of the PABD into the pEGFPC1 vector leading to pEGFP-Spo20PABD-WT for use in microscopy of mammalian cells was documented in (32, 42).
Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean + SEM. The difference between means was assessed by the Single Factor Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) test. Probability of p<0.05 indicated a significant difference.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work has been supported by grant HL056653 from the National Institutes of Health (NIH/NHBLI) to J.G.C and from grant 229102 from Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine, also to J.G.C. The authors wish to thank Dr. Mary C. Dinauer and Christophe Marchal for their help generating the pMIEG-PLD vectors and Dr. Michael Frohman for providing the PA sensor and to Dr. Frohman and to Dr. H Alex Brown for guidance in the use of inhibitors. We also thank Dr. Cambronero’s lab members Qing Ye, Sam Kantonen, Madhu Mahankali, Nate Hatton and Ramya Ganesan, for their excellent help and care with the mice studies.
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E, Ferlay J. Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(5):1133–1145. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Benson JR, Jatoi I. The global breast cancer burden. Future Oncol. 2012;8(6):697–702. doi: 10.2217/fon.12.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G, Yu Y. Breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2012;9(5):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lorusso G, Ruegg C. New insights into the mechanisms of organ-specific breast cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22(3):226–233. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 2006;12(8):895–904. doi: 10.1038/nm1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kang DW, Min do S. Platelet derived growth factor increases phospholipase D1 but not phospholipase D2 expression via NFkappaB signaling pathway and enhances invasion of breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010;294(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reich R, Blumenthal M, Liscovitch M. Role of phospholipase D in laminin-induced production of gelatinase A (MMP-2) in metastatic cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1995;13(2):134–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00133618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25(1):9–34. doi: 10.1007/s10555-006-7886-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Williger BT, Ho WT, Exton JH. Phospholipase D mediates matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in phorbol ester-stimulated human fibrosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(2):735–738. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.2.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Park MH, Ahn BH, Hong YK, Min do S. Overexpression of phospholipase D enhances matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and glioma cell invasion via protein kinase C and protein kinase A/NF-kappaB/Sp1-mediated signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(2):356–365. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taves J, Rastedt D, Canine J, Mork D, Wallert MA, Provost JJ. Sodium hydrogen exchanger and phospholipase D are required for alpha1-adrenergic receptor stimulation of metalloproteinase-9 and cellular invasion in CCL39 fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;477(1):60–66. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kantonen S, Hatton N, Mahankali M, Henkels KM, Park H, Cox D, et al. A novel phospholipase D2-Grb2-WASp heterotrimer regulates leukocyte phagocytosis in a two-step mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(22):4524–4537. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05684-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Knapek K, Frondorf K, Post J, Short S, Cox D, Gomez-Cambronero J. The molecular basis of phospholipase D2-induced chemotaxis: elucidation of differential pathways in macrophages and fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(18):4492–4506. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00229-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yamada Y, Hamajima N, Kato T, Iwata H, Yamamura Y, Shinoda M, et al. Association of a polymorphism of the phospholipase D2 gene with the prevalence of colorectal cancer. J Mol Med. 2003;81(2):126–131. doi: 10.1007/s00109-002-0411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhao Y, Ehara H, Akao Y, Shamoto M, Nakagawa Y, Banno Y, et al. Increased activity and intranuclear expression of phospholipase D2 in human renal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;278(1):140–143. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cho JH, Hong SK, Kim EY, Park SY, Park CH, Kim JM, et al. Overexpression of phospholipase D suppresses taxotere-induced cell death in stomach cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1783(5):912–923. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Riebeling C, Muller C, Geilen CC. Expression and regulation of phospholipase D isoenzymes in human melanoma cells and primary melanocytes. Melanoma Res. 2003;13(6):555–562. doi: 10.1097/00008390-200312000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen Y, Zheng Y, Foster DA. Phospholipase D confers rapamycin resistance in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2003;22(25):3937–3942. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Noh DY, Ahn SJ, Lee RA, Park IA, Kim JH, Suh PG, et al. Overexpression of phospholipase D1 in human breast cancer tissues. Cancer Lett. 2000;161(2):207–214. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(00)00612-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sanematsu F, Nishikimi A, Watanabe M, Hongu T, Tanaka Y, Kanaho Y, et al. Phosphatidic acid-dependent recruitment and function of the Rac activator DOCK1 during dorsal ruffle formation. J Biol Chem. 2013 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nishikimi A, Fukuhara H, Su W, Hongu T, Takasuga S, Mihara H, et al. Sequential regulation of DOCK2 dynamics by two phospholipids during neutrophil chemotaxis. Science. 2009;324(5925):384–387. doi: 10.1126/science.1170179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shi M, Zheng Y, Garcia A, Xu L, Foster DA. Phospholipase D provides a survival signal in human cancer cells with activated H-Ras or K-Ras. Cancer Lett. 2007;258(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Buchanan FG, McReynolds M, Couvillon A, Kam Y, Holla VR, Dubois RN, et al. Requirement of phospholipase D1 activity in H-RasV12-induced transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(5):1638–1642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406698102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Min DS, Kwon TK, Park WS, Chang JS, Park SK, Ahn BH, et al. Neoplastic transformation and tumorigenesis associated with overexpression of phospholipase D isozymes in cultured murine fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22(10):1641–1647. doi: 10.1093/carcin/22.10.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Joseph T, Wooden R, Bryant A, Zhong M, Lu Z, Foster DA. Transformation of cells overexpressing a tyrosine kinase by phospholipase D1 and D2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;289(5):1019–1024. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhong M, Shen Y, Zheng Y, Joseph T, Jackson D, Foster DA. Phospholipase D prevents apoptosis in v-Src-transformed rat fibroblasts and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;302(3):615–619. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Foster DA, Xu L. Phospholipase D in cell proliferation and cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1(11):789–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Henkels KM, Peng HJ, Frondorf K, Gomez-Cambronero J. A comprehensive model that explains the regulation of phospholipase D2 activity by phosphorylation-dephosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(9):2251–2263. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01239-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gomez-Cambronero J. New concepts in phospholipase D signaling in inflammation and cancer. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010;10:1356–1369. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Monovich L, Mugrage B, Quadros E, Toscano K, Tommasi R, LaVoie S, et al. Optimization of halopemide for phospholipase D2 inhibition. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17(8):2310–2311. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Su W, Yeku O, Olepu S, Genna A, Park JS, Ren H, et al. 5-Fluoro-2-indolyl des-chlorohalopemide (FIPI), a phospholipase D pharmacological inhibitor that alters cell spreading and inhibits chemotaxis. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;75(3):437–446. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.053298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Scott SA, Selvy PE, Buck JR, Cho HP, Criswell TL, Thomas AL, et al. Design of isoform-selective phospholipase D inhibitors that modulate cancer cell invasiveness. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5(2):108–117. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Price JE. Metastasis from human breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;39(1):93–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01806081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sossey-Alaoui K, Safina A, Li X, Vaughan MM, Hicks DG, Bakin AV, et al. Down-regulation of WAVE3, a metastasis promoter gene, inhibits invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 2007;170(6):2112–2121. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stasinopoulos I, O'Brien DR, Wildes F, Glunde K, Bhujwalla ZM. Silencing of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibits metastasis and delays tumor onset of poorly differentiated metastatic breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5(5):435–442. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zheng Y, Rodrik V, Toschi A, Shi M, Hui L, Shen Y, et al. Phospholipase D couples survival and migration signals in stress response of human cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(23):15862–15868. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600660200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Knoepp SM, Chahal MS, Xie Y, Zhang Z, Brauner DJ, Hallman MA, et al. Effects of active and inactive phospholipase D2 on signal transduction, adhesion, migration, invasion, and metastasis in EL4 lymphoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74(3):574–584. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.040105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chen Q, Hongu T, Sato T, Zhang Y, Ali W, Cavallo JA, et al. Key roles for the lipid signaling enzyme phospholipase d1 in the tumor microenvironment during tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Sci Signal. 2012;5(249):ra79. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.You J, Mi D, Zhou X, Qiao L, Zhang H, Zhang X, et al. A positive feedback between activated extracellularly regulated kinase and cyclooxygenase/lipoxygenase maintains proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2009;150(4):1607–1617. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Henkels KM, Farkaly T, Mahankali M, Segall JE, Gomez-Cambronero J. Cell Invasion of Highly Metastatic MTLn3 Cancer Cells Is Dependent on Phospholipase D2 (PLD2) and Janus Kinase 3 (JAK3) J Mol Biol. 2011;408(5):850–862. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zeniou-Meyer M, Zabari N, Ashery U, Chasserot-Golaz S, Haeberle AM, Demais V, et al. Phospholipase D1 production of phosphatidic acid at the plasma membrane promotes exocytosis of large dense-core granules at a late stage. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(30):21746–21757. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702968200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Frondorf K, Henkels KM, Frohman MA, Gomez-Cambronero J. Phosphatidic acid (PA) is a leukocyte chemoattractant that acts through S6 kinase signaling. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:15837–15847. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.070524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mahankali M, Peng HJ, Cox D, Gomez-Cambronero J. The mechanism of cell membrane ruffling relies on a phospholipase D2 (PLD2), Grb2 and Rac2 association. Cell Signal. 2011;23(8):1291–1298. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gomez-Cambronero J, Frye T, Baumann M. Ribosomal p70S6K basal activity increases upon induction of differentiation of myelomonocytic leukemic cell lines HL60, AML14 and MPD. Leuk Res. 2004;28(7):755–762. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2003.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Henkels KM, Mahankali M, Gomez-Cambronero J. Increased cell growth due to a new lipase-GEF (Phospholipase D2) fastly acting on Ras. Cell Signal. 2013;25(1):198–205. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Peng HJ, Henkels KM, Mahankali M, Marchal C, Bubulya P, Dinauer MC, et al. The Dual Effect of Rac2 on Phospholipase D2 Regulation That Explains both the Onset and Termination of Chemotaxis. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(11):2227–2240. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01348-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Peng HJ, Henkels KM, Mahankali M, Dinauer MC, Gomez-Cambronero J. Evidence for two CRIB domains in phospholipase D2 (PLD2) that the enzyme uses to specifically bind to the small GTPase Rac2. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(18):16308–16320. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.206672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zouwail S, Pettitt TR, Dove SK, Chibalina MV, Powner DJ, Haynes L, et al. Phospholipase D activity is essential for actin localization and actin-based motility in Dictyostelium. Biochem J. 2005;389(Pt 1):207–214. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tsukahara T, Tsukahara R, Fujiwara Y, Yue J, Cheng Y, Guo H, et al. Phospholipase D2-dependent inhibition of the nuclear hormone receptor PPARgamma by cyclic phosphatidic acid. Mol Cell. 2010;39(3):421–432. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jiang H, Luo JQ, Urano T, Frankel P, Lu Z, Foster DA, et al. Involvement of Ral GTPase in v-Src-induced phospholipase D activation. Nature. 1995;378(6555):409–412. doi: 10.1038/378409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jang JH, Lee CS, Hwang D, Ryu SH. Understanding of the roles of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid through their binding partners. Prog Lipid Res. 2012;51(2):71–81. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2011.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Itoh T, Hasegawa J, Tsujita K, Kanaho Y, Takenawa T. The tyrosine kinase Fer is a downstream target of the PLD-PA pathway that regulates cell migration. Sci Signal. 2009;2(87):ra52. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gomez-Cambronero J. Biochemical and cellular implications of a dual lipase-GEF function of phospholipase D2 (PLD2) J Leukoc Biol. 2012;92(3):461–467. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0212073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shen Y, Zheng Y, Foster DA. Phospholipase D2 stimulates cell protrusion in v-Src-transformed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Su W, Chen Q, Frohman MA. Targeting phospholipase D with small-molecule inhibitors as a potential therapeutic approach for cancer metastasis. Future Oncol. 2009;5(9):1477–1486. doi: 10.2217/fon.09.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nielsen SE, Young JF, Daneshvar B, Lauridsen ST, Knuthsen P, Sandstrom B, et al. Effect of parsley (Petroselinum crispum) intake on urinary apigenin excretion, blood antioxidant enzymes and biomarkers for oxidative stress in human subjects. Br J Nutr. 1999;81(6):447–455. doi: 10.1017/s000711459900080x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Neiman AM. Prospore membrane formation defines a developmentally regulated branch of the secretory pathway in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1998;140(1):29–37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.140.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Neiman AM, Katz L, Brennwald PJ. Identification of domains required for developmentally regulated SNARE function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2000;155(4):1643–1655. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nakanishi H, de los Santos P, Neiman AM. Positive and negative regulation of a SNARE protein by control of intracellular localization. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15(4):1802–1815. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E03-11-0798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Weimbs T, Low SH, Chapin SJ, Mostov KE, Bucher P, Hofmann K. A conserved domain is present in different families of vesicular fusion proteins: a new superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(7):3046–3051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.7.3046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]