Abstract
Variant chloroplast fructose 1,6-diphosphate aldolases were found in Pisum sativum when 10 commercial varieties were examined for electrophoretically distinct species of chloroplast triose phosphate isomerase, phosphoglyceric acid kinase, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and aldolase. When reciprocal crosses are made, both aldolases appear in individuals in the F1 generation. Backcrossing gives offspring having aldolases characteristic of the homozygous or of the heterozygous parent; the inheritance is therefore not maternal but Mendelian. Clearly this chloroplast reductive pentose phosphate cycle enzyme is under nuclear gene control in P. sativum.
Full text
PDF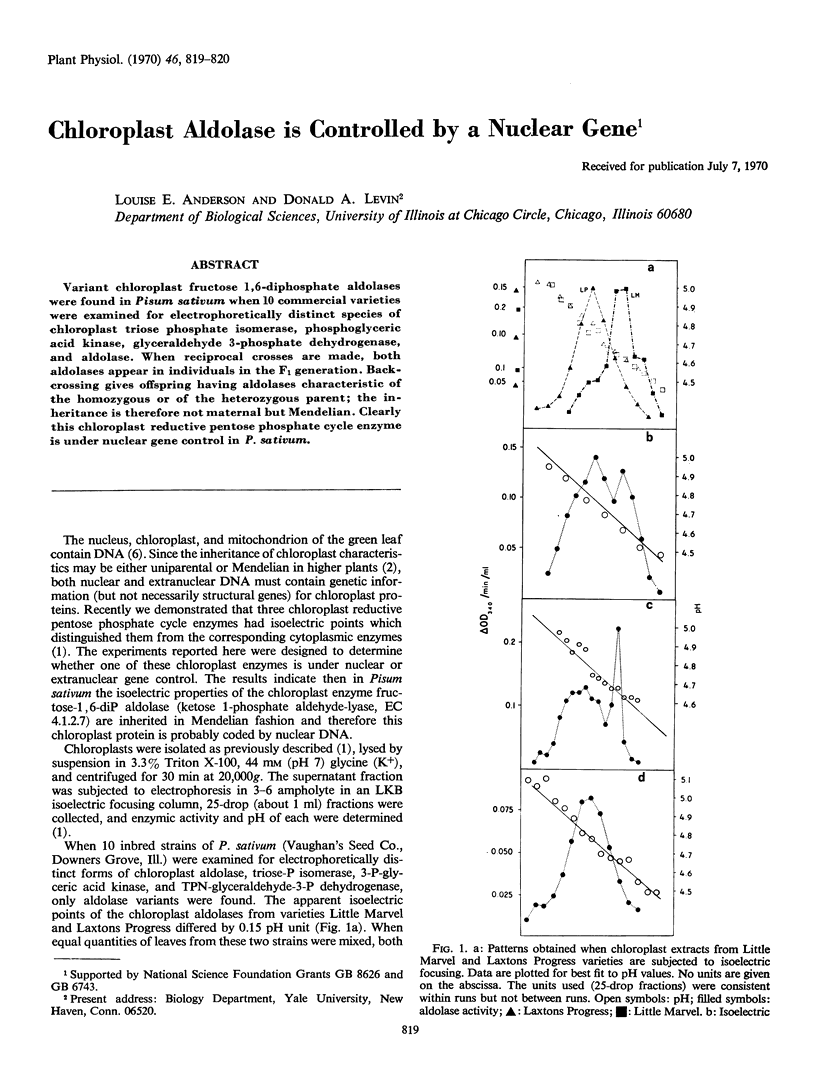

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson L. E., Advani V. R. Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes: three distinct isoenzymes associated with the reductive pentose phosphate cycle. Plant Physiol. 1970 May;45(5):583–585. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.5.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo G. P., Scandalios J. G. Nuclear gene control of mitochondrial malic dehydrogenase in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):104–111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N. S., Smillie R. M. Evidence for the direction of chloroplasts ribosomal RNA synthesis by chloroplast DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):598–603. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman F., Stewart J. W., Margoliash E., Parker J., Campbell W. The structural gene for yeast cytochrome C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1498–1504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surzycki S. J. Genetic functions of the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardi: effect of rifampin on chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1327–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A. Genetic control of beta-hydroxybutyric dehydrogenase in Paramecium aurelia. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):941–941. doi: 10.1038/219941a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A. Genetics of NADP isocitrate dehydrogenase in Paramecium aurelia. Nature. 1970 Jan 10;225(5228):181–182. doi: 10.1038/225181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari K. K., Wildman S. G. Function of chloroplast DNA. I. Hybridization studies involving nuclear and chloroplast DNA with RNA from cytoplasmic (80S) and chloroplast (70S) ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):569–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



