Abstract
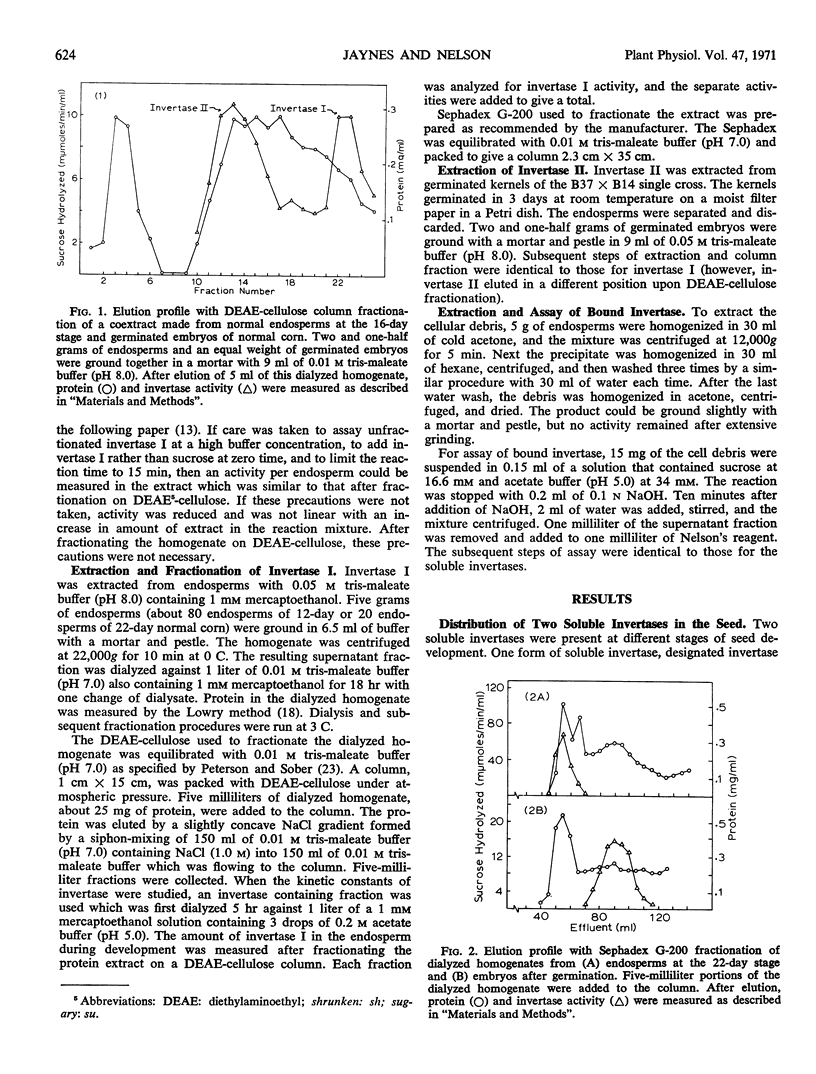
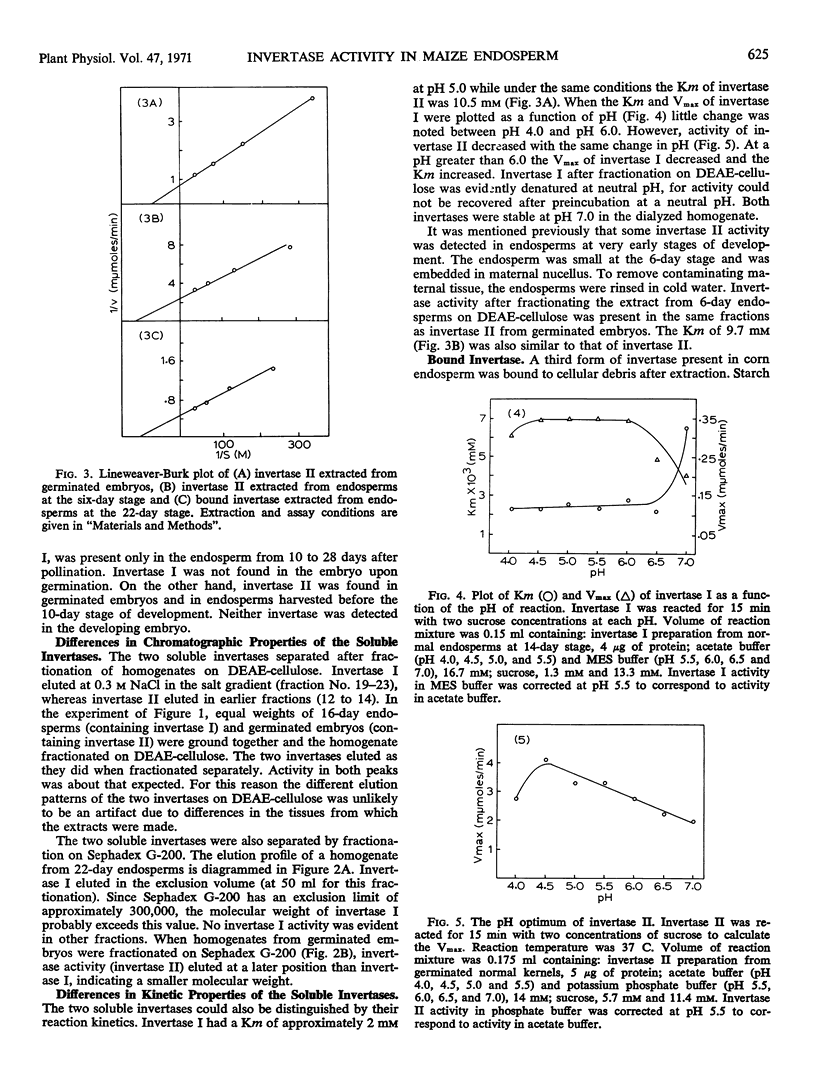
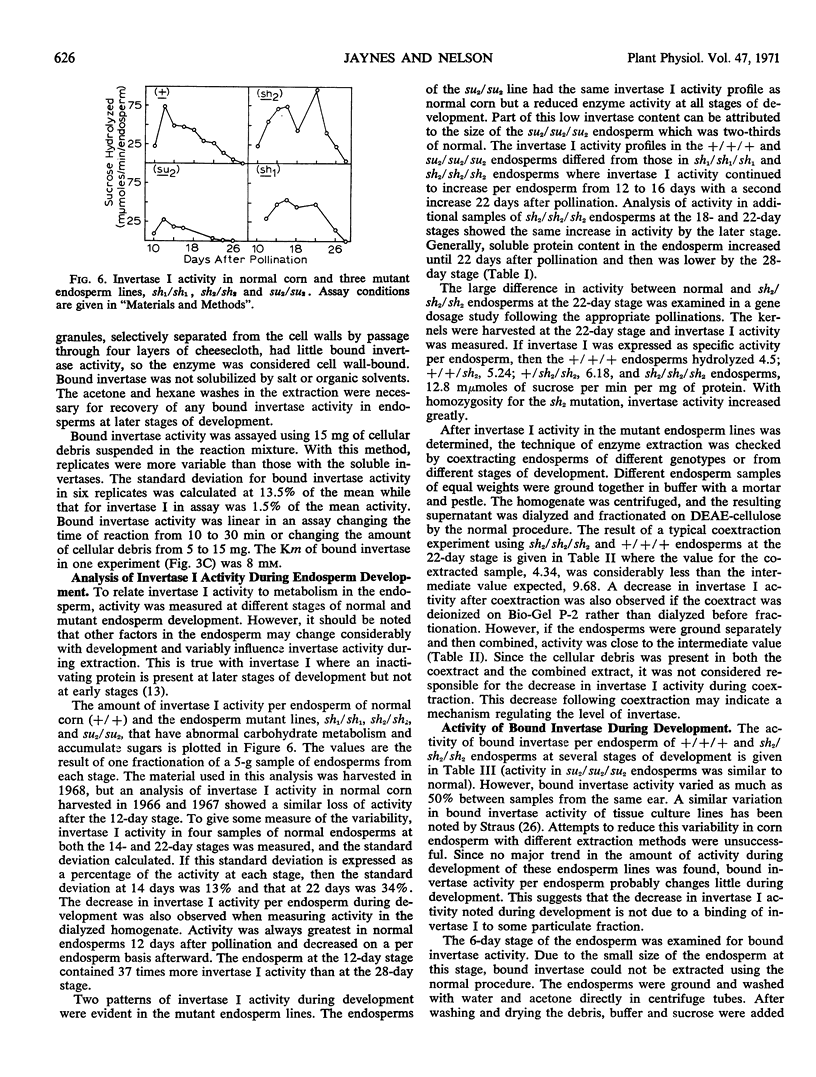
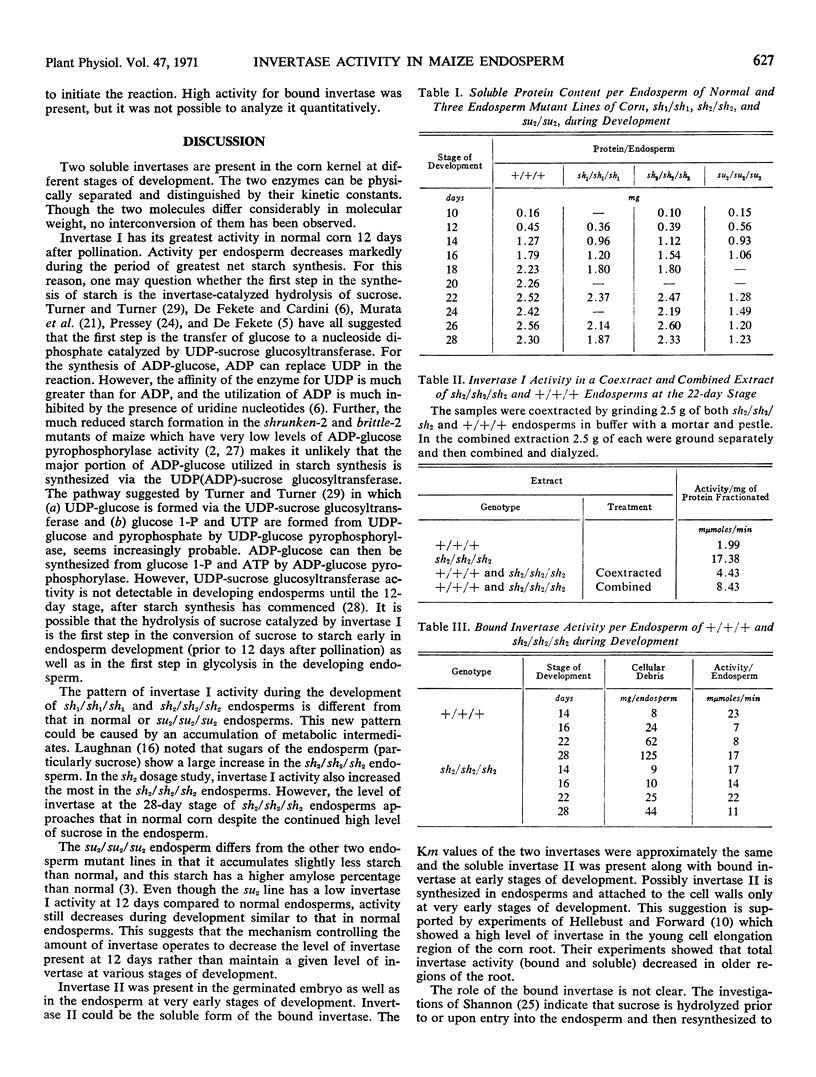
A bound invertase and two soluble invertases are found in the developing endosperm of maize (Zea mays L.). The two soluble invertases can be separated on diethylaminoethyl-cellulose and Sephadex columns and distinguished by their kinetic constants. One soluble invertase, invertase I, is present from the 10- to 28-day stages of endosperm development with maximal activity per normal endosperm at the 12-day stage. In two endosperm mutant lines, shrunken-1 and shrunken-2, there is a second increase in invertase I activity later in development which could be a secondary effect caused by the abnormal metabolism in these lines. Another soluble invertase, invertase II, is present in the embryo upon germination and is also found in the very young developing endosperm (6-day stage). The third form of invertase, bound invertase, is present in the endosperm by the 6-day stage, and its activity remains approximately constant during development.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper R. A., Greenshields R. N. The partial purification and some properties of two sucrases of Phaseolus vulgaris. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):357–364. doi: 10.1042/bj0920357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. B., Preiss J. Presence of ADP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase in Shrunken-2 and Brittle-2 Mutants of Maize Endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jul;44(7):1058–1062. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.7.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN J., HALL M. A. ENZYME FORMATION IN HIGHER-PLANT TISSUES. DEVELOPMENT OF INVERTASE AND ASCORBATE-OXIDASE ACTIVITIES IN MATURE STORAGE TISSUE OF HELIANTHUS TUBEROSUS L. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:403–410. doi: 10.1042/bj0950403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gascón S., Neumann N. P., Lampen J. O. Comparative study of the properties of the purified internal and external invertases from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1573–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Sacher J. A., Glasziou K. T. Sugar Accumulation Cycle in Sugar Cane. I. Studies on Enzymes of the Cycle. Plant Physiol. 1963 May;38(3):338–343. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.3.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes T. A., Nelson O. E. An invertase inactivator in maize endosperm and factors affecting inactivation. Plant Physiol. 1971 May;47(5):629–634. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivilaan A., Beaman T. C., Bandurski R. S. Enzymatic activities associated with cell wall preparations from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1961 Sep;36(5):605–610. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.5.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriedemann P., Beevers H. Sugar Uptake and Translocation in the Castor Bean Seedling II. Sugar Transformations During Uptake. Plant Physiol. 1967 Feb;42(2):174–180. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.2.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughnan J. R. The Effect of the sh(2) Factor on Carbohydrate Reserves in the Mature Endosperm of Maize. Genetics. 1953 Sep;38(5):485–499. doi: 10.1093/genetics/38.5.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METZENBERG R. L. ENZYMICALLY ACTIVE SUBUNITS OF NEUROSPORA INVERTASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 26;89:291–302. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURATA T., SUGIYAMA T., AKAZAWA T. ENZYMIC MECHANISM OF STARCH SYNTHESIS IN RIPENING RICE GRAINS. II. ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE GLUCOSE PATHWAY. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul;107:92–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressey R. Potato sucrose synthetase: purification, properties, and changes in activity associated with maturation. Plant Physiol. 1969 May;44(5):759–764. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.5.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONGINEDEFEKETE M. A., CARDINI C. E. MECHANISM OF GLUCOSE TRANSFER FROM SUCROSE INTO THE STARCH GRANULE OF SWEET CORN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:173–184. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon J. C. Carbon-14 Distribution in Carbohydrates of Immature Zea mays. Kernels Following CO(2) Treatment of Intact Plants. Plant Physiol. 1968 Aug;43(8):1215–1220. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.8.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus J. Invertase in Cell Walls of Plant Tissue Cultures. Plant Physiol. 1962 May;37(3):342–348. doi: 10.1104/pp.37.3.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Nelson O. E. Starch-deficient maize mutant lacking adenosine dephosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase activity. Science. 1966 Jan 21;151(3708):341–343. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3708.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Salamini F., Nelson O. E. Enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in the developing endosperm of maize. Plant Physiol. 1970 Aug;46(2):299–306. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



