Abstract
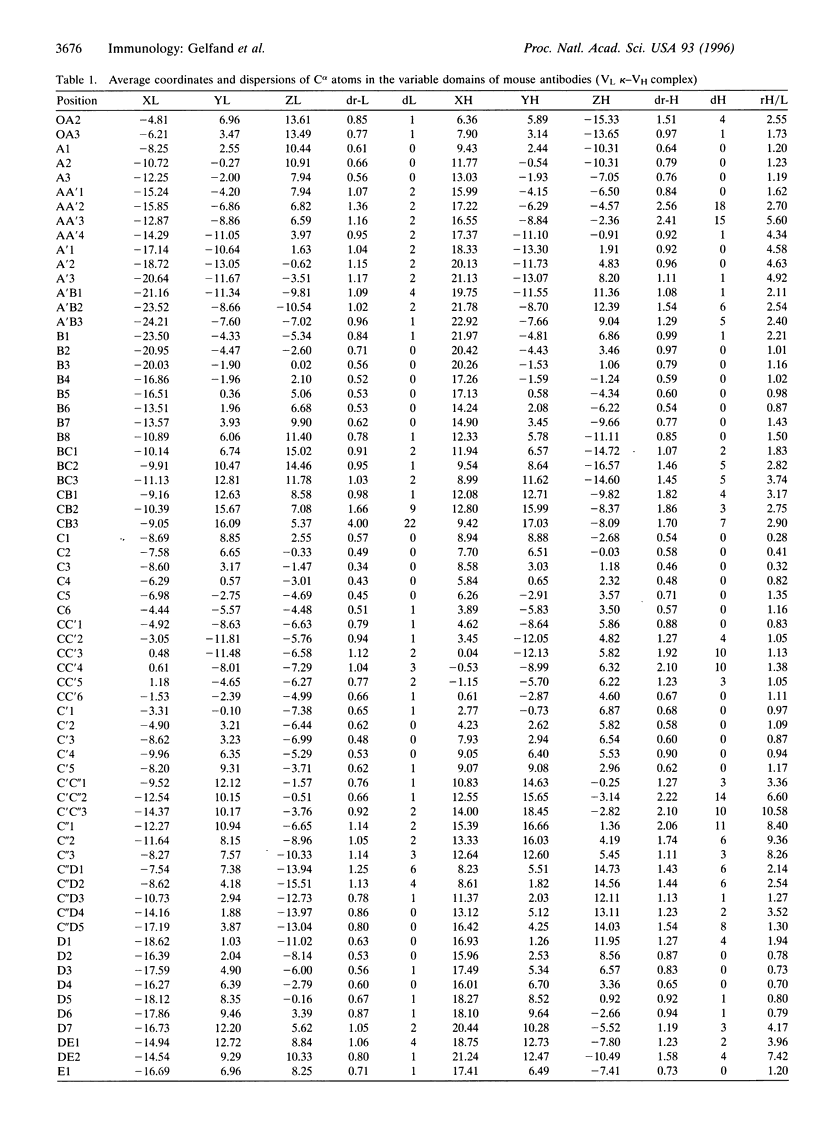
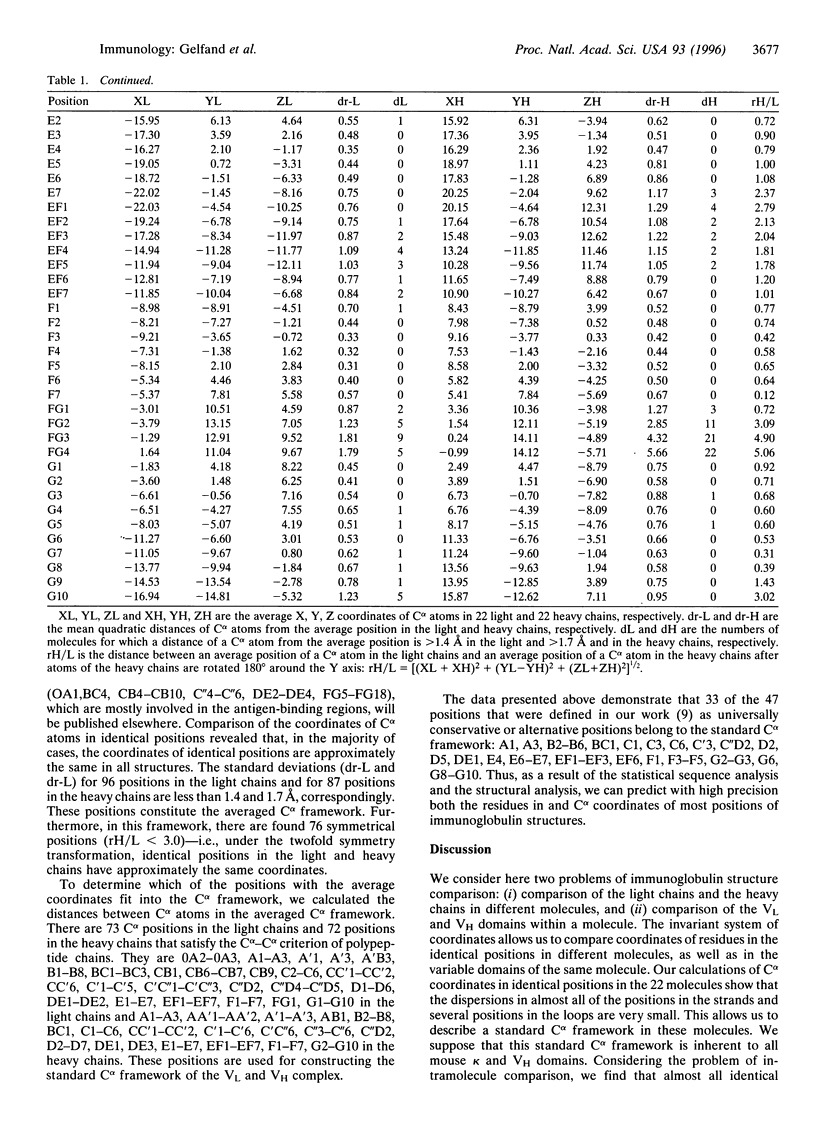
A new approach of comparing protein structures that does not involve the procedure of superposition is suggested. An invariant system of coordinates for immunoglobulin molecules that is based on the geometrical symmetry inherent to the variable domain light-chain (VL)-heavy-chain (VH) complex is described. The coordinates of the Calpha atoms in 22 immunoglobulin structures are calculated in the invariant system of coordinates. We found that 76 identical positions in this Calpha framework are symmetrical about the twofold axis. Comparison of the identical positions in these molecules allows us to select 96 positions in the light chains and 87 positions in the heavy chains whose Calpha atom coordinates are approximately the same. To check whether the average coordinates of Calpha atoms in these positions complies with the stereochemical requirements, we calculated Calpha-Calpha distances. Seventy-three positions of the light chains and 72 positions of the heavy chains satisfy the Calpha-Calpha distance criterion. The Calpha atoms in these positions are used for constructing the "standard" Calpha framework of VL and VH complexes. The average coordinates of Calpha atoms are presented.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diamond R. On the multiple simultaneous superposition of molecular structures by rigid body transformations. Protein Sci. 1992 Oct;1(10):1279–1287. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstein M., Altman R. B. Average core structures and variability measures for protein families: application to the immunoglobulins. J Mol Biol. 1995 Aug 4;251(1):161–175. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpaz Y., Chothia C. Many of the immunoglobulin superfamily domains in cell adhesion molecules and surface receptors belong to a new structural set which is close to that containing variable domains. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 13;238(4):528–539. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm L., Sander C. Protein structure comparison by alignment of distance matrices. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):123–138. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Rossmann M. G. Comparison of protein structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:397–420. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R., Wolfson H. J. Efficient detection of three-dimensional structural motifs in biological macromolecules by computer vision techniques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10495–10499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A., Botha J. D., Pastore A., Lesk A. M. A method for multiple superposition of structures. Acta Crystallogr A. 1992 Jan 1;48(Pt 1):11–14. doi: 10.1107/s010876739100867x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Orengo C. A. Protein structure alignment. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



