Abstract
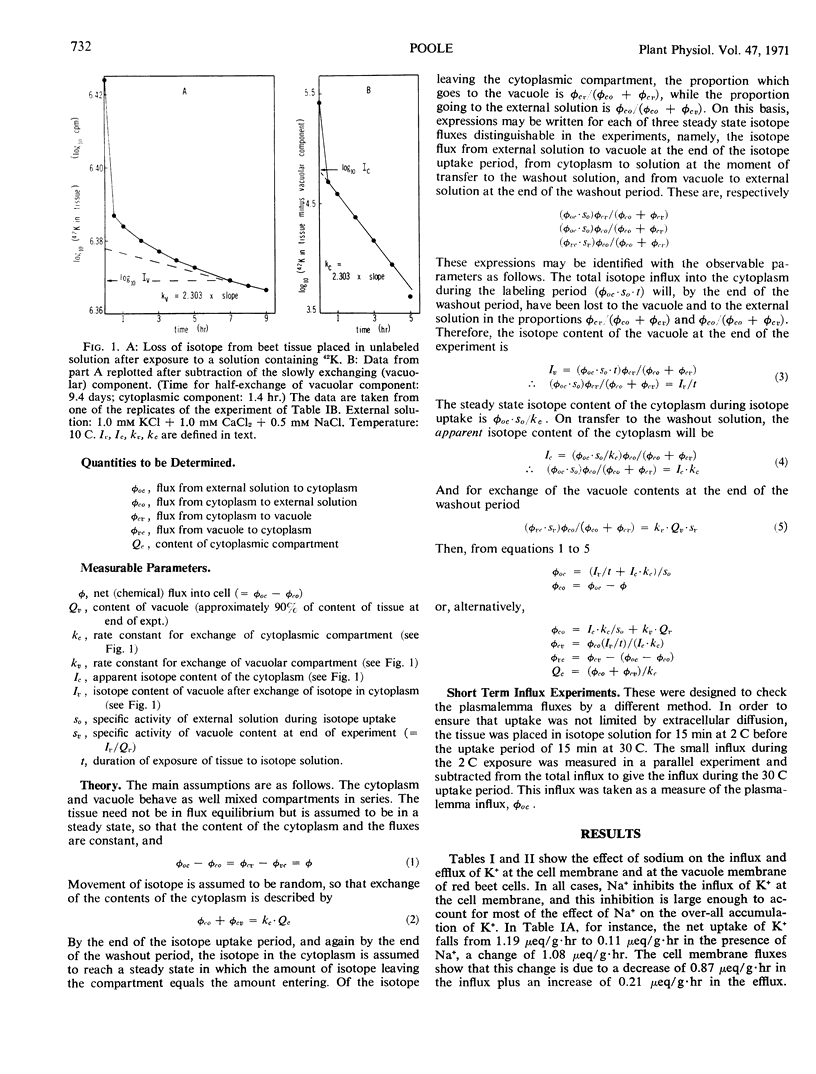
Slices of red beet (Beta vulgaris) washed for 5 to 6 days are known to accumulate Na+ in preference to K+ from solutions containing both ions. The present work, using ion concentrations of 1.0 mm or less, with Ca2+ added in some cases, shows that Na+ strongly inhibits K+ influx at the cell membrane (plasmalemma) while K+ efflux is increased to a lesser extent. This result from compartmental analysis is confirmed by short (15-minute) influx experiments, which indicate an immediate inhibitory effect of Na+ on K+ influx at the cell membrane. It is concluded that cation selectivity, even when Na+ is favored for uptake, is primarily determined at the cell membrane. Nevertheless, a high level of K+ in the cytoplasm is maintained during Na+ influx, by an inhibition of K+ transfer to the vacuole.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cram W. J. Compartmentation and exchange of chloride in carrot root tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):339–353. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram W. J. Short term influx as a measure of influx across the plasmalemma. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jul;44(7):1013–1015. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.7.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton B. Relationship of Cell Transmembrane Electropotential to Potassium and Sodium Accumulation Ratios in Oat and Pea Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1963 Sep;38(5):581–585. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.5.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton B. Steady State Sodium and Rubidium Effluxes in Pisum sativum Roots. Plant Physiol. 1967 May;42(5):685–690. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G., Saddler H. D. Active sodium and potassium transport in cells of barley roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):44–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. J. Development and Characteristics of Sodium-selective Transport in Red Beet. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jun;47(6):735–739. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.6.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


